Scientists have built a “computational microscope” that can simulate the atomic and subatomic forces that drive molecular interactions. This tool will streamline efforts to understand the chemistry of life, model large molecular systems and develop new pharmaceutical and industrial agents, the researchers say. They report their findings in the journal Nature Methods. The scientists combined two computational approaches…
Shape-Shifting Agent Targets Harmful Bacteria in the Stomach
A new shape-shifting polymer can target and kill Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the stomach without killing helpful bacteria in the gut. Such a treatment could improve the digestive health of billions of people worldwide who contract H. pylori infections. The antimicrobial agent morphs into a bacterial hole-puncher in the stomach’s acidic environment and reverts to an amorphous, inactive structure…
Researchers Develop Origami-Inspired Robot
New research from a team of University of Illinois Mechanical Science and engineering professors and students, published as an invited paper in Smart Materials and Structures, details how origami structures and bio-inspired design can be used to create a crawling robot. Assistant professors Aimy Wissa and Sameh Tawfick, along with graduate student Alexander Pagano and undergraduates…
Opto-Mechanical Technique Circumvents Mechanical Losses Using the Action of Light
Energy loss due to scattering from material defects is known to set limits on the performance of nearly all technologies that we employ for communications, timing, and navigation. In micro-mechanical gyroscopes and accelerometers, such as those commonly found in cellphones today, microstructural disorder impacts measurement drift and overall accuracy of the sensor, analogous to how…
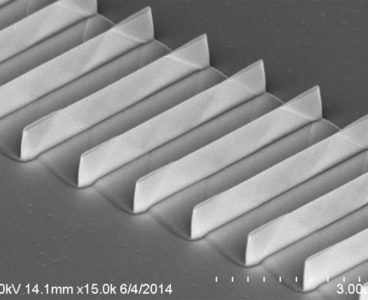
GaN-on-Silicon Tech Moves to Scalable Mobility Transistors
A team of University of Illinois researchers has recently advanced gallium nitride (GaN)-on-silicon transistor technology by optimizing the composition of the semiconductor layers that make up the device. Working with industry partners Veeco and IBM, the team created the high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) structure on a 200 mm silicon substrate with a process that…
Farming Adaptations Needed to Combat Climate Change
Sorghum is a staple food crop in West African countries whose crop yields already suffer from long droughts and unpredictable rainfall. Using heat-tolerant varieties of sorghum as a new management practice shows the most potential as an adaptation for maintaining crop yield as global warming raises the temperatures in West Africa. This study’s unique framework…
Desert Elephants Pass on Knowledge—Not Mutations—to Survive
Despite reported differences in appearance and behavior, DNA evidence finds that Namibian desert elephants share the same DNA as African savanna elephants. However, Namibian desert-dwelling elephants should be protected so they can continue to pass on their unique knowledge and survival skills to future generations. “The ability of species such as elephants to learn and…
Measure of Age in Soil Nitrogen Could Help Precision Agriculture
What’s good for crops is not always good for the environment. Nitrogen, a key nutrient for plants, can cause problems when it leaches into water supplies. University of Illinois engineers developed a model to calculate the age of nitrogen in corn and soybean fields, which could lead to improved fertilizer application techniques to promote crop…
Chemical Etching Method Helps Transistors Stand Tall
Smaller and faster has been the trend for electronic devices since the inception of the computer chip, but flat transistors have gotten about as small as physically possible. For researchers pushing for even faster speeds and higher performance, the only way to go is up. University of Illinois researchers have developed a way to etch…