Researchers at NIST and Sharp Laboratories of America, Inc. have discovered new optical properties in sheet-like materials that could eventually make flat-screen televisions, laptops, and other light-emitting appliances more energy-efficient (Journal of Physical Chemistry, “High-Temperature Photoluminescence in Colloidal ‘Quasi’ 2D Materials”).
Known as semiconductor nanoplatelets (NPLs), the materials are just a few atoms thick and made of cadmium telluride. Created with standard chemistry methods, NPLs are eventually intended to work as light-converting elements in consumer devices.
Nanoplatelets could replace the phosphor coatings that are currently used to create full-color light in TV screens and other display and lighting technologies. In such displays, light emitting diodes (LEDs) are used to shine light through the phosphors to create a full-color spectrum.
Although phosphors create fantastic, true-to-life colors that are easy to turn into dynamic pictures on screens, the light-conversion process needs to become more energy-efficient. In addition, replacing phosphors could further increase a display’s dynamic range, making possible even blacker blacks and brighter colors than is possible today.
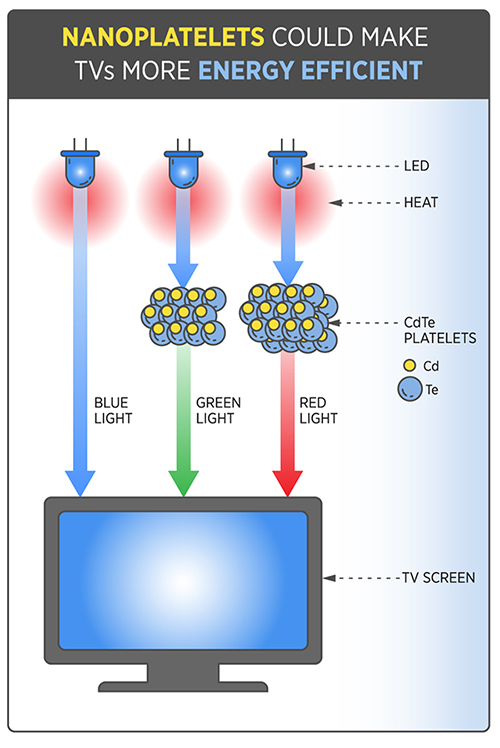
Image: K. Irvine/NIST
Recently, researchers and engineers have developed tiny spherical structures called quantum dots (QD) to replace phosphor coating for the light conversion. However, the color quality of light produced by QDs, which are placed directly on a blue LED source, is hard to control due to a phenomenon known as thermal quenching. The light from QDs dramatically dims due to inevitable heating in excess of 212°F (100 °C) from the LED source commonly used in today’s televisions and monitors.
Like QDs, NPLs are designed to emit multicolored light. Both QDs and NPLs are only a few nanometers thick—about ten thousand times narrower than a strand of human hair. But it’s much easier to tailor NPLs’ color-converting properties because it is determined only by the nanoplatelets’ thickness, a much easier property to control than the size of a three-dimensional QD. In addition, the NIST and Sharp Laboratories research has demonstrated that the light from NPLs does not get quenched at elevated temperatures, which is critical for next-generation lighting technology.
More work is needed before the NPLs will be ready for wide-scale market use. But eventually, these optically active nanoplatelets may be as associated with reducing energy waste in lighting and display technologies, as blood platelets are with reducing bleeding in hospital patients. Since about 15 percent of the world’s electricity consumption is currently used for lighting, these tiny sheets of cadmium telluride material may make a big difference in energy efficiency. Developing cadmium-free NPLs is one of the next problems that scientists aim to solve.
Source: NIST




