World Speed Record for Polymer Simulations Shattered by Over a Hundred-Fold
From a humble plastic bag to ultra-light airplane wings – polymers are everywhere. These molecules are long chains of atoms that are chemically joined to play many roles that we all love (organic photovoltaics) and hate (indestructible plastic pollution). Polymers are useful in liquid form as well: the difference between tomato puree and ketchup is…
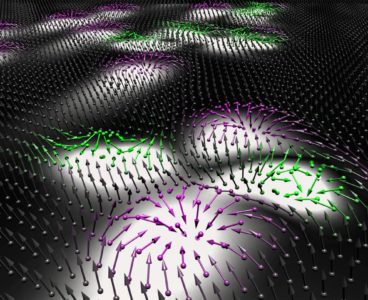
Magnetic Antiparticles Offer New Horizons for Information Technologies
Nanosized magnetic particles called skyrmions are considered highly promising candidates for new data storage and information technologies. Now, physicists have revealed new behaviour involving the antiparticle equivalent of skyrmions in a ferromagnetic material. The researchers demonstrated their findings using advanced computer simulations that can accurately model magnetic properties of nanometre-thick materials. The results are published…
Developing the Next Generation of Graphene
The material graphene has many incredible properties, but to date it has been difficult to use on a large scale in industry, because it loses its unique properties and goes back to its origin graphite. Researcher Mamoun Taher has developed a new form of graphene that can solve the problem. “The challenge has been to…
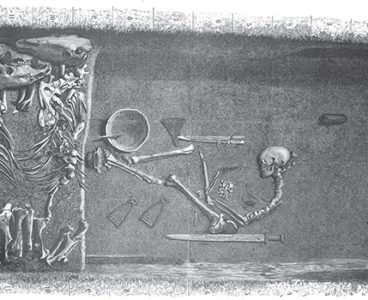
First Genetic Proof That Women Were Viking Warriors
New DNA evidence uncovered by researchers at Uppsala University and Stockholm University shows that there were in fact female Viking warriors. The remains of an iconic Swedish Viking Age grave now reveal that war was not an activity exclusive to males – women could be found in the higher ranks at the battlefield. The study…
Fossil Footprints Challenge Established Theories of Human Evolution
Newly discovered human-like footprints from Crete may put the established narrative of early human evolution to the test. The footprints are approximately 5.7 million years old and were made at a time when previous research puts our ancestors in Africa – with ape-like feet. Ever since the discovery of fossils of Australopithecus in South and East Africa…
Nanomaterials Hold Promise of Eco-Friendly Hydrogen Production
In an article in the journal Energy and Environmental Science, researchers from Uppsala University, Sweden, present a type of low-cost and environmental-friendly organic polymer nano-material as photocatalysts for hydrogen generation, and propose the working mechanism of the photocatalytic reactive site. Development of photocatalysts for light driven hydrogen generation from water is an ideal way to…
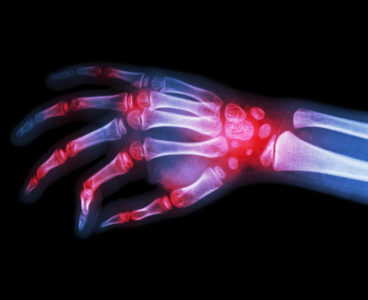
New Tool for Prognosis and Choice of Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Live Cell Imaging Using a Smartphone
A recent study from Uppsala University shows how smartphones can be used to make movies of living cells, without the need for expensive equipment. The study is published in the open access journal PLOS ONE, making it possible for laboratories around the world to do the same thing. Live imaging of cells is a very powerful…
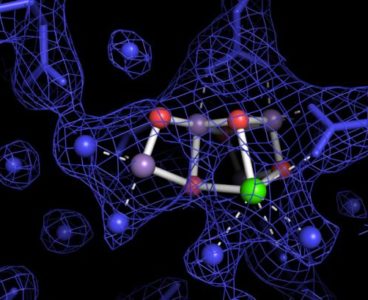
Watching How Plants Make Oxygen
Chameolonic Properties Make Large Molecules into Possible Drugs
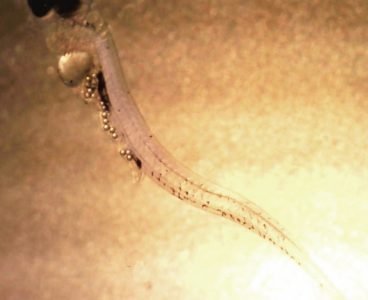
Microplastic Particles Threaten Fish Larvae
In a new study, published in Science, researchers from Uppsala University found that larval fish exposed to microplastic particles during development displayed changed behaviors and stunted growth which lead to greatly increased mortality rates. The researchers discovered that larval perch that had access to microplastic particles only ate plastic and ignored their natural food source of…