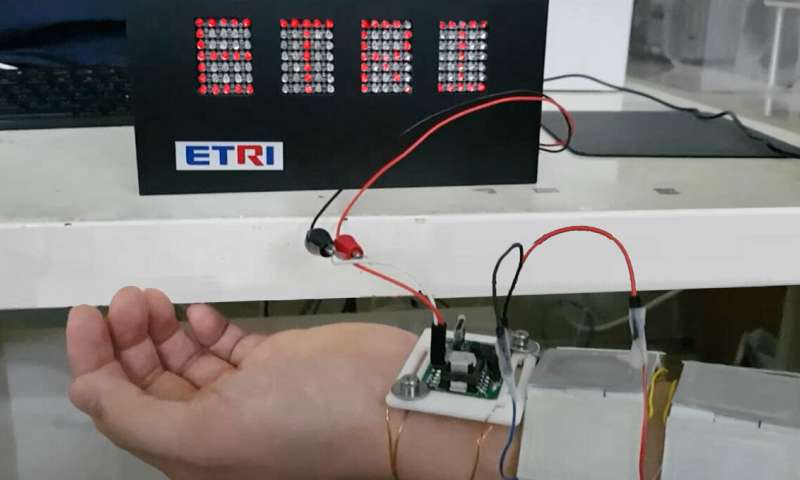
Wearing thermal electric devices that supply power based on body temperature are attached to the skin to illuminate the LED display. Credit: The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) in South Korea developed a thermoelectric module that generates electricity using human body heat. The module, which is 5 cm in width and 11 cm in length, can convert body heat energy into electricity and amplify it to power wearable devices.
When a patch-like structure is attached upon the thermoelectric device, a temperature difference occurs between the skin and the structure, imitating the sweat glands structure. This core technology is called “biomimetic heat sink.” It increases the output of the thermoelectric module by five times that of conventional products, maximizing the energy efficiency.
The device also incorporates the power management integrated circuit technology that keeps efficiency above 80 percent even at low voltages and converts it to a chargeable voltage. In particular, the research team succeeded in generating a 35 microwatts per square centimeters (uW/cm2) output, which is 1.5 times higher than the 20 uW/cm2 output previously developed by U.S researchers.
It has been confirmed that when six devices are modularized in a bundle, they can generate up to a commercialization level of 2~3 milliwatts (mW). Unlike disposable batteries, they can continuously generate energy from the human body temperature. In fact, the research team succeeded in lighting the letters “ETRI” on the LED display board by boosting the voltage generated from the six devices attached to the wrist of an adult without any batteries.
In addition, a dry adhesion method that utilizes nano structure was used to attach to the skin contact area, whereas for the outer part of the module, micro structure was used to prevent easy tearing. This micro-nano hierarchical structure facilitate more stable adhesion on the human skin which have various roughness.
The research team is currently carrying out a follow-up study to implement the power management circuit in one chip. The purpose of the study is to improve wearability in a moving situation while decreasing the discomfort of wearing patches. ETRI predicts the technology to be commercialized in two to three years.




