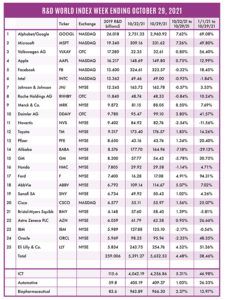
The R&D World Index (RDWI) for the week ending October 29, 2021, closed at 5,632.53 for the 25 companies in the R&D World Index. The Index was up 4.48% (or 241.26 basis points) from the week ending October 22, 2021. The stock of 15 R&D World Index members gained value from 0.75% (Apple) to 8.50% (Merck & Co.). The stock of 10 R&D World Index members lost value from -0.32% (Facebook) to -7.18% (Alibaba).
RDW Index member Eli Lilly & Co. last week submitted a new treatment for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease for approval to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The drug, donanemab, submission comes after the FDA approved Biogen’s Alzheimer’s drug, Aduhelm. Both drugs target amyloid, a substance that forms plaques in the brain and is considered by researchers to advance preliminary effects of the disease. Lilly will seek accelerated approval of its drug and is expected to complete its application in the next several months.
The U.S. General Accounting Office (GAO) issued a report last week stating that the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) needs to better coordinate and prioritize its R&D concerning its nuclear waste cleanup efforts. The DOE has been responsible for significant contamination from more than 40 years of nuclear weapons production. Its R&D in these efforts has been substantial but has declined over the past ten years. The report’s recommendations include 1) develop a system to collect R&D information, 2) develop a system to prioritize that R&D across the agency’s full environmental management (EM) sector and 3) deploy a risk-informed decision-making system to monitor and evaluate its nuclear R&D.
The Salk Institute for Biological Studies and the Scripps Research organization, both located in La Jolla, Calif., announced last week that they will both undergo major expansions over the next several years with new research facility construction. The nearby University of San Diego will also build a new home for its Hertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science, along with another stand-alone biomedical lab complex. These four projects combined will cost up to $800 million to build and create the San Diego area as the U.S.’s third largest life sciences cluster, according to the commercial real estate company CBRE. Scripps is expected to start its $100 million complex construction this month, with Salk starting its $250 million complex early next year. The Salk expansion will be its first since 1995.
Israel and the European Union (EU) finalized an agreement last week for Jerusalem to join the EU’s largest research and innovation program, Horizon Europe. The $111 billion deal (in grants) is expected to be finalized in December after both sides complete their internal ratification processes. The fact that Israel, the UK and Switzerland are not in the EU, but received the most research funding from Horizon 2020 led to changes in the financial arrangements with EU-associated non-member states. Israel is expected to pay more than $3 billion into the Horizon program.
Inflation continues to be a pesky economic statistic complicating budgeting plans for 2022, including those for R&D. The Federal Reserve’s statements that inflation growth beyond its 2% target ceiling was just an economic reaction to the pandemic and its effects have proven to be overly conservative as overall prices, outside of those related to the pandemic, continue to surge. The Fed has recently shown less conviction that inflation will subside in mid to late-2022 and is now expecting to support as many as three rate increases in 2022. Fed chairman, Jerome Powell was noted as saying that “supply-side constraints have actually gotten worse in some cases… and now we’re getting upward pressure on energy.” Economic risks are being seen that there may be more persistent economic supply bottlenecks and to continued higher inflation, possible past 2022. The U.S. Department of Labor noted last week that prices on some goods which appeared to moderate this past summer, are now seen to be rising again. The Fed has a scheduled policy meeting this week (November 2-3) during which many of these issues will be addressed and changes possibly will be made.
Panasonic, the Osaka, Japan, supplier of batteries to Tesla, last week announced that it had solved most of the production issues with its new 4680 cylindrical battery used to power electric vehicles (EVs). Production volumes of these new larger, more efficient batteries are expected to be delivered to Tesla in early to mid-2022, replacing the smaller units that Panasonic has been supplying for more than 10 years. Tesla and Panasonic jointly operate Tesla’s Nevada Gigafactory, which for years was operating at a loss, but is now profitable.
The value of carbon-offset markets is expected to double in 2021, according to a report last week by data provider, Ecosystem Marketplace. Carbon reduction credits are created by private companies developing forests, for example, and bought by large commercial companies such as Microsoft and Royal Dutch Shell to reduce their net carbon emissions. The create/buy carbon credit process is controversial and creates a confusing carbon-offset marketplace. Varying prices also create a scenario where companies are now looking to make outright emission cuts rather than purchase carbon-offset credits.
Saudi Arabia last week, ahead of a United Nations climate summit, pledged to reduce its net carbon emissions to zero by 2060. Unfortunately, the pledge does not include carbon dioxide emissions from the massive amounts of oil exported by Saudi Arabia (the world’s largest oil exporter) to countries like China and India. The 2060 date chosen by Saudi Arabia was made based on when most future climate technologies will be mature. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has recommended countries to reach net zero emissions by 2050.
Lithium-ion battery developer, StoreDot, Herzliya, Israel, announced last week that it will build a new production and R&D facility in California for its extreme fast charging (XFC) 4680 automotive batteries with production complete by 2024. The 4680 connotation, similar to that noted in the Panasonic item above, refers to the 46-mm battery diameter and its 80-mm height. The company has already begun research into its even more advanced extreme energy density (XED) solid-state batteries with the aim to catch up to its XFC production plans by 2028.
Austin, Texas-based Lennar Corp. and construction technology firm Icon announced last week that they will start building 3-D printed housing in the Austin area in 2022. Icon’s 3-D printed houses use concrete framing instead of the traditional wood or metal. The company’s 15.5-ft tall printers can build the exterior and interior wall system for a 2,000-foot2 one story house in about a week. Lennar will complete the house using traditional construction methods. Icon’s 3D technologies have been approved by local Austin building jurisdictions but obtaining municipal approvals in other areas could be a challenge according to the developers.
R&D World’s R&D Index is a weekly stock market summary of the top international companies involved in R&D. The top 25 industrial R&D spenders in 2019 were selected based on the latest listings from Schonfeld & Associates’ June 2020 R&D Ratios & Budgets. These 25 companies include pharmaceutical (10 companies), automotive (6 companies) and ICT (9 companies) who invested a cumulative total of nearly 260 billion dollars in R&D in 2019, or approximately 10% of all the R&D spent in the world by government, industries and academia combined, according to R&D World’s 2021 Global R&D Funding Forecast. The stock prices used in the R&D World Index are tabulated from NASDAQ, NYSE and OTC common stock prices for the companies selected at the close of stock trading business on the Friday preceding the online publication of the R&D World Index.



Tell Us What You Think!