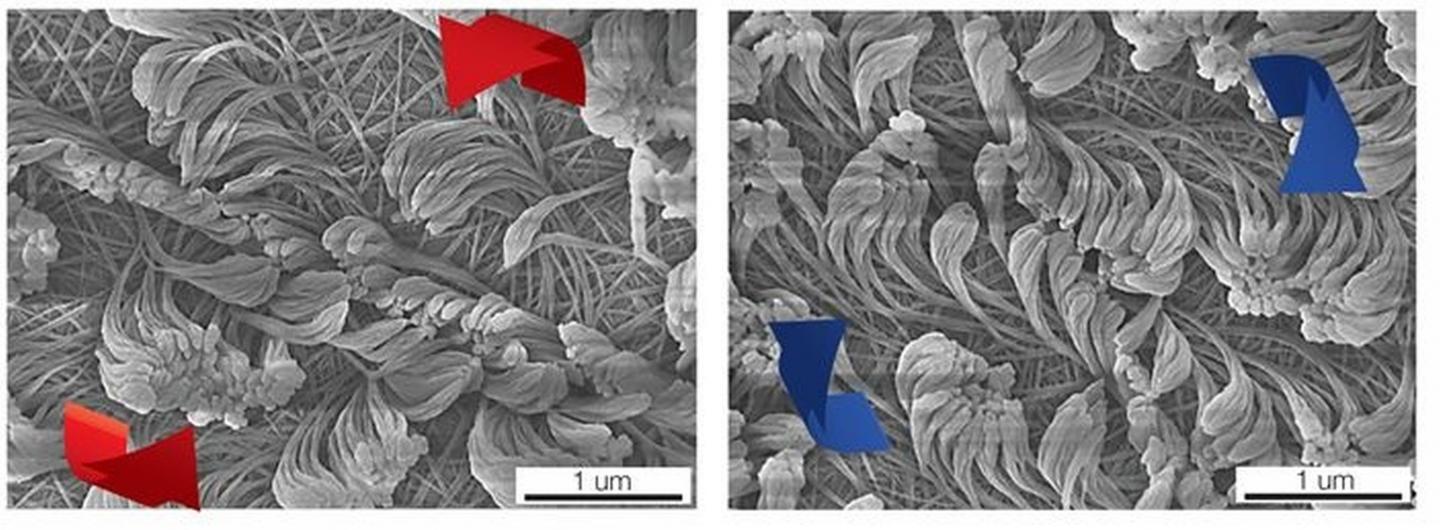
These are nanofibers with different directions of rotation. Illustration: Kenneth Cheng, University of Michigan
Polymer pelts made of the finest of fibers are suitable for many different applications, from coatings that adhere well and are easy to remove to highly sensitive biological detectors. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) together with scientists in the United States have now developed a cost-effective process to allow customized polymer nanofibers to grow on a solid substrate through vapor deposition of a liquid crystal layer with reactive molecules. The researchers report on their innovative method in the journal Science. (DOI: 10.1126/science.aar8449)
Surfaces with specially aligned fibers are quite abundant in nature and perform different functions such as sensing, adhering and self-cleaning. For example, the feet of geckos are covered with millions of hairs that allow them to adhere to surfaces and pull off again very easily. The synthesis of such surfaces from man-made materials opens up new perspectives for different applications. However, methods previously available for the production of polymer pelts on solid bases have been costly. What’s more important, the size, shape and alignment of the fibers can only be controlled to a limited extent with conventional methods.
Researchers at the Institute of Functional Interfaces (IFG) of KIT, as well as at the University of Michigan, the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, have now developed a simple and therefore cost-effective process that allows polymer pelts to grow in a self-organized way. The research group led by Professor Joerg Lahann, Head of the Department of New Polymers and Biomaterials at KIT’s IFG and Director of the Biointerfaces Institute of the University of Michigan, present the new process in the journal Science. First of all, they cover a carrier with a thin layer of liquid crystals, which are substances that are liquid, have directional properties and are otherwise used especially for screens and displays (liquid crystal displays – LCDs). Next, the liquid crystal layer is exposed to activated molecules by vapor deposition. These reactive monomers penetrate the liquid crystalline layer and grow from the substrate into the liquid in the form of fine fibers.
As a result, polymer nanofibers are created that can be customized in length, diameter, shape and arrangement. The complex but precisely structured polymer pelts formed by the fibers are attractive for many different applications, especially for biological detectors, bioinstructive surfaces that interact with their environment, and for coatings with new properties. This also includes surfaces with dry adhesion properties similar to those of gecko feet, although adhesion in nanofibers is based on a special spatial arrangement of the atoms in the molecules (chirality – handedness).
The German Research Foundation (DFG) funded the work at the “Molecular Structuring of Soft Matter” Collaborative Research Center (CRC). In the 3D Matter Made to Order (3DMM2O) cluster of KIT and the University of Heidelberg, which will be funded in the Excellence Strategy by the federal and state governments from January 2019, the focus will also be on customized materials. The 3DMM2O Excellence Cluster, in which the Head of KIT’s IFG, Professor Christof Wöll, is involved as one of the main researchers, combines natural and engineering sciences, focusing on three-dimensional additive production technologies from a molecular to macroscopic level.




