
A researcher holds a small, nanostructured device that uses sunlight to disinfect water. By harnessing a broad spectrum of sunlight, it works faster than devices that use only ultraviolet rays. Image: Jin Xie/Stanford University
In many parts of the world, the only way to make germy water safe is by boiling, which consumes precious fuel, or by putting it out in the sun in a plastic bottle so ultraviolet rays will kill the microbes. But because UV rays carry only 4 percent of the sun’s total energy, the UV method takes six to 48 hours, limiting the amount of water people can disinfect this way.
Now, researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University have created a nanostructured device, about half the size of a postage stamp, that disinfects water much faster than the UV method by also making use of the visible part of the solar spectrum, which contains 50 percent of the sun’s energy.
In experiments reported in Nature Nanotechnology, sunlight falling on the little device triggered the formation of hydrogen peroxide and other disinfecting chemicals that killed more than 99.999 percent of bacteria in just 20 minutes. When their work was done the killer chemicals quickly dissipated, leaving pure water behind.
“Our device looks like a little rectangle of black glass. We just dropped it into the water and put everything under the sun, and the sun did all the work,” says Chong Liu, lead author of the report. She is a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Yi Cui, a SLAC/Stanford associate professor and investigator with SIMES, the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences at SLAC.
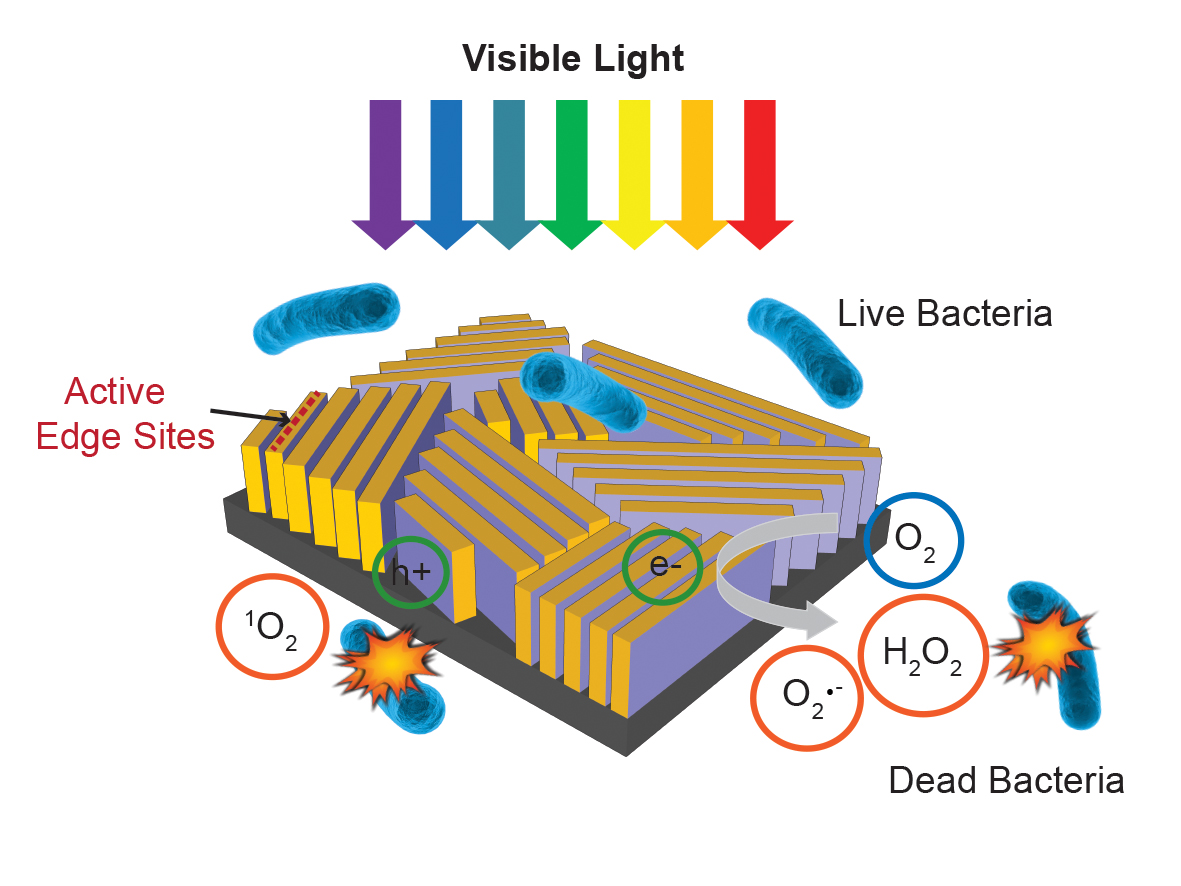
This nanostructured device, about half the size of a postage stamp, uses sunlight to quickly disinfect water. It consists of thin flakes of molybdenum disulfide arranged like walls on a glass surface and topped with a thin layer of copper. Light falling on the walls triggers formation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and other “reactive oxygen species” that kill bacteria. Image: C. Liu et al., Nature Nanotechnology
Under an electron microscope the surface of the device looks like a fingerprint, with many closely spaced lines. Those lines are very thin films — the researchers call them “nanoflakes” — of molybdenum disulfide that are stacked on edge, like the walls of a labyrinth, atop a rectangle of glass.
In ordinary life, molybdenum disulfide is an industrial lubricant. But like many materials, it takes on entirely different properties when made in layers just a few atoms thick. In this case it becomes a photocatalyst: When hit by incoming light, many of its electrons leave their usual places, and both the electrons and the “holes” they leave behind are eager to take part in chemical reactions.
By making their molybdenum disulfide walls in just the right thickness, the scientists got them to absorb the full range of visible sunlight. And by topping each tiny wall with a thin layer of copper, which also acts as a catalyst, they were able to use that sunlight to trigger exactly the reactions they wanted — reactions that produce “reactive oxygen species” like hydrogen peroxide, a commonly used disinfectant, which kill bacteria in the surrounding water.
Molybdenum disulfide is cheap and easy to make — an important consideration when making devices for widespread use in developing countries, Cui says. It also absorbs a much broader range of solar wavelengths than traditional photocatalysts.
The method is not a cure-all; for instance, it doesn’t remove chemical pollutants from water. So far it’s been tested on only three strains of bacteria, although there’s no reason to think it would not kill other bacterial strains and other types of microbes, such as viruses. And it’s only been tested on specific concentrations of bacteria mixed with less than an ounce of water in the lab, not on the complex stews of contaminants found in the real world.
Still, “It’s very exciting to see that by just designing a material you can achieve a good performance. It really works,” says Liu, who has gone on to work on a project in Cui’s lab that is developing air filters for combating smog. “Our intention is to solve environmental pollution problems so people can live better.”
The work was funded by the Department of Energy Office of Science through SIMES, and carried out in collaboration with Professor Alexandria Boehm’s group in the Stanford department of civil and environmental engineering.




