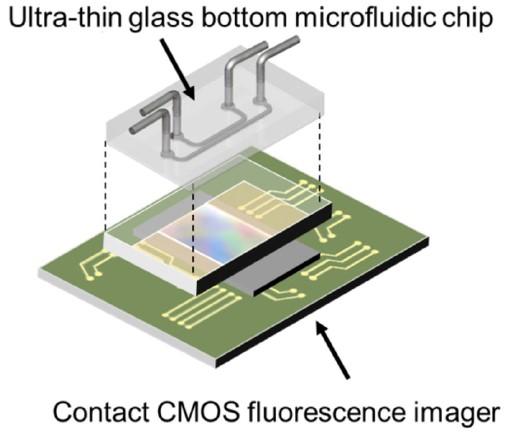
A diagram of the on-chip fluorescence imaging platform showing how the ultra-thin glass bottom microfluidic chip sits on top of the contact CMOS fluorescence imager. Source: Takehara et al.
Fluorescence microscopy gives researchers incredible power to illuminate the tiniest structures and capture the real-time activities of live cells by tagging biological molecules with a veritable rainbow of fluorescent dyes. This power comes at a cost: The technology can be expensive and time-consuming and, so far, has resisted attempts at automation.
This situation may be changing however, with the introduction of microfluid chip-based platforms. One such newly developed platform has been developed by a team of Japanese researchers. Their system enables scientists to rapidly image fluorescent cells grown inside the chip using a CMOS image sensor, the same technology found in the camera of a smartphone. The new system, described this week in AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, has numerous potential uses in biomedical research.
“Conventional tabletop-type optical microscopes are powerful tools for researchers, but they are not truly adequate for fully automated systems because of the expense and the necessity of well-trained technicians,” said Hiroaki Takehara, who researches automated cell processing devices at the University of Tokyo and is one of the study’s authors.
To develop an on-chip system, he teamed up with co-author Jun Ohta of the Nara Institute of Science and Technology, an expert in CMOS image sensor technology.
Other groups have developed chip-based fluorescent microscopy systems previously, but those setups required the sample to sit directly on the image sensor chip, which introduces the risk of cross-contamination. These systems cannot be truly high-throughput because the sensor chips must be washed in between use.
Takehara and colleagues developed disposable chips to overcome these limitations. The chip contains microfluidic channels specially designed for culturing cells and the introduction of culture media, drugs and other biological molecules. The chip has an ultra-thin glass bottom that minimizes the distance between the cells and the contact sensor below. A CMOS image sensor detects the fluorescence emitted by the cells, turns it into an electronic signal and then reconstructs the image.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of their system, the researchers grew cells containing fluorescent dyes in their nuclei within the microchannels. When they exposed cells to endothelial growth factor (EGF), which causes cell proliferation, the cultures gave off a more intense fluorescence signal than cultures that were not treated with EGF, indicating that the sensor detected cell growth.
The authors acknowledge that the on-chip fluorescence microscopy platform yields images with poorer spatial resolution than those of conventional fluorescence microscopes, but offers the advantage of being compatible with fully automated systems. The platform’s small size and affordability also make it attractive for use in implantable devices for measuring glucose or even brain activity.
In future work, Takehara plans to explore the use of the platform for monitoring stem cell production for use in regenerative medicine and for screening new drugs.
“The excessive cost of developing novel pharmaceutical drugs and the urgent requirement for [affordable] screening technology has become a pressing issue,” Takehara said. “A fully automated system, from sample handling to detection, without the necessity of well-trained technicians is a key technology, and serves a pivotal role in the development of cell-based cost-effective screening.”



