A new idea to use super-polished silicon wafers as the heart of a telescope is set to reveal more of the hot, high-energy Universe, peering back into its turbulent history.
A new idea to use super-polished silicon wafers as the heart of a telescope is set to reveal more of the hot, high-energy Universe, peering back into its turbulent history.
Invisible X-rays tell us about the very hot matter in the Universe – black holes, supernovas and superheated gas clouds. Today’s X-ray observatories, ESA’s XMM-Newton, and NASA’s Chandra, were launched in the last century, and are still delivering world-class science. But they are starting to age.
To replace them, ESA is planning a much more capable X-ray observatory for launch in 2028, which would probe 10 to 100 times deeper into the Universe than the current generation of X-ray telescopes.
“This demands a whole new type of X-ray mirror,” explains Marcos Bavdaz, leading the technology push for ESA’s future science missions. “To reach the kind of size needed, this new mission’s mirrors will have to be 10 times lighter than XMM’s, while delivering even sharper images.”
 The problem is that energetic X-rays do not behave like typical light waves – try to reflect them with a standard mirror and they are absorbed inside. Instead, X-rays can only be reflected at shallow angles, like stones skimming along water.
The problem is that energetic X-rays do not behave like typical light waves – try to reflect them with a standard mirror and they are absorbed inside. Instead, X-rays can only be reflected at shallow angles, like stones skimming along water.
That means multiple mirrors must be stacked together to build a large-enough telescope. XMM has 174 gold-plated nickel mirrors, nested inside one another like Russian dolls.
But to reach the performance required for ESA’s next X-ray mission, tens of thousands of densely packed mirror plates will be needed. How can this be done?
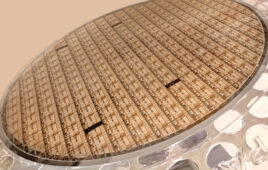
A new approach is required. “Silicon pore optics,” developed by ESA, draws on high-tech equipment and materials from the semiconductor industry.
“We make use of industrial silicon wafers, normally used to manufacture microprocessors,” adds Eric Wille, optical system engineer for the X-ray optics development.
“We take advantage of their stiffness and super-polished surface, stacking a few dozen at a time together to form a single ‘mirror module.’”
Many hundreds of these modules will be fitted together to form the optics of the X-ray mission.
 Grooves are cut into the wafers, leaving stiffening ribs and paper-thin mirrors, which are then covered with reflective metal. For maximum accuracy, semiconductor manufacturing techniques are applied for the stacking process.
Grooves are cut into the wafers, leaving stiffening ribs and paper-thin mirrors, which are then covered with reflective metal. For maximum accuracy, semiconductor manufacturing techniques are applied for the stacking process.
“Stacking is done by a specially designed robot, aiming for micron-scale precision,” Eric describes. “We’ve seen big jumps in quality as the robotics improve.”
 “All the stacking takes place in a cleanroom, since tiny dust particles risk large deformations in the mirror stack.
“All the stacking takes place in a cleanroom, since tiny dust particles risk large deformations in the mirror stack.
“The semiconductor industry is improving the quality of silicon wafers, which will further improve the mirror quality in future.”
Release Date: May 16, 2014
Source: European Space Agency