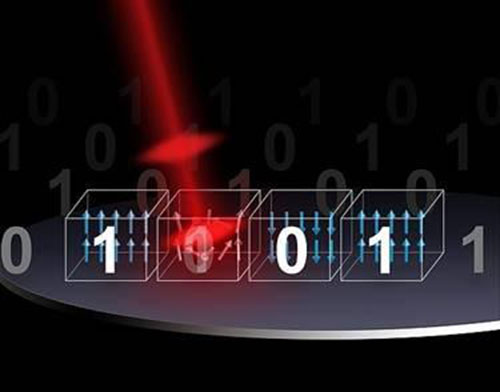
All-optical switching. Data is stored in the form of ‘bits,’ which contains digital 0 (North Poles down) or 1 (North Poles up). Data writing is achieved by ‘switching’ the direction of the poles via the application of short laser pulses (in red). (Credit: Eindhoven University of Technology)
Light is the most energy-efficient way of moving information. Yet, light shows one big limitation: it is difficult to store. As a matter of fact, data centers rely primarily on magnetic hard drives. However, in these hard drives, information is transferred at an energy cost that is nowadays exploding. Researchers of the Institute of Photonic Integration of the Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) have developed a ‘hybrid technology’ which shows the advantages of both light and magnetic hard drives. Ultra-short (femtosecond) light pulses allow data to be directly written in a magnetic memory in a fast and highly energy-efficient way. Moreover, as soon as the information is written (and stored), it moves forward leaving space to empty memory domains to be filled in with new data. This research, published in Nature Communications, promises to revolutionize the process of data storage in future photonic integrated circuits.
Data are stored in hard drives in the form of “bits,” tiny magnetic domains with a North and a South pole. The direction of these poles (“magnetization”) determines whether the bits contain a digital 0 or a 1. Writing the data is achieved by “switching” the direction of the magnetization of the associated bits.
Synthetic ferrimagnets
Conventionally, the switching occurs when an external magnetic field is applied, which would force the direction of the poles either up (1) or down (0). Alternatively, switching can be achieved via the application of a short (femtosecond) laser pulse, which is called all-optical switching, and results in a more efficient and much faster storage of data.
Mark Lalieu, Ph.D. candidate at the Applied Physics Department of TU/e: “All-optical switching for data storage has been known for about a decade. When all-optical switching was first observed in ferromagnetic materials – amongst the most promising materials for magnetic memory devices – this research field gained a great boost.” However, the switching of the magnetization in these materials requires multiple laser pulses and, thus, long data writing times.
Storing data a thousand times faster
Lalieu, under the guidance of Reinoud Lavrijsen and Bert Koopmans, was able to achieve all-optical switching in synthetic ferrimagnets—a material system highly suitable for spintronic data applications—using single femtosecond laser pulses, thus exploiting the high velocity of data writing and reduced energy consumption.
So how does all-optical switching compare to modern magnetic storage technologies? Lalieu: “The switching of the magnetization direction using the single-pulse all-optical switching is in the order of picoseconds, which is about a 100 to 1000 times faster than what is possible with today’s technology. Moreover, as the optical information is stored in magnetic bits without the need of energy-costly electronics, it holds enormous potential for future use in photonic integrated circuits.”
‘On-the-fly’ data writing
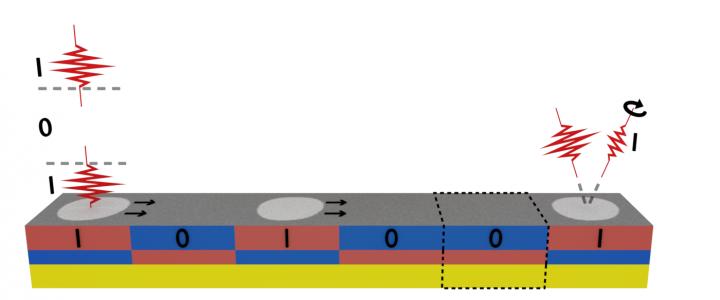
On-the-fly data writing in racetrack memory devices. The magnetic bits (1’s and 0’s) are written by laser pulses (red pulses, left side), and data is transported along the racetrack towards the other side (black arrows). In the future, data might be also read-out optically (red pulses, right side). (Credit: Eindhoven University of Technology)
In addition, Lalieu integrated all-optical switching with the so-called racetrack memory—a magnetic wire through which the data, in the form of magnetic bits, is efficiently transported using an electrical current. In this system, magnetic bits are continuously written using light, and immediately transported along the wire by the electrical current, leaving space to empty magnetic bits and, thus, new data to be stored.
Koopmans: “This ‘on the fly’ copying of information between light and magnetic racetracks, without any intermediate electronic steps, is like jumping out of a moving high-speed train to another one. From a ‘photonic Thalys’ to a ‘magnetic ICE’, without any intermediate stops. You will understand the enormous increase in speed and reduction in energy consumption that can be achieved in this way.”
What’s next?
This research was performed on micrometric wires. In the future, smaller devices in the nanometer scale should be designed for better integration on chips. In addition, working towards the final integration of the photonic memory device, the Physics of Nanostructure group is currently also busy with the investigation on the read-out of the (magnetic) data, which can be done all-optically as well.




