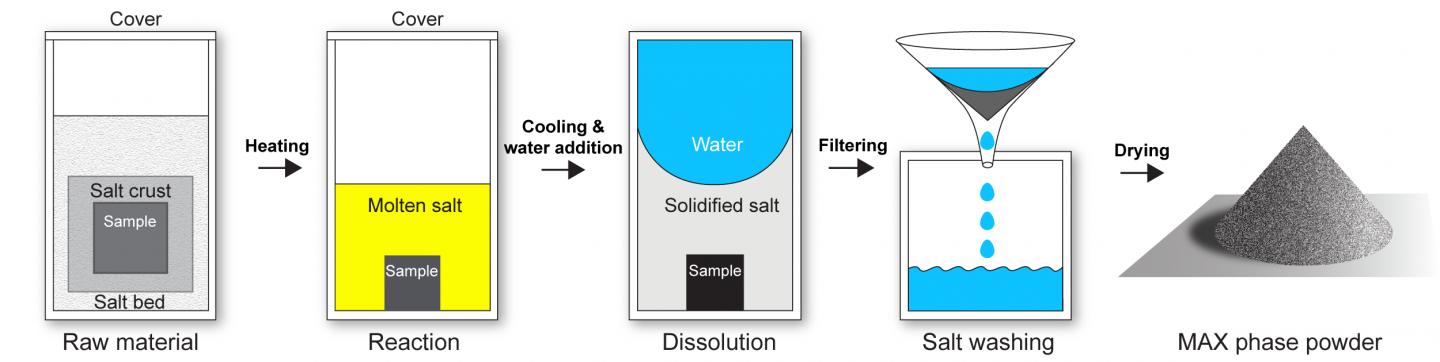
Schematic representation of the process. Image: Forschungszentrum Jülich/Apurv Dash
MAX phases are viewed as promising materials for the future, for example for turbines in power plants and aircraft, space applications, or medical implants. A new method developed by scientists from Forschungszentrum Jülich now makes it possible to produce this desirable material class on an industrial scale for the first time: a crust of salt protects the raw material from oxidation at a production temperature of more than 1,000 degrees Celsius—and can then simply be washed off with water.
The method, which was recently published in the journal Nature Materials, can also be applied to other high-performance materials.
MAX phases unite the positive properties of both ceramics and metals. They are heat resistant and lightweight like ceramics, yet less brittle, and can be plastically deformed like metals. Furthermore, they are the material basis of MXenes, a largely unexplored class of compound that are similar to the “miracle material” graphene and have extraordinary electronic properties.
“In the past, there was no suitable method for producing MAX phases in powder form, which would be advantageous for further industrial processing. This is why MAX phases have not played any practical role in industrial application so far,” explains Junior Professor Dr. Jesus Gonzalez-Julian, young investigators group leader at Forschungszentrum Jülich.
MAX phases are produced at temperatures higher than 1,000 degrees Celsius. At such high temperatures, the materials would normally react with atmospheric oxygen and oxidize, which is why they are usually produced in a vacuum or in a protective atmosphere of argon. The Jülich method is astonishingly simple by comparison: the researchers encapsulate the raw material with a salt-potassium bromide—which melts during the production process. A vacuum or argon atmosphere for additional protection is no longer needed.
“A bath of molten salt thus protects the material and prevents it from coming in contact with atmospheric oxygen,” explains Apurv Dash, lead author of the study published in Nature Materials and doctoral researcher at Forschungszentrum Jülich.
At the same time, the salt acts as a separating agent: the components no longer bond together to form a compact solid, and allow the direct production of fine-grained powders. This is important because it avoids an additional long, energy-intensive milling process. As a positive side effect, the salt bath also reduces the synthesis temperature necessary to form the desired compound, which will additionally cut energy and production costs.
Methods using molten salt have been used for the powder production of non-oxide ceramics for some time. However, they require a protective argon atmosphere instead of atmospheric air, which increases both the complexity and production costs.
“Potassium bromide, the salt we use, is special because when pressurized, it becomes completely impermeable at room temperature. We have now demonstrated that it is sufficient to encapsulate the raw materials tightly enough in a salt pellet to prevent contact with oxygen—even before the melting point of the salt is reached at 735 degrees Celsius. A protective atmosphere is thus no longer necessary,” says Dash.
As with many scientific discoveries a little bit of luck played its part in inventing the method: vacuum furnaces are scarce because they are so expensive and they take a lot of effort to clean. To produce his powder, the Jülich doctoral researcher therefore resorted to testing a normal air furnace—successfully!
The new method is not limited to a certain material. The researchers have already produced a multitude of different MAX phases and other high-performance materials, such as titanium alloys for bioimplants and aircraft engineering. As a next step, the scientists are now planning to investigate industrial processes with which these powders can be processed further.




