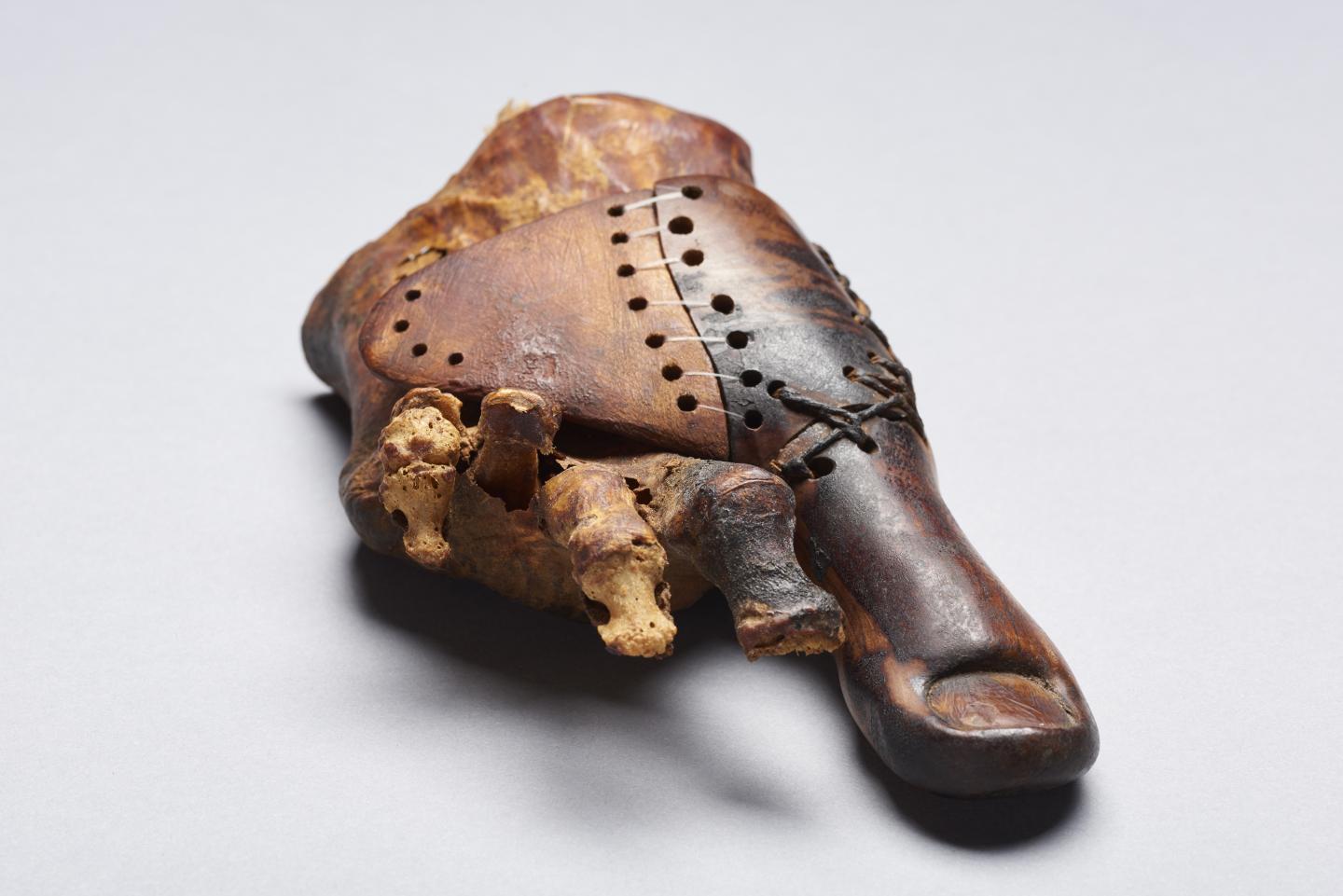
Toe prosthesis of a female burial from the Theban tomb TT95, early first millennium BC. Egyptian Museum Cairo, JE100016a.
It is likely to be one of the oldest prosthetic devices in human history: Together with other experts, Egyptologists from the University of Basel have reexamined an artificial wooden big toe. The find is almost 3000 years old and was discovered in a female burial from the necropolis of Sheikh ´Abd el-Qurna close to Luxor. This area is currently being studied using state-of-the-art methods.
The international team investigated the one-of-a-kind prosthesis using modern microscopy, X-ray technology, and computer tomography. They were able to show that the wooden toe was refitted several times to the foot of its owner, a priest’s daughter. The researchers also newly classified the used materials and identified the method with which the highly developed prosthesis was produced and utilized. Experts from the Egyptian Museum in Cairo – where the prosthetic device was brought to after it had been found – and the Institute of Evolutionary Medicine at the University of Zurich were also involved in this study.
The artificial toe from the early first millennium BC testifies to the skills of an artisan who was very familiar with the human physiognomy. The technical know-how can be seen particularly well in the mobility of the prosthetic extension and the robust structure of the belt strap. The fact that the prosthesis was made in such a laborious and meticulous manner indicates that the owner valued a natural look, aesthetics and wearing comfort and that she was able to count on highly qualified specialists to provide this.
Life histories of a burial ground
The prosthesis from the Early Iron Age was found in a plundered shaft tomb that was cut into the bedrock of an older, long time idle burial chapel at the graveyard hill of Sheikh ´Abd el-Qurna to the west of Luxor. This chapel belongs to a group of monumental rock-cut tombs from the late 15th century BC which were built for a small upper class that was close to the royal family. Since the end of 2015, the University of Basel has been studying this ancient Egyptian elite cemetery, its long history of usage, and surroundings.
For this project, funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation, microanalytic, scientifically oriented methods, as well as precision technology for surveying and photography were used. The researchers are looking into the materiality of archaeological remains and are thus gaining insight into the life histories of building structures and objects. These material biographies can provide information about the manufacturing practices, usages, personal skills, habits and preferences of people who were in contact with these objects.
A necropolis in 3-D
The oldest known tombs from Sheikh ´Abd el-Qurna date back to the early second millennium BC. The cemetery saw its heyday in the 15th century BC. However, many of these rock-cut structures were reused and in parts remodeled several times for burials during the first millennium BC. Much later, they served as dwellings mostly for locals – a process that began with the early Christian hermits and only ended in the early 20th century.
Together with the experts for geodesy and geology from the ETH Zurich, the Basel team of archaeologists is scientifically assessing the natural and artificial structures of the excavation area and its surroundings. The specialists are currently developing geometric precise digital elevation, landscape, and architecture models for this area. These will then be combined to an archaeological and geological 3-D map that will illustrate the morphology of the terrain as well as the investigated subterranean structures. On that basis, the researchers want to reconstruct and simulate the development of the cemetery and its use phases.