An award-winning Vanderbilt University researcher used plasmonics to develop a new kind of nanotweezers that can rapidly trap and detect molecules, viruses, and DNA — a device transformative for medicine that also has color printing applications.
Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Justus Ndukaife and his Purdue University collaborators poked holes in gold film smaller than the wavelength of light. Squeezing light into such small volumes is enabled by surface plasmon resonance, a phenomenon that causes molecules to be trapped near the film, making them available for study under powerful microscopes.
The result is what’s commonly known as a lab-on-a-chip — a new way of detecting and diagnosing cancer, viruses, or any number of ailments.
Ndukaife’s nanotweezers require less laser power, have more potential to trap and stabilize molecules, and allow for higher resolution than previous versions used for lab-on-a-chip applications.
He says they also have the potential for using broadband wavelength light source to assemble gold and silicon nanoparticles, which could have applications for permanent, non-fading color printing.
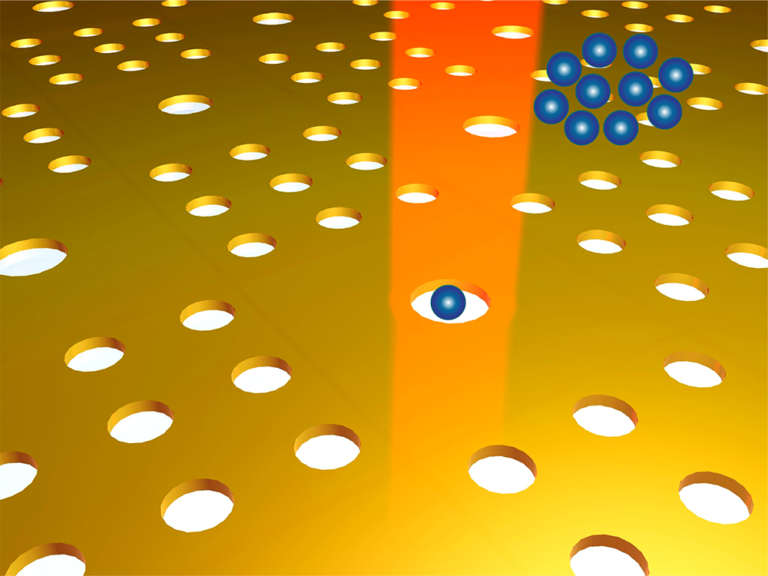
Squeezing light into nano-size volumes is enabled by surface plasmon resonance, a phenomenon that causes molecules to be trapped near the film, making them available for study under powerful microscopes. Image: Justus Ndukaife/Vanderbilt University
His results recently were published in the journal ACS Nano. The work was made possible by the National Science Foundation’s Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers grant DMR-1120923.
Ndukaife, who won the 2017 Chorafas Foundation Prize in Physics for his nanotweezers work, also recently was selected for the Carnegie African Diaspora Fellowship Program. He will work with the University of Nigeria, Nsukka on development and testing of a lab-on-a-chip device for isolation and concentration of e-coli bacteria.
Ndukaife’s project is part of a broader initiative that will pair 55 CADFP scholars with one of 43 higher education institutions and collaborators in Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania and Uganda to work together on curriculum co-development, research, graduate teaching, training and mentoring in the coming months.
The fellowships cover all expenses for African-born scholars to work with host universities across the continent, helping people there and building relationships with U.S. institutions.
Source: Vanderbilt University




