Q-CTRL, a developer of useful quantum technologies through quantum control infrastructure software, introduces its quantum sensing division, which has become one of the largest in the world. The team will showcase its capabilities publicly for the first time at the Army Quantum Technology Challenge (QTC) in Adelaide on August 10 and 11. Q-CTRL is delivering…
R&D 100 winner of the day: OH0TA OVMed Medical Image Sensor
OmniVision’s OH0TA OVMed medical image sensor is the world’s smallest commercially available image sensor. With a package size of just 0.55 mm x 0.55 mm, featuring a 1.0-micron pixel and a 1/31 optical format, it is smaller than the Guinness World Record held by its predecessor and quadruples resolution and provides wafer-level optics in a…
R&D 100 winner of the day: BLK247 from Leica Geosystems, part of Hexagon
The Leica Geosystems BLK247 is a smart 3D surveillance system that uses sensor fusion technology — a combination of video cameras, thermal imaging and LiDAR — along with edge computing and AI to instantly detect and report physical changes within a space. The BLK247 is multi-sensor device that provides 360° horizontal by 270° vertical field-of-view…
Sandia Labs shows advanced wayfinding tech could finally become compact, fieldable
From Sandia National Laboratories Don’t let the titanium metal walls or the sapphire windows fool you. It’s what’s on the inside of this small, curious device that could someday kick off a new era of navigation. For over a year, the avocado-sized vacuum chamber has contained a cloud of atoms at the right conditions for…
CAL Analytics’ research to detect and track lower altitude aircraft in Ohio
CAL Analytics, a company specializing in the development of automated and autonomous systems, will receive funding from the Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT) office of Statewide Planning & Research to conduct research on “Open Framework Standards for A Combined Aircraft Sensor Network.” The research objective is to develop a means to detect and track lower…
Next-generation remote monitoring solution supports uncompromised sample safety and integrity
Biotechnology, pharmaceutical, clinical and academic laboratories can now benefit from a next-generation remote monitoring solution designed to enable sample protection, workflow efficiencies, asset/cost optimization and regulatory compliance. With the option for an on-premise or cloud setup, the Thermo Scientific Smart-Vue Pro Wireless Monitoring Solution provides real-time, continuous monitoring of critical laboratory equipment parameters and immediately…
Cryptographic “tag of everything” could protect the supply chain
Rob Matheson | MIT News Office To combat supply chain counterfeiting, which can cost companies billions of dollars annually, MIT researchers have invented a cryptographic ID tag that’s small enough to fit on virtually any product and verify its authenticity. A 2018 report from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development estimates about $2 trillion…
Low-cost “smart” diaper can notify caregiver when it’s wet
By Jennifer Chu | MIT News Office For some infants, a wet diaper is cause for an instant, vociferous demand to be changed, while other babies may be unfazed and happy to haul around the damp cargo for lengthy periods without complaint. But if worn too long, a wet diaper can cause painful rashes, and…
Sensing technology could improve machine learning precision for manufacturing, electric vehicles, smart homes
The same small piece of technology that one day may help train welding robots and monitor electric vehicles could enable energy companies to better power smart homes and factories. Purdue University innovators have developed a sensing module that works with machine learning for applications ranging from electric cars to manufacturing and home design. The technology…
Bacterial Sensors Hacked by Synthetic Biologists
Rice University synthetic biologists have hacked bacterial sensing with a plug-and-play system that could be used to mix-and-match tens of thousands of sensory inputs and genetic outputs. The technology has wide-ranging implications for medical diagnostics, the study of deadly pathogens, environmental monitoring and more. In a project spanning almost six years, Rice bioengineer Jeff Tabor…
‘Spidey Senses’ Assist Autonomous Machines with Sight
What if drones and self-driving cars had the tingling “spidey senses” of Spider-Man? They might actually detect and avoid objects better, says Andres Arrieta, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Purdue University, because they would process sensory information faster. Better sensing capabilities would make it possible for drones to navigate in dangerous environments and…
Smart Device Finds Food Contaminants in Real Time
Fast, accurate and affordable food safety testing is now possible. Thanks to a portable scanner, farmers, food manufacturers and retailers can now do their own tests in the field, eliminating costly and time-consuming lab tests. Consumers place importance on different things in the foods they consume. Some insist on locally grown or organic food. Others…
