An international team of researchers affiliated with UNIST has discovered a novel method for the synthesis of ultrathin semiconductors. This is a unique growth mechanism, which yielded nanoscopic semiconductor ribbons that are only a few atoms thick.
This breakthrough has been jointly conducted by Distinguished Professor Feng Ding and Dr. Wen Zhao from the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) at UNIST, in collaboration with the National University of Singapore (NUS), the National Institute for Materials Science (NIMS), the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), and Shenzhen University.
In the study (Nature Materials, “Vapour–liquid–solid growth of monolayer MoS2 nanoribbons”), the research team has successfully fabricated MoS2 nanoribbons via vapor-liquid-solid (VLS) growth mechanism, a type of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process.
Chemical vapor deposition or CVD is a generic name for a group of processes whereby a solid material is deposited from a vapor by a chemical reaction occurring on or in the vicinity of a normally heated substrate surface. It is the most widely adopted industrial techniques for producing semiconducting thin films and nanostructures.
“The range of structures that can be controllably synthesized by the current methods is still limited in terms of morphology, spatial selectivity, crystal orientation, layer number and chemical composition,” the research team noted. “Therefore, developing versatile growth methods is essential to the realization of highly integrated electronic and photonic devices based on these materials.
“The current CVD-based growth process relies on the inherent dynamics of the precursors to diffuse and self-organize on the substrate surface, which results in crystallites with characteristic triangular or hexagonal shapes,” says Zhao. “This unique growth mechanism of the nanoscopic semiconductor ribbons that are only a few atoms thick is an exciting discovery.” In the study, she performed density functional theory based molecular dynamic (DFT-MD) simulations of the MoS2 precipitation process.
The proposed mechanism of VLS growth differs from commonly known CVD technique, as it involves the precursors introduced in the vapor phase form a liquid droplet intermediate before condensing into a solid product.
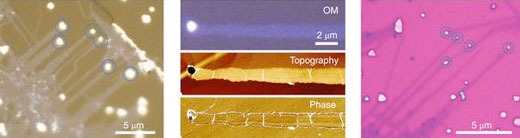
From left are 1) Optical images of MoS2 ribbons grown on a NaCl crystal, 2) Optical microscopy (OM) and corresponding AFM topography and phase images of a ribbon, and 3) Optical image of the ribbons transferred onto a SiO2/Si substrate. Image: UNIST
The team noted that the morphology of the growth product was, however, unlike what is normally expected from a VLS growth, which typically yields cylindrical or tubular structures rather than ribbons. Their observation suggests that the liquid droplet migrates on the substrate surface in a rather ordered manner, leaving behind a track of ultrathin crystal.
“Because the liquid droplet migrates on the substrate surface in a rather ordered manner, the morphology of the growth product yielded cylindrical or tubular structures rather than ribbons.” says Zhao.
This time, however, the horizontal growth of predominantly monolayer MoS2 ribbons was obtained via VLS growth, a unique growth mechanism that has not been reported until now.
Their observation revealed that the VLS growth of monolayer MoS2 is triggered by the reaction between MoO3 and NaCl, which results in the formation of molten Na-Mo-O droplets. These droplets mediate the growth of MoS2 ribbons in the “crawling mode” when saturated with sulfur. The locally well-defined orientations of the ribbons reveal the regular horizontal motion of the droplets during growth.
Assisting the growth of MoS2 ribbons, like painting with a an ink droplet
In order to gain insight into the liquid-solid transformation, Ding’s team performed density functional theory based molecular dynamic (DFT-MD) sumulations of the precipitation process. The simulation showed the attachment of molybdenum (Mo) and sulfur (S) to the previously established MoS2.
“It is worth noting that MoS2 is not oxidized despite the presence of large numbers of oxygen atoms,” says the research team. “We also observe the nucleation of MoS2 clusters in regions that are rich in Mo and S atoms, further supporting the feasibility of liquid-mediated nucleation and growth of MoS2.”
“This study has prompted questions about surface and interface growth of nanomaterials,” says Ding. “By identifying a suitable liquid-phase intermediate compound, we believe that it will be possible to realize the direct 1D growth of a range of van der Waals layered materials.”
The team anticipates that many other materials can be grown using a similar approach. Their short-term goal is to understand the growth mechanism better and to control the morphology of the ribbons.
“Our work identified many interesting questions about surface and interface growth of nanomaterials,” says Professor Goki Eda at the National University of Singapore (NUS), the corresponding author of this study. “We predict that the ability to directly grow complex structures will greatly facilitate the realization of high performance nanoelectronic circuits.”
The team noted that their results provide insight into the distinct VLS growth mode of 2D MoS2 and demonstrate the potential of their implementation in nanoelectronic devices.
Source: UNIST