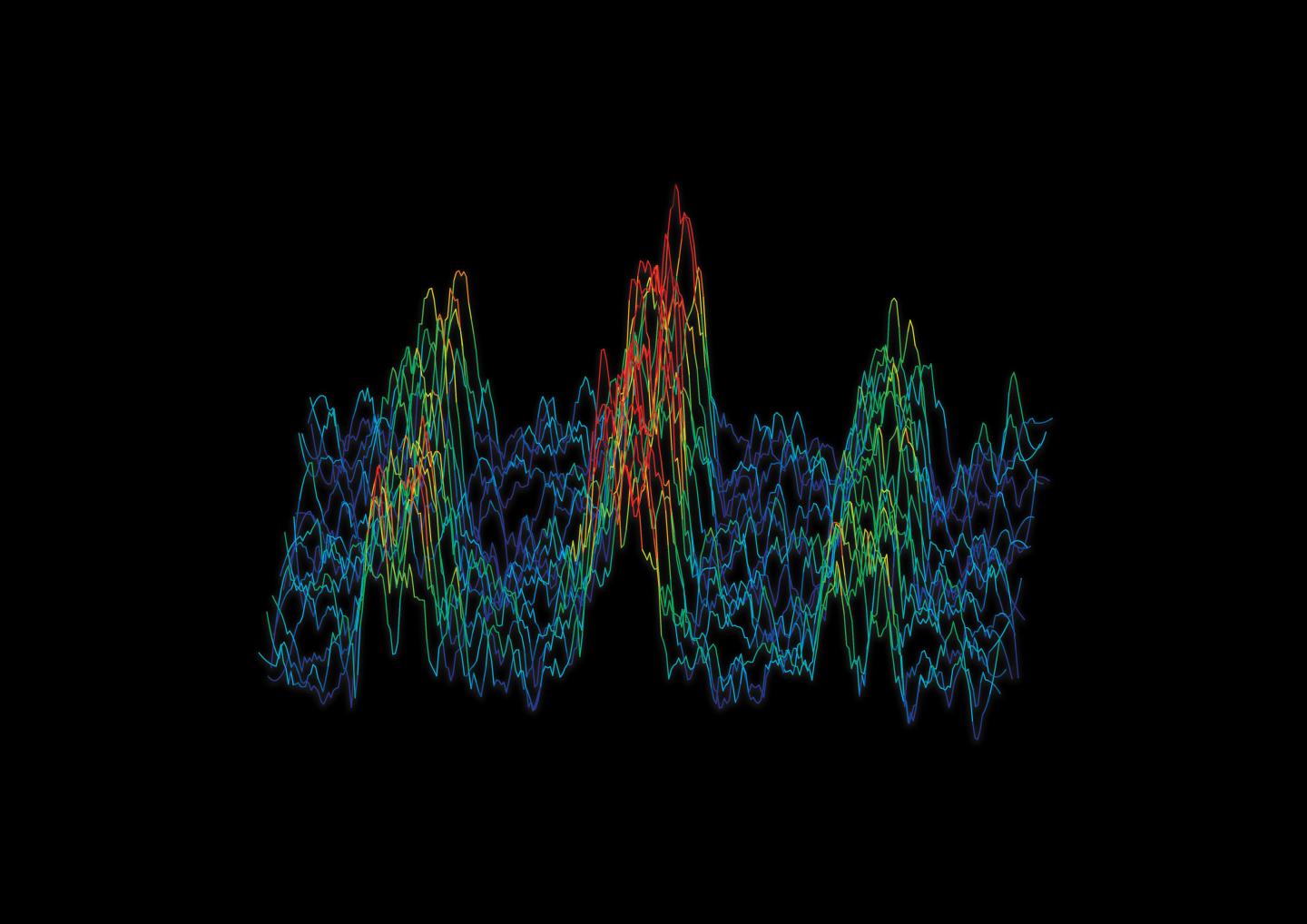
The frequency spectrum of an engineered molecule. The three peaks represent three different configurations of spins within the atomic nuclei, and the distance between the peaks depends on the exact distance between atoms forming the molecule. Credit: Dr. Sam Hile
Australian scientists have achieved a new milestone in their approach to creating a quantum computer chip in silicon, demonstrating the ability to tune the control frequency of a qubit by engineering its atomic configuration. The work has been published in Science Advances.
A team of researchers from the Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T) at UNSW Sydney have successfully implemented an atomic engineering strategy for individually addressing closely spaced spin qubits in silicon.
The researchers built two qubits – one an engineered molecule consisting of two phosphorus atoms with a single electron, and the other a single phosphorus atom with a single electron – and placed them just 16 nanometres apart in a silicon chip.
By patterning a microwave antenna above the qubits with precision alignment, the qubits were exposed to frequencies of around 40GHz. The results showed that when changing the frequency of the signal used to control the electron spin, the single atom had a dramatically different control frequency compared to the electron spin in the molecule of two phosphorus atoms.
The UNSW researchers collaborated closely with experts at Purdue University, who used powerful computational tools to model the atomic interactions and understand how the position of the atoms impacted the control frequencies of each electron even by shifting the atoms by as little as one nanometre.
“Individually addressing each qubit when they are so close is challenging,” says UNSW Scientia Professor Michelle Simmons, Director CQC2T and co-author of the paper.
“The research confirms the ability to tune neighbouring qubits into resonance without impacting each other.”
Creating engineered phosphorus molecules with different separations between the atoms within the molecule allows for families of qubits with different control frequencies. Each molecule can be operated individually by selecting the frequency that controls its electron spin.
“We can tune into this or that molecule – a bit like tuning in to different radio stations,” says Sam Hile, lead co-author of the paper and Research Fellow at UNSW.
“It creates a built-in address which will provide significant benefits for building a silicon quantum computer.”
Tuning in and individually controlling qubits within a 2 qubit system is a precursor to demonstrating the entangled states that are necessary for a quantum computer to function and carry out complex calculations.
These results show how the team – led by Professor Simmons – have further built on their unique Australian approach of creating quantum bits from precisely positioned individual atoms in silicon.
By engineering the atomic placement of the atoms within the qubits in the silicon chip, the molecules can be created with different resonance frequencies. This means that controlling the spin of one qubit will not affect the spin of the neighbouring qubit, leading to fewer errors – an essential requirement for the development of a full-scale quantum computer.
“The ability to engineer the number of atoms within the qubits provides a way of selectively addressing one qubit from another, resulting in lower error rates even though they are so closely spaced,” says Professor Simmons.
“These results highlight the ongoing advantages of atomic qubits in silicon.”
This latest advance in spin control follows from the team’s recent research into controllable interactions between two qubits.