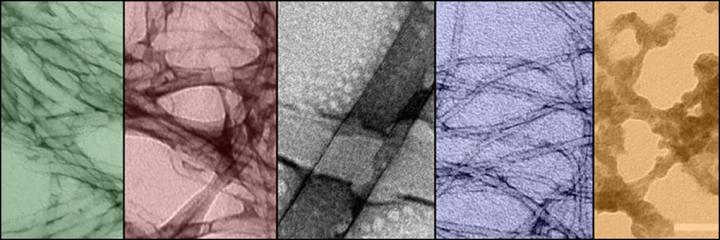
These are Transmission Electron Microscopy images of the self-assembling nanostructures, also visible to the naked eye. Source: OIST
Traditional chemistry is immensely powerful when it comes to producing very diverse and very complex microscopic chemical molecules. But one thing out of reach is the synthesis of large structures up to the macroscopic scale, which would require tremendous amounts of chemicals as well as an elaborate and complicated technique. For this purpose, scientists rely instead on “self-assembling” molecules, compounds that can interact with other copies of themselves to spontaneously congregate into spheres, tubes or other desired shapes. Using this approach, researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) now reports in Chemical Communications new self-assembling molecules that can transform into novel, exotic and previously unobserved shapes by simply using UV light to force them to rearrange differently into “metastable” states.
When designing self-assembly structures, scientists typically aim for the state of lowest energy — or “ground state,” in which the structure would be at its highest stability. Less stable shapes are usually dismissed as incorrect and undesirable. However, this “ground state” being very stable makes it arduous to break down the structure if you wish to alter its shape. In this research, OIST scientists inserted a weakness into their ground-state self-assembled structures, resulting in structures requiring only a small nudge to collapse. In this case, the nudge is the use of ultraviolet light to snip a specific bond between two atoms within the molecule, splitting the structure into smaller fragments. The fragments are then able to co-assemble into less stable — called metastable — but novel and exotic shapes.
“This report is about a new concept in material science,” explained Prof. Zhang from the Bioinspired Soft Matter Unit and author of the study. “We converted a self-assembling phenomenon into co?assembling in a spatially and temporally controllable manner using light. Eventually, we constructed exotic heterogeneous nanostructures inaccessible though conventional synthetic path.”
This new concept led to a fascinating discovery: because the remaining fragments are tightly packed following the collapse from the initial structure, they can form novel and exotic structures which are not attainable if you just mix the same molecules in free motion. Imagine these nanostructures made from Lego bricks: initially you have 2×5 bricks – 2 studs wide and 5 studs long – self-assembling into a nanofiber. Ultraviolet light will split these 2×5 bricks into two smaller pieces, for example a 2×3 brick and a 2×2 brick, destroying the entire fiber-like structure. But because these smaller bricks remain pre-organized spatially staying close to each other, they can easily recombine themselves into new shapes visible with the naked eye. In contrast, if in a separate experiment you just mix 2×3 and 2×2 Lego bricks in a random manner in a bucket with varying distances between bricks, their lack of spatial organization prevents the assembly of such novel nanostructures.
According to Prof. Zhang, the ability to create new structures is vital: “In material science, the function is always related to the structure. If you create a different structure, you manipulate the function and even create new applications.” For example, the toxicity of a molecule in a nanofiber shape might be much lower or higher than the same molecule assembled in a spherical shape.”
The present research performed at OIST strongly suggests the initial conditions are the most critical parameter influencing the final shape taken by self-assembling molecules. “If you know how the molecules pack with each other from the parameters of the initial state, then it will give you more clues to aim towards a specific macroscopic shape,” commented Prof. Zhang.
This shapeshifting ability holds great potential for biological applications. Prof. Zhang suggested, “For example you introduce the molecule into a living organism and it adopts a certain structure. Then using light, you break a chemical bond and then the molecule will switch to another structure with the function you want.”
In pharmaceutical design, such a concept would allow a drug to reach its target in a living organism – an organ or a tumor – in an inactive state, thus limiting potential side effects. Once broken down in this targeted location, the drug would reshape itself into a different structure with therapeutic activity.
Prof. Zhang concluded, “For now, using ultraviolet light as we do is not ideal as it is toxic for living cells. The next step for us is to move towards more biocompatible self-assembling structures with better adaptability to living systems.”



