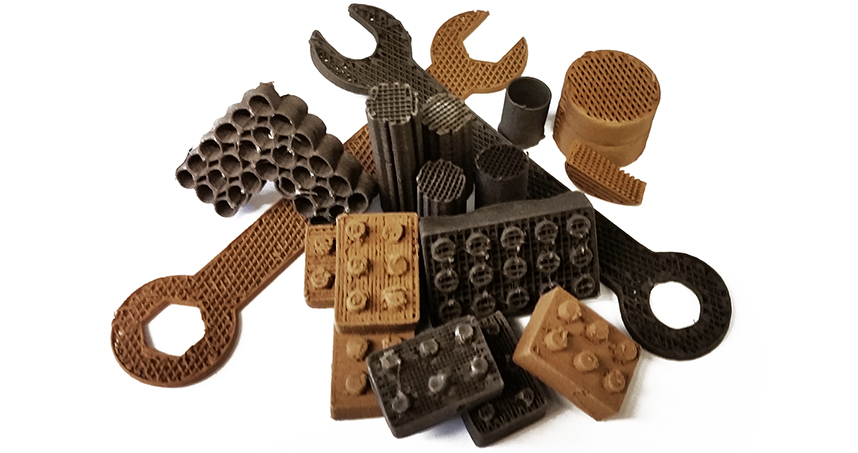
Tools and building blocks made by 3D printing with lunar and Martian dust.
When humans begin to colonize the moon and Mars, they will need to be able to make everything from small tools to large buildings using the limited surrounding resources.
Northwestern Engineering’s Ramille Shah and her Tissue Engineering and Additive Manufacturing (TEAM) Laboratory have demonstrated the ability to 3D-print structures with simulants of Martian and lunar dust. This work uses an extension of their “3D-painting process,” a term that Shah and her team use for their novel 3D inks and printing method, which they previously employed to print hyperelastic “bone,” 3D graphene and carbon nanotubes, and metals and alloys.
“For places like other planets and moons, where resources are limited, people would need to use what is available on that planet in order to live,” says Shah, assistant professor of materials science and engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering and of surgery in the Feinberg School of Medicine. “Our 3D paints really open up the ability to print different functional or structural objects to make habitats beyond Earth.”
Partially supported by a gift from Google and performed at Northwestern’s Simpson Querrey Institute, the research was recently published in Nature Scientific Reports. Adam Jakus, a Hartwell postdoctoral fellow in Shah’s TEAM lab, was the paper’s first author. Two former Northwestern Engineering undergraduates, Katie Koube, who currently works as an engineer for SpaceX, and Nicholas Geisendorfer, who is now a graduate student in Shah’s lab, co-authored the work.
Shah’s research uses NASA-approved lunar and Martian dust simulants, which have similar compositions, particle shapes, and sizes to the dusts found on lunar and Martian surfaces. Shah’s team created the lunar and Martian 3D paints using the respective dusts, a series of simple solvents, and biopolymer, then 3D printed them with a simple extrusion process. The resulting structures are over 90 percent dust by weight.
Despite being made of rigid micro-rocks, the resulting 3D-painted material is flexible, elastic, and tough — similar to rubber. This is the first example of rubber-like or soft materials resulting from lunar and Martian simulant materials. The material can be cut, rolled, folded, and otherwise shaped after being 3D painted, if desired.
“We even 3D-printed interlocking bricks, similar to Legos, that can be used as building blocks,” Shah says.
Shah and David Dunand, the James N. and Margie M. Krebs Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, are currently collaborating to optimize ways to fire these 3D-painted structures in a furnace, which is an optional process that can transform the soft, rubbery objects into hard, ceramic-like structures. In the context of the broader 3D-painting technology, this work highlights the potential to use a single 3D printer on another planet to create structures from all kinds of materials.
Even though colonizing other planets might take a while, Shah believes that it’s never too soon to start planning.
Source: Northwestern University