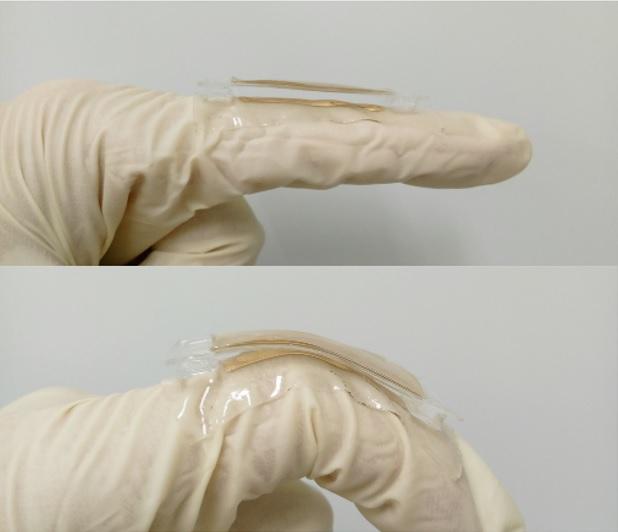
This is a prototype of the triboelectric nanogenerator.
Imagine if rather than being tethered to an outlet to charge a smartphone, simply moving was enough to power electronic devices.
Researchers from the University of Buffalo have developed a small metallic tab called a triboelectric nanogenerator that when attached to the body can generate electricity from bending a finger and other simple movements.
“No one likes being tethered to a power outlet or lugging around a portable charger,” lead author Qiaoqiang Gan, PhD, an associate professor of electrical engineering in UB’s School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, said in a statement. “The human body is an abundant source of energy. We thought: ‘Why not harness it to produce our own power?’”
The tab consists of two thin layers of gold with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)—a silicon based polymer used in contact lenses and other products—sandwiched in between.
The researchers stretched one of the layers of gold, causing it to crumple upon release and create what looks like a miniature mountain range. When the force is reapplied from movements— including finger bending—the motion leads to friction between the gold layers and PDMS.
“This causes electrons to flow back and forth between the gold layers,” lead author, Yun Xu, PhD, professor from the Institute of Semiconductors (IoP) at the Chinese Academy of Science, said in a statement. “The more friction, the greater the amount of power is produced.”
The tab, which is 1.5 centimeters long by one centimeter wide, delivers a maximum voltage of 124 volts, a maximum current of 10 microamps and a maximum power density of 0.22 milliwatts per square centimeter. While that is not enough to quickly charge a smartphone, it can light 48 red LED lights simultaneously.
The researchers will now attempt to improve the tab’s performance by using larger pieces of gold, which when stretched and folded together are expected to deliver even more electricity.
They also plan to develop a portable battery to store energy produced by the tab.
Triboelectric charging occurs when certain materials become electrically charged after coming into contact with a different material. The majority of everyday static electricity is triboelectric.
Researchers have created several nanogenerators that utilize the triboelectric effect, the majority of which are difficult to manufacture because they require complex lithography or are not cost effective.




