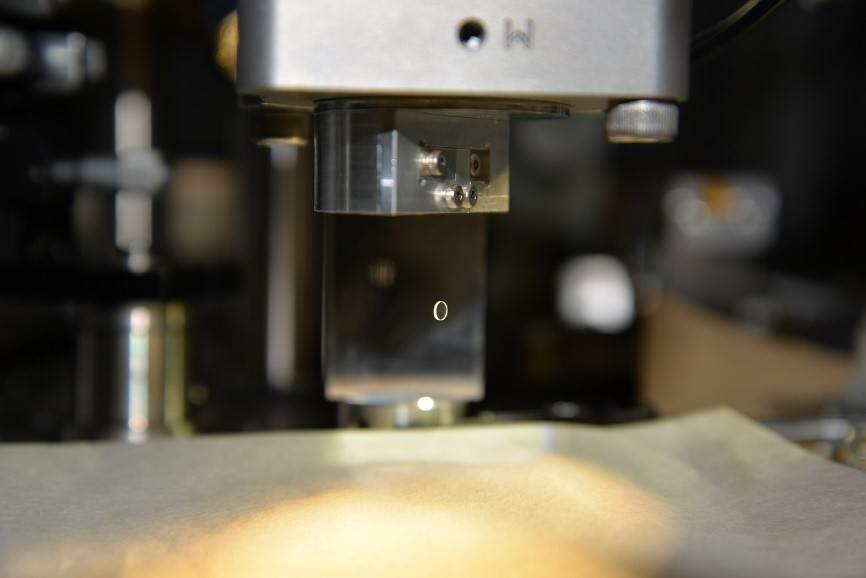
mg-scale suspended mirror. Image: Nobuyuki Matsumoto, Tohoku University
One of the most unknown phenomena in modern physics is gravity. Its measurement and laws remain somewhat of an enigma. Researchers at Tohoku University have revealed important information about a new aspect of the nature of gravity by probing the smallest mass-scale.
Professor Nobuyuki Matsumoto has led a team of researchers to develop a gravity sensor based on monitoring the displacement of a suspended mirror, which allows for measuring the gravity of the smallest mass ever.
The research team was interested in whether the nature of gravity is classical or quantum.
“Within the past hundred years, our understanding of nature has deepened based on quantum theory and general relativity. In order to keep moving forward with this progress, it is necessary to understand more about the nature of gravity,” said Matsumoto.
Until now the smallest mass for which humans have measured a gravitational field is about 100g, which is surprisingly larger than the mass scale of a common pencil (~10g). Because the gravitational force is much weaker than other forces, such as the electromagnetic force, it is difficult to measure gravity generated by small masses.
Matsumoto stated that “the system was made based on the technology developed for gravitational wave detectors, e.g. laser stabilization, a vibration isolation stage, high vacuum and noise hunting. Unlike gravitational wave detectors, we used a triangular optical cavity, not a linear optical cavity in order to decrease the noise level of the displacement sensor and maintain stable operation of the sensor. Our system’s noise level, due to the Brownian motion of the suspended mirror, is one of the smallest in the world.”
Development of such a gravity sensor will pave the way for a new class of experiments where gravitational coupling between small masses in quantum regimes can be achieved.