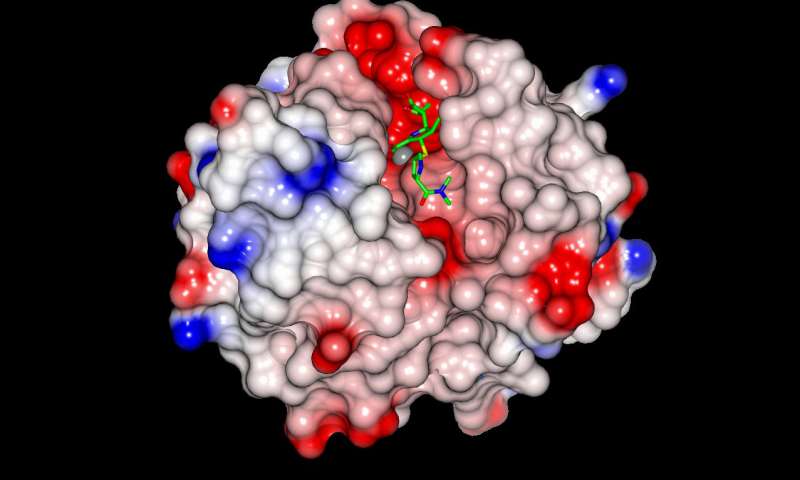
Antibiotic (green) bound to the VIM enzyme (solid surface). Credit: University of Bristol
A research team from the University of Bristol is unlocking a crucial mechanism of antibiotic resistance in an effort to find new ways to block the growing threat of resistance.
A family of bacterial protein called the Verona Imipenemase (VIM) beta-lactamases is known to cause a form of antibiotic resistance that is particularly concerning because it can inactivate antibiotics like penicillin that comprise over half of the global antibacterial market. However, in the new study, the researchers uncovered near-atomic level structural detail of VIM proteins, a discovery that could yield new approaches to thwart antibiotic resistance.
“Our work explains how the products of one family of resistance genes recognize penicillin-type antibiotics and suggests routes to blocking this resistance in future treatments,” Jim Spencer, PhD, Reader in Microbiology in the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at the University of Bristol, said in a statement.
The VIM proteins protect bacteria from beta-lactams by binding and subsequently inactivating them to prevent their attack on target bacteria. To block the VIM protein mediated resistance, the researchers zeroed in on identifying exactly how they bind to the antibiotics.
“We sought to understand how VIM recognizes its target antibiotics,” Spencer said.
To determine the protein’s atomic arrangement, the researchers fired high intensity X-rays produced in particle accelerators called synchrotrons at the protein and observed the way in which the X-rays are scattered.
Surprising variation has been previously identified in two specific regions of VIM proteins, making it difficult to explain how different VIM family members could all bind antibiotics. By collecting near-atomic level crystallographic data on one VIM protein family member, the research team was able to identify a key component of the antibiotic binding mechanism.
They also compared the structure of one of the family members with other VIM protein family members to confirm the identified component to be a common feature within the entire family.
“The VIM beta-lactamases are a family of enzymes that vary from one another in the region responsible for antibiotic binding; our work explains how antibiotics can bind to different types of VIM beta-lactamase despite these variations,” Spencer said. “Knowledge of the mechanisms by VIM beta-lactamases bind antibiotics will enable researchers to replicate these interactions in molecules designed to block their activity, and so reverse antibiotic resistance.”
The researchers are now attempting to design molecules that bind to the VIM proteins.




