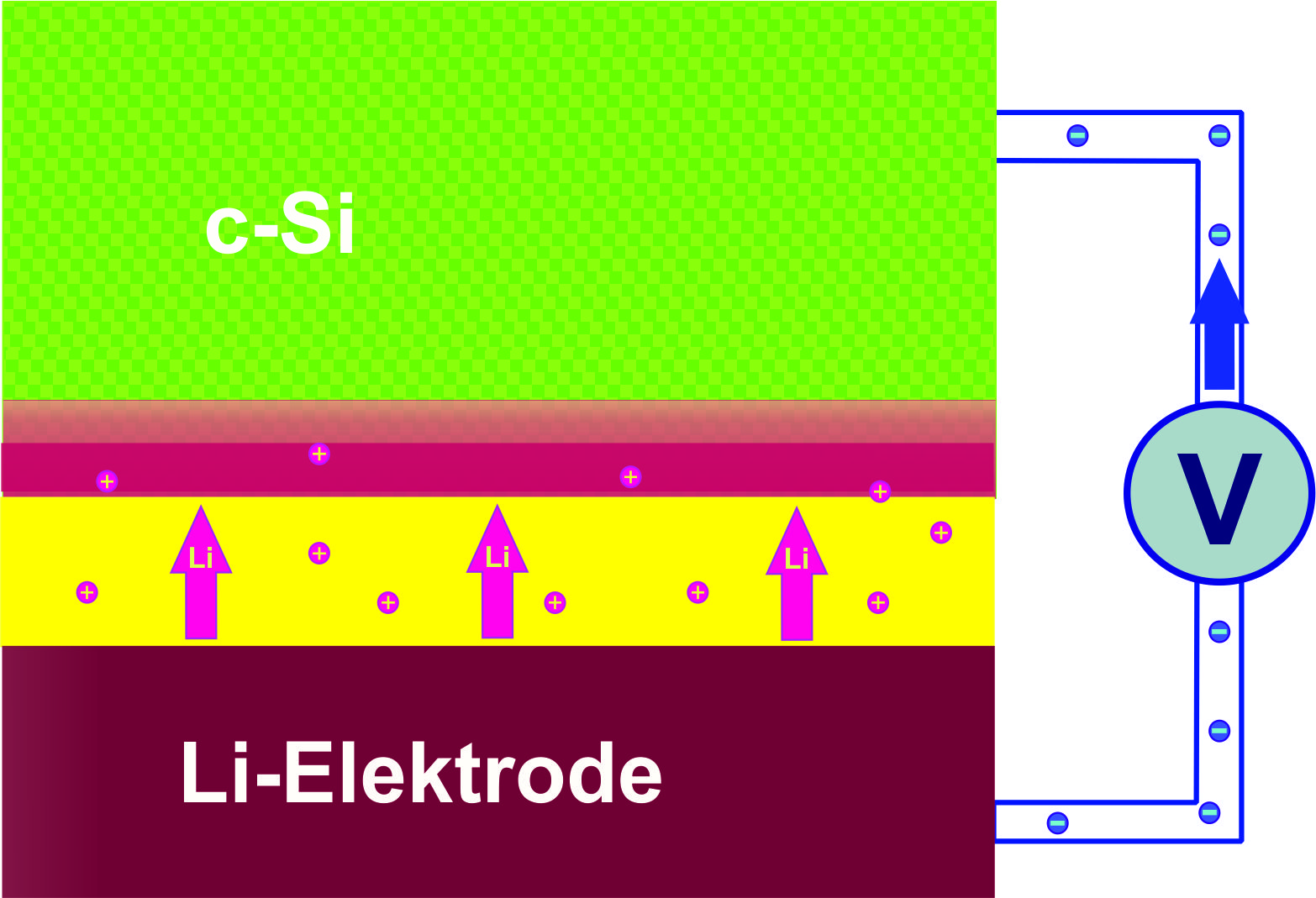
Lithium ions migrate through the electrolyte (yellow) into the layer of crystalline silicon (c-Si). During the charging cycle, a 20-nm layer (red) develops on the silicon electrode adsorbing extreme quantities of lithium atoms. Image: HZB
The capacity of lithium-ion batteries might be increased by six times by using anodes made of silicon instead of graphite. A team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) Institute of Soft Matter and Functional Materials has observed for the first time in detail how lithium ions migrate into thin films of silicon. It was shown that extremely thin layers of silicon would be sufficient to achieve the maximal load of lithium.
The results are published in the journal ACSnano.
The team was able to show through neutron measurements made at the Institut Laue-Langevin in Grenoble, France, that lithium ions do not penetrate deeply into the silicon. During the charge cycle, a 20-nm anode layer develops containing an extremely high proportion of lithium. This means extremely thin layers of silicon would be sufficient to achieve the maximal load of lithium.
Lithium-ion batteries provide laptops, smart phones, and tablet computers with reliable energy. However, electric vehicles have not gotten as far along with conventional lithium-ion batteries. This is due to currently utilized electrode materials such as graphite only being able to stably adsorb a limited number of lithium ions, restricting the capacity of these batteries. Semiconductor materials like silicon are therefore receiving attention as alternative electrodes for lithium batteries. Bulk silicon is able to absorb enormous quantities of lithium. However, the migration of the lithium ions destroys the crystal structure of silicon. This can swell the volume by a factor of three, which leads to major mechanical stresses.
Now a team from the HZB Institute for Soft Matter and Functional Materials headed by Professor Matthias Ballauff has directly observed for the first time a lithium-silicon half-cell during its charging and discharge cycles. “We were able to precisely track where the lithium ions adsorb in the silicon electrode using neutron reflectometry methods, and also how fast they were moving,” comments Dr. Beatrix-Kamelia Seidlhofer, who carried out the experiments using the neutron source located at the Institute Laue-Langevin.
She discovered two different zones during her investigations. Near the boundary to the electrolytes, a roughly 20-nm layer formed having extremely high lithium content: 25 lithium atoms were lodged among 10 silicon atoms. A second adjacent layer contained only one lithium atom for ten silicon atoms. Both layers together are less than 100 nm thick after the second charging cycle.
After discharge, about one lithium ion per silicon node in the electrode remained in the silicon boundary layer exposed to the electrolytes. Seidlhofer calculates from this that the theoretical maximum capacity of these types of silicon-lithium batteries lies at about 2300 mAh/g. This is more than six times the theoretical maximum attainable capacity for a lithium-ion battery constructed with graphite (372 mAh/g).
These are substantial findings that could improve the design of silicon electrodes: very thin silicon films should be sufficient for adsorbing the maximum possible amount of lithium, which in turn would save on material and especially on energy consumed during manufacture — less is more!
Source: Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin




