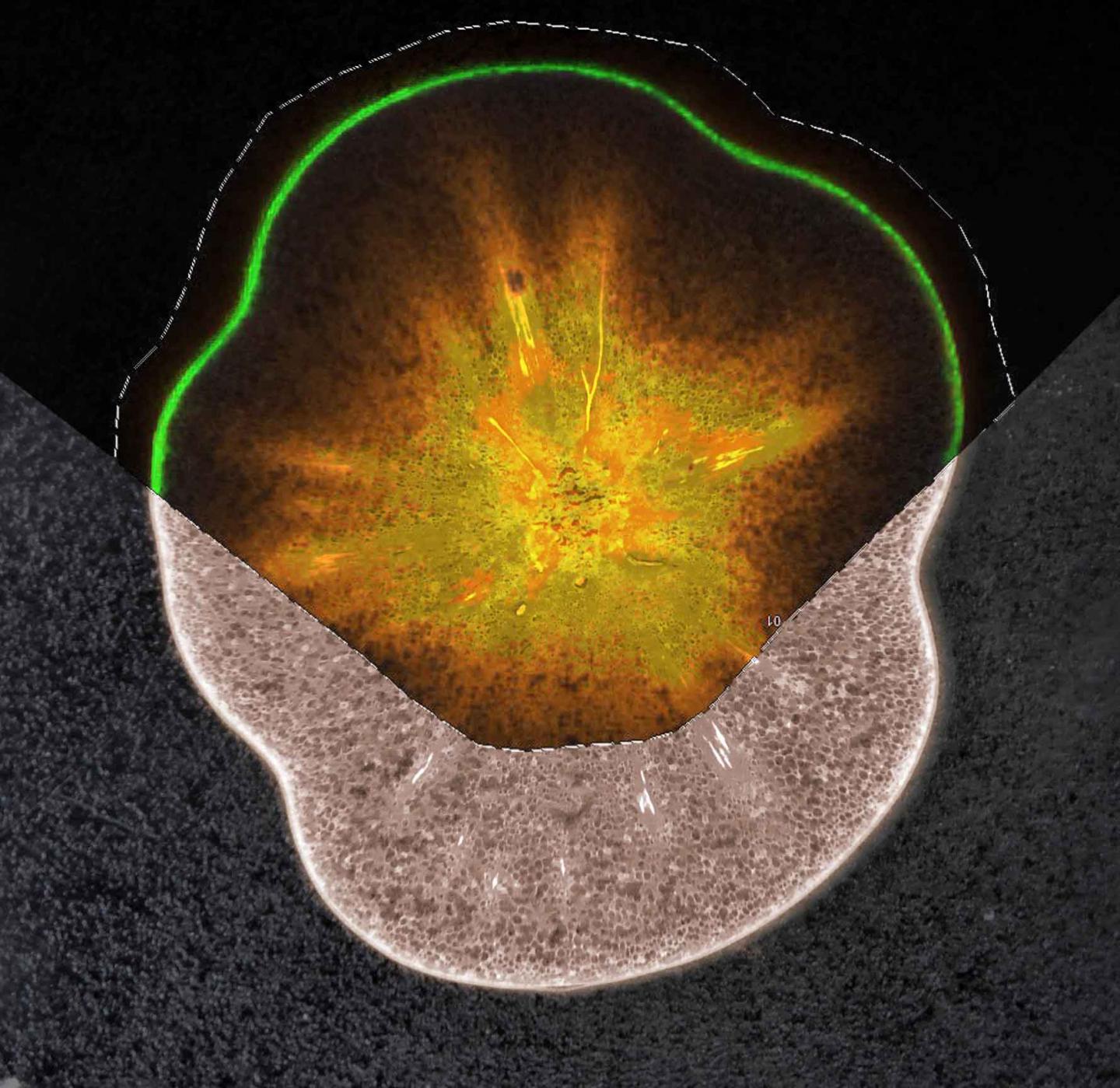
This is a section of a ripe tomato sample showing the distribution of sucrose (orange) in the flesh and of an antioxidant (green) in the fruit skin tissue; mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) technology was used to map the molecules. Source: Weizmann Institute of Science
Here’s a reason not to peel tomatoes: A new method of plant analysis, developed at the Weizmann Institute of Science, has identified healthful antioxidants in tomato skins. In fact, as reported recently in Nature Communications, the new method reveals that biologically active plant substances typically associated with particular plant species — including those providing health benefits — are much more prevalent across the plant kingdom than was previously thought.
Plants produce, in total, an estimated million-plus organic chemicals, and each plant is believed to contain as many as 15,000, on average. To address the challenge of identifying the majority of such “specialized metabolites” in any given plant, Dr. Nir Shahaf and other members of a team headed by Prof. Asaph Aharoni of Weizmann’s Plant and Environmental Sciences Department created a database of plant metabolites, called WeizMass. Shahaf then developed a computer tool, MatchWeiz, which makes it possible to identify the metabolites by checking experimental results from the metabolic analysis of a particular plant against the database.
Using these new tools, the scientists identified more than twenty metabolites that had never before been reported in tomatoes, including certain antioxidants in the skin. When the researchers then compared the analysis of tomatoes with that of duckweed and the research model Arabidopsis thaliana, they discovered an overlap in specialized metabolite content among these strikingly different species.
These and other results suggest that plant species are not as specialized in their metabolism as has been commonly assumed. In other words, valuable substances produced by exotic plants may potentially be derived from more common species. The Weizmann team has found, for instance, that both duckweed and Arabidopsis thaliana contain — albeit in smaller amounts — certain metabolites used in traditional medicine that until now have been isolated only from such oriental medicinal plants as maidenhair tree (Ginkgo biloba), ginger (Zingiber officinale) and rock pine (Orostachys japonicus).
“WeizMass and MatchWeiz can serve as extremely powerful tools for studying plant metabolism and identifying metabolites with useful biological activity, including potential drugs,” says Aharoni.
WeizMass and MatchWeiz are not limited to the study of plant metabolites but may also be used to investigate the biology of other living systems, including animal and human metabolism.




