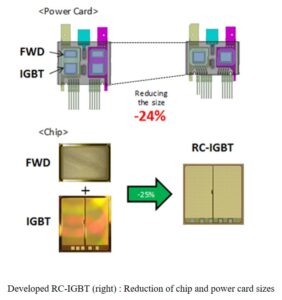
 Environmentally conscious hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which are driven partly by an electric motor controlled by a power control unit (PCU), are currently increasing in popularity. Toyota’s research efforts have led to downsizing the power cards and reducing the power loss of the PCU. On the power card, an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) and a free wheel diode (FWD) are placed in parallel. A power device that integrates an IGBT and an FWD is called a reverse conductive (RC)-IGBT. The RC-IGBT is well known to be effective for device chip and power card size reduction. Toyota’s researchers have developed the first lower power loss RC-IGBT with operating current of 400 A for use in the PCUs of HEVs. Toyota’s RC-IGBT achieves a 25% smaller device chip. Moreover, 13% reduction of power loss was also achieved. The developed RC-IGBT reduced 40% power loss of the HEV PCUs than that of prior generations. The RC-IGBT contributes to expansion of the HEV line-up, thereby reducing CO2 emissions.
Environmentally conscious hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which are driven partly by an electric motor controlled by a power control unit (PCU), are currently increasing in popularity. Toyota’s research efforts have led to downsizing the power cards and reducing the power loss of the PCU. On the power card, an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) and a free wheel diode (FWD) are placed in parallel. A power device that integrates an IGBT and an FWD is called a reverse conductive (RC)-IGBT. The RC-IGBT is well known to be effective for device chip and power card size reduction. Toyota’s researchers have developed the first lower power loss RC-IGBT with operating current of 400 A for use in the PCUs of HEVs. Toyota’s RC-IGBT achieves a 25% smaller device chip. Moreover, 13% reduction of power loss was also achieved. The developed RC-IGBT reduced 40% power loss of the HEV PCUs than that of prior generations. The RC-IGBT contributes to expansion of the HEV line-up, thereby reducing CO2 emissions.




Tell Us What You Think!