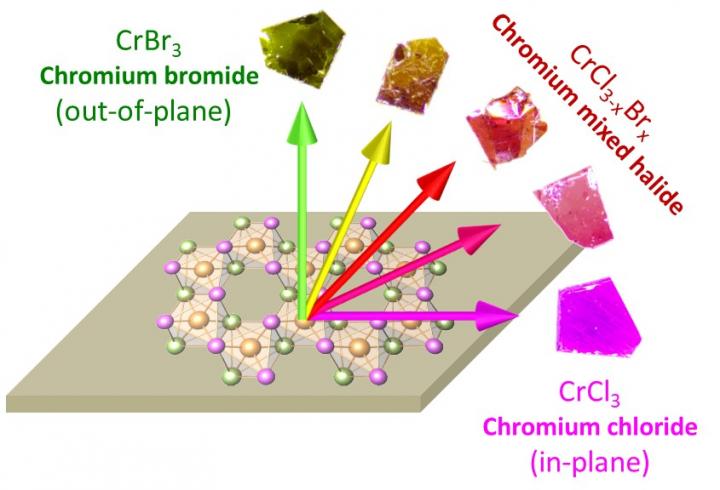
Chromium chloride and chromium bromide were known in the past as transition-metal halides with in-plane and out-of-plane magnetization. Boston College researchers have discovered a way of making mixed halides with all the composition between these two parameters. The result of this “mixed halide chemistry” was a combination of chromium chloride and bromide where adjustments to the ratio of chlorine to bromine can be varied continuously. The team observed a continuous change of magnetization from in-plane to out-of-plane as it adjusted the ratio. Small crystals of chromium mixed halides with different chlorine to bromine ratios are shown in the image. Credit: Fazel Tafti, Boston College
Physicists, chemists, and materials scientists have been probing the nature of layered magnetic materials for several decades, searching for clues to the properties of these materials that are more complex than they appear.
Layered material resembles the structure of a book. From a distance, it looks like a solid three-dimensional object but when examined more closely, it is made from the stacking of many flat, two-dimensional sheets similar to the pages of a book.
During the past decade, scientists have pursued the “exfoliation” of layered magnetic materials, a process by which a material is systematically cleaved until a single atomic sheet is isolated.
A single atomic sheet of a magnetic layered material allows researchers to fabricate atomically flat, ultrathin magnetic devices. As an example, scientists have constructed ultrathin “magnetic memories” – single atomic sheets where information is stored in the directional orientation of the magnetization of the atoms.
The magnetization of a layered material is typically oriented either parallel or perpendicular to the plane of atoms. In other words, magnetization tends to point either “in-plane” or “out-of-plane” — indicating what is known as a magnetic anisotropy.
So far, scientists were aware of only the in-plane or the out-of-plane limits of magnetic anisotropy. In other words, the ability to control the orientation of the magnetism was defined by just the two parameters of anisotropy.
In a new report in Advanced Materials, researchers from Boston College demonstrate that magnetic anisotropy can be continuously tuned between the two limits of in-plane and out-of-plane. The team reports it achieved this advance in the arena of ultrathin magnetic devices by successfully pointing the magnetization toward any direction of space instead of only in-plane or out-of-plane.
“In addition to magnetization direction, our team showed that all properties of these layered material including light absorption, distance between the layers, and temperature of magnetic transition can be continuously controlled to any desired value,” said Boston College Assistant Professor of Physics Fazel Tafti, lead author of the paper. “This is a leap of progress in tuning materials properties for optical and magnetic device industry.”
To make the material, a team led by Tafti and Boston College Associate Professor of Physics Kenneth Burch developed a “mixed-halide chemistry” approach where researchers combined different halide atoms, such as chlorine or bromine, around a transition metal such as chromium.
By adjusting the relative composition of chlorine to bromine, the researchers were able to adjust an internal parameter at the atomic level known as the spin-orbit coupling which is the source of magnetic anisotropy, said Tafti.
The tuning methodology allows for the engineering of the amount of spin-orbit coupling and the orientation of magnetic anisotropy at an atomic level, the team reported.
Tafti said advancing these types of materials will form the basis of next-generation ultrathin magnetic devices. In the future, these devices may one day replace the transistors and electric chips used today. Because of their atomic scale, Tafti said, further advances will likely shrink the size of magnetic devices as capabilities allow magnetic information to be composed on these atomically flat sheets.
“From here, we will continue to push the frontiers of magnetic layered materials by making mixed halides of transition metals other than chromium,” said Tafti. “Our team demonstrated that the mixed halide chemistry is not limited to chromium and can be generalized to over 20 other transition metals. The co-leader of the project, Kenneth Burch, is trying to artificially interface different magnetic layers so the properties of one layer would affect the adjacent one. Such metamaterials can change the propagation of light in one layer based on the direction of magnetism in the neighboring layer and vice versa – a property known as the magneto-optical effect.”



