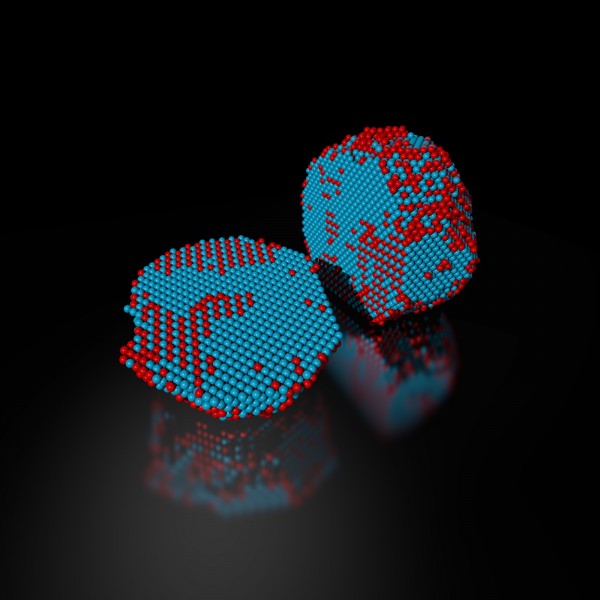
The precise 3-D atomic composition of an iron-platinum nanoparticle is revealed in this reconstruction, with iron atoms in red and platinum atoms in blue. Credit: Colin Ophus and Florian Niekiel, Berkeley Lab
Scientists used one of the world’s most powerful electron microscopes to map the precise location and chemical type of 23,000 atoms in an extremely small particle made of iron and platinum.
The 3D reconstruction reveals the arrangement of atoms in unprecedented detail, enabling the scientists to measure chemical order and disorder in individual grains, which sheds light on the material’s properties at the single-atom level. Insights gained from the particle’s structure could lead to new ways to improve its magnetic performance for use in high-density, next-generation hard drives.
What’s more, the technique used to create the reconstruction, atomic electron tomography (which is like an incredibly high-resolution CT scan), lays the foundation for precisely mapping the atomic composition of other useful nanoparticles. This could reveal how to optimize the particles for more efficient catalysts, stronger materials, and disease-detecting fluorescent tags.
Microscopy data was obtained and analyzed by scientists from the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) at the Molecular Foundry, in collaboration with Foundry users from UCLA, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and the United Kingdom’s University of Birmingham. The research is reported Feb. 2 in the journal Nature.
Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and the patterns in which they’re arranged dictate a material’s properties. These patterns can also be exploited to greatly improve a material’s function, which is why scientists are eager to determine the 3-D structure of nanoparticles at the smallest scale possible.
“Our research is a big step in this direction. We can now take a snapshot that shows the positions of all the atoms in a nanoparticle at a specific point in its growth. This will help us learn how nanoparticles grow atom by atom, and it sets the stage for a materials-design approach starting from the smallest building blocks,” says Mary Scott, who conducted the research while she was a Foundry user, and who is now a staff scientist. Scott and fellow Foundry scientists Peter Ercius and Colin Ophus developed the method in close collaboration with Jianwei Miao, a UCLA professor of physics and astronomy.
Their nanoparticle reconstruction builds on an achievement they reported last year in which they measured the coordinates of more than 3,000 atoms in a tungsten needle to a precision of 19 trillionths of a meter (19 picometers), which is many times smaller than a hydrogen atom. Now, they’ve taken the same precision, added the ability to distinguish different elements, and scaled up the reconstruction to include tens of thousands of atoms.
Importantly, their method maps the position of each atom in a single, unique nanoparticle. In contrast, X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy plot the average position of atoms from many identical samples. These methods make assumptions about the arrangement of atoms, which isn’t a good fit for nanoparticles because no two are alike.
“We need to determine the location and type of each atom to truly understand how a nanoparticle functions at the atomic scale,” says Ercius.
A TEAM approach
The scientists’ latest accomplishment hinged on the use of one of the highest-resolution transmission electron microscopes in the world, called TEAM I. It’s located at the National Center for Electron Microscopy, which is a Molecular Foundry facility. The microscope scans a sample with a focused beam of electrons, and then measures how the electrons interact with the atoms in the sample. It also has a piezo-controlled stage that positions samples with unmatched stability and position-control accuracy.
The researchers began growing an iron-platinum nanoparticle from its constituent elements, and then stopped the particle’s growth before it was fully formed. They placed the “partially baked” particle in the TEAM I stage, obtained a 2-D projection of its atomic structure, rotated it a few degrees, obtained another projection, and so on. Each 2-D projection provides a little more information about the full 3-D structure of the nanoparticle.
They sent the projections to Miao at UCLA, who used a sophisticated computer algorithm to convert the 2-D projections into a 3-D reconstruction of the particle. The individual atomic coordinates and chemical types were then traced from the 3-D density based on the knowledge that iron atoms are lighter than platinum atoms. The resulting atomic structure contains 6,569 iron atoms and 16,627 platinum atoms, with each atom’s coordinates precisely plotted to less than the width of a hydrogen atom.
Translating the data into scientific insights
Interesting features emerged at this extreme scale after Molecular Foundry scientists used code they developed to analyze the atomic structure. For example, the analysis revealed chemical order and disorder in interlocking grains, in which the iron and platinum atoms are arranged in different patterns. This has large implications for how the particle grew and its real-world magnetic properties. The analysis also revealed single-atom defects and the width of disordered boundaries between grains, which was not previously possible in complex 3-D boundaries.
“The important materials science problem we are tackling is how this material transforms from a highly randomized structure, what we call a chemically-disordered structure, into a regular highly-ordered structure with the desired magnetic properties,” says Ophus.
To explore how the various arrangements of atoms affect the nanoparticle’s magnetic properties, scientists from DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory ran computer calculations on the Titan supercomputer at ORNL—using the coordinates and chemical type of each atom—to simulate the nanoparticle’s behavior in a magnetic field. This allowed the scientists to see patterns of atoms that are very magnetic, which is ideal for hard drives. They also saw patterns with poor magnetic properties that could sap a hard drive’s performance.
“This could help scientists learn how to steer the growth of iron-platinum nanoparticles so they develop more highly magnetic patterns of atoms,” says Ercius.
Adds Scott, “More broadly, the imaging technique will shed light on the nucleation and growth of ordered phases within nanoparticles, which isn’t fully theoretically understood but is critically important to several scientific disciplines and technologies.”
The Molecular Foundry is a DOE Office of Science User Facility. The research was primarily supported by the Department of Energy’s Office of Science.




