The next generation of carbon nanotubes could be used as a clean-up crew for toxic sludge and contaminated water.
Researchers at Rochester Institute of Technology have enhanced single-walled carbon nanotubes to offer a more effective and sustainable approach to water treatment and remediation than the standard industry materials—silicon gels and activated carbon.
“This aspect is new–taking knowledge of carbon nanotubes and their properties and realizing, with new processing and characterization techniques, the advantages nanotubes can provide for removing contaminants for water,” John-David Rocha, an assistant professor in the School of Chemistry and Materials Science in RIT’s College of Science, said in a statement.
Rocha and fellow researcher Reginald Rogers are advancing nanotube technology for environmental remediation and water filtration for home use.
“We have shown that we can regenerate these materials,” Rogers, an assistant professor of chemical engineering in RIT’s Kate Gleason College of Engineering, said in a statement. “In the future, when your water filter finally gets saturated, put it in the microwave for about five minutes and the impurities will get evaporated off.”
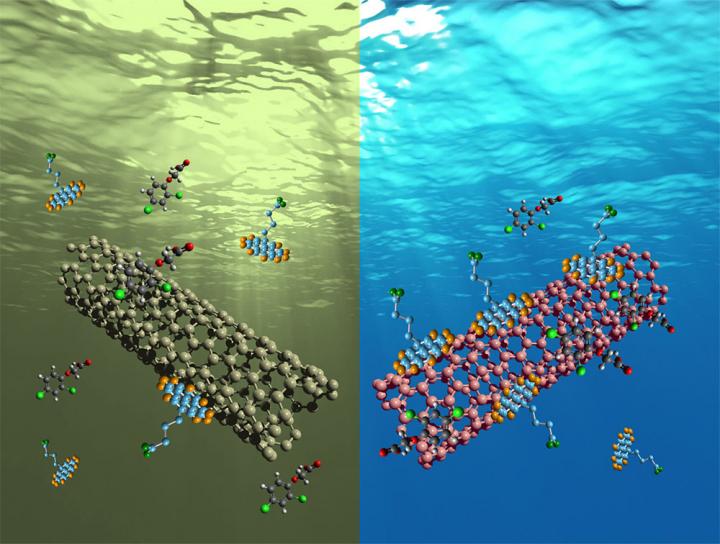
Carbon nanotubes are storage units measuring about 50,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. Carbon reduced to the nanoscale defies the rules of physics and operates in a world of quantum mechanics in which small materials become mighty.
“We know carbon as graphite for our pencils, as diamonds, as soot,” Rocha said. “We can transform that soot or graphite into a nanometer-type material known as graphene.”
A single-walled carbon nanotube is made when a sheet of graphene is rolled up, causing the physical change to alter the material’s chemical structure, which determines how it behaves.
This results in one of the most heat conductive and electrically conductive materials in the world, according to Rocha.
“These are properties that only come into play because they are at the nanometer scale,” he said.
The research team is now creating new techniques for manipulating the tiny materials and Rocha already developed a method for isolating high-quality, single walled carbon nanotubes and for sorting them according to their semiconductive or metallic properties.
Rogers redistributed the pure carbon nanotubes into thin papers akin to carbon-copy paper.
“Once the papers are formed, now we have the adsorbent–what we use to pull the contaminants out of water,” Rogers said.
Rogers said the filtration process works because “carbon nanotubes dislike water” and only the organic contaminants in the water stick to the nanotube, not the water molecules.
“This type of application has not been done before,” Rogers said. “Nanotubes used in this respect is new.”




