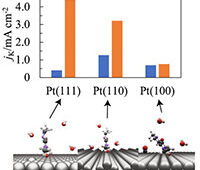
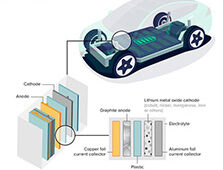
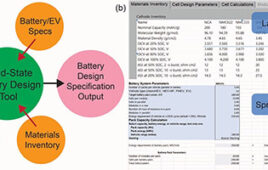
Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd., (MHI), has developed Japan’s first cargo container-type
large-capacity energy storage system that uses a lithium-ion rechargeable
battery. The system is capable of providing power of up to one megawatts (MW),
and its mobility makes the system suitable for a wide range of applications,
including emergency use. The actual system has been installed at the Nagasaki
Shipyard & Machinery Works of MHI in Nagasaki
Prefecture, Japan,
to begin verification testing for a power stabilization system application from
early July towards the commercialization of the system.
The
container-type “megawatt-class large-capacity energy storage system
(ESS)” consists of a 40 ft-long container unit, which houses more than
2,000 units of lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, and a 20 ft-long container
unit, in which two power conditioners are installed. Power conditioners are
used for direct current (DC)/alternating current (AC) conversion and their
input/output control. Each container unit can be moved by container trailers.
The system has the capacity to store 408 kWh (kilowatt hour) of power and is
designed to have a system efficiency of 90%.
The
power storage system is capable of providing electricity for some 100
households for three to eight hours. By using multiple units of the system,
power output can be increased to the level of several tens of thousands of
kilowatts.
The
system installed for verification testing in Nagasaki is currently being adjusted towards
an in-plant electric-load leveling test. Testing will be conducted envisaging
such cases as short-cycle conditioning to level fluctuations of electricity
generated, including power produced by wind power and solar cells, and medium-
and long-cycle conditioning for a period of several hours. It will also test
the system for a micro-grid application to enable a stable supply of
electricity by storing power from renewable energy, for the use in the areas
where connections to regular power transmission/distribution grids are
difficult.
The
research and development activities of large-capacity energy storage systems
are advanced mainly in countries and regions that depend largely on renewable
energy, such as wind power and solar energy, which are vulnerable to
fluctuations in weather conditions. Where a substantial portion of the entire
power supply relies on such sources, instability in power generation has been a
challenge to solve. The verification testing of the energy storage system using
high power density lithium-ion rechargeable batteries is actively being
conducted in the US and Europe as a promising technology. The mobile
container-type ESS is especially advantageous due to its variety of applicable
usages, including its ability to power sources for large-scale outdoor events,
construction sites and mobile power charge stations for electric vehicles, in
addition to power supply stabilization and serving as an emergency-use power
source.
Mitsubishi Heavy
Industries, Ltd., www.mhi.co.jp