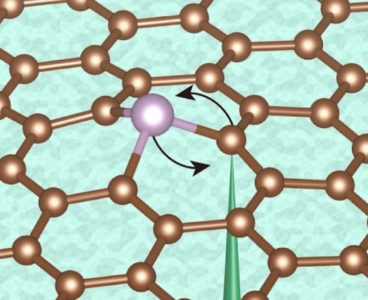
Electron Beam Manipulates Atoms One at a Time
The ultimate degree of control for engineering would be the ability to create and manipulate materials at the most basic level, fabricating devices atom by atom with precise control. Now, scientists at MIT, the University of Vienna, and several other institutions have taken a step in that direction, developing a method that can reposition atoms…
Displacement Sensor Developed to Measure Gravity of Smallest Source Mass Ever
One of the most unknown phenomena in modern physics is gravity. Its measurement and laws remain somewhat of an enigma. Researchers at Tohoku University have revealed important information about a new aspect of the nature of gravity by probing the smallest mass-scale. Professor Nobuyuki Matsumoto has led a team of researchers to develop a gravity…
Blood and Sweat Enhance Training App
The 20,000 entrants who ran the Stockholm Marathon in 2018 may remember what a warm day it was, and how many of them were forced to quit due to the hot weather. KTH Royal Institute of Technology researcher Gaston Crespo and his colleagues have developed a multifaceted measuring technology that is able to detect a…
Smartphones Sniff Out Disease
Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, is the fifth most common cause of cancer-related deaths in Europe. Because of the lack of early signs specifically related to the disease, it’s usually only detected at an advanced stage—when treatment is for the most part ineffective. Driven to improve stomach and other cancer survival rates, for…
Innovative New Sensor Reacts to Light, Heat, Touch
Inspired by the behavior of natural skin, researchers at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics have developed a sensor that will be suitable for use with electronic skin. It can measure changes in body temperature, and react to both sunlight and warm touch. Robotics, prostheses that react to touch, and health monitoring are three fields in…
Researchers Develop New Power Supply for Synthetic Skins
Sensor Sniffs out Spoiled Milk Prior to Opening
Expiration dates on milk could eventually become a thing of the past with new sensor technology from Washington State University scientists. Researchers from the Department of Biological Systems Engineering (BSE), the WSU/UI School of Food Science and other departments have developed a sensor that can “smell” if milk is still good or has gone bad.…
A New Look at 2D Magnets using Diamond Quantum Sensors
For the first time, physicists at the University of Basel have succeeded in measuring the magnetic properties of atomically thin van der Waals materials on the nanoscale. They used diamond quantum sensors to determine the strength of the magnetization of individual atomic layers of the material chromium triiodide. In addition, they found a long-sought explanation…
Sensor Finds Rare Metals Used in Smartphones
A more efficient and cost-effective way to detect lanthanides, the rare earth metals used in smartphones and other technologies, could be possible with a new protein-based sensor that changes its fluorescence when it binds to these metals. A team of researchers from Penn State developed the sensor from a protein they recently described and subsequently…
A New Path to Achieving Invisibility without the Use of Metamaterials
A pair of researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) describes a way of making a submicron-sized cylinder disappear without using any specialized coating. Their findings could enable invisibility of natural materials at optical frequency and eventually lead to a simpler way of enhancing optoelectronic devices, including sensing and communication technologies. Making objects invisible…
New Device Helps Heal Fractured Bones
Threading a needle is hard, but at least you can see it. Think about how challenging it must be to thread a screw through a rod inside a bone in someone’s leg. Rice University seniors at the Brown School of Engineering set out to help doctors simplify the process of repairing fractured long bones in…
Handheld Device Quickly Monitors Quality of Drinking Water
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a portable device, inspired by the ability of the human body, to detect trace levels of heavy metals in drinking water in just five minutes. The secret lies in an organic substance within the circulating human bloodstream, called a chelating agent, which can detect and…
Pin-sized Sensors Embedded in Smartphones Could ID Chemicals
Imagine pointing your smartphone at a salty snack you found at the back of your pantry and immediately knowing if its ingredients had turned rancid. Devices called spectrometers can detect dangerous chemicals based on a unique “fingerprint” of absorbed and emitted light. But these light-splitting instruments have long been both bulky and expensive, preventing their…