
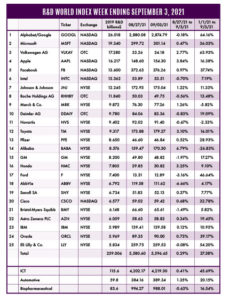
The R&D World Index (RDWI) for the week ending September 3, 2021, closed at 5,596.65 for the 25 companies in the R&D World Index. The Index was up 0.29% (or 16.05 basis points) from the week ending August 27, 2021. The stock of 15 R&D World Index members gained value from 0.12% (IBM) to 6.79% (Alibaba). The stock of 10 R&D World Index members lost value from -0.08% (Eli Lilly & Co.) to -6.66% (AbbVie).
The U.S. Department of Labor last week announced that the U.S. economy added 235,000 jobs in August, less than half of economists’ preliminary estimates of 720,000 jobs. The August numbers were also lower than the 1.1 million gains in July, 962,000 gains in June and 559,000 in May. While monthly job gains are slowing, the unemployment rate fell to 5.2% in August, from 5.4% in July and 5.9% in June. Professional job hirings (which includes researchers) dropped slightly to 74,000 in August from 75,000 in July. Economists blame the continuing COVID-19 pandemic, and in particular its Delta variant on the job rate drops, siting the business hesitations as consumers become more cautious and actual decreases in job hirings in the hotel and food service sectors. Typical fall school hirings have also been affected which were abnormally increased over the summer as parents attempted to have their children ‘catch up.” Economists expect the September job rates to be more of the same — the early September COVID-19 statistics are actually higher than they were in mid-August.
China’s Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp. (SMIC) announced last week that it was collaborating with Shanghai’s Lin-Gang Free Trade Zone Administration to build an $8.9 billion chip production facility in the city. The facility expects to specialize in 28-nanometer process nodes and produce 100,000 12-in. wafers/month when completed by 2025. SMIC joins the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC), South Korea’s Samsung Electronics, and the U.S.’s Global Foundries and Intel in announcing multi-billion-dollar expansion plans over the next several years to meet the demand of the current chip shortage, especially in the automotive industry.
The Biden administration issued a memorandum to all government agencies last week outlining their R&D priorities for the upcoming FY2023 budget proposals. These priorities include pandemic readiness and prevention, climate change, research and innovation in emerging and critical technologies, innovation for equity and national security and economic resilience. The memo asks agencies to collaborate to advance public-private partnerships and foster R&D in U.S. industries to support artificial intelligence (AI), quantum information science, microelectronics, advanced communications, robotics, high-performance computing, biotechnology and space technologies. Agencies were requested to leverage these technologies and utilize the vast government datasets to enable large-scale data analyses and high-resolution modeling and simulations.
Germany’s Porsche automaker announced last week that it will create a new R&D facility in Shanghai and a small-scale assembly site in Malaysia, which will open in 2022. The new R&D site joins other Porsche R&D facilities in Sweden, South Africa and California. The new Shanghai facility joins Porsche Digital China, established in 2020 and the 20-year-long established Porsche Engineering China. China is Porsche’s largest single market, with nearly 89,000 deliveries in 2020.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences announced last week that its prototype Mars surface cruise drone had passed a final acceptance review on August 20, 2021. The proposed rotocraft, similar in design to NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratories’ Ingenuity helicopter currently operating on Mars, is one of three technology projects being developed at China’s National Space Science Center (NSSC). Also, the National Natural Science Foundation of China last week announced a five-year plan for researchers to study the assembly of ultra-large spacecraft (up to 0.6 km in length). Preliminary research will study the challenges of developing lightweight structures and subsequent on-orbit assembly and control (utilizing space-based power technologies, 3-D printers, and permanent manned space stations).
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Pittsburgh, announced last week that it is working with Emerald Cloud Lab, South San Francisco, to build a $40 million 20,000 ft2 cloud computing lab in Pittsburgh modeled after Emerald’s existing California facility. The new lab is expected to be used by pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. CMU researchers using the Cloud Lab will have remote access to more than 100 scientific instruments using Emerald’s proprietary software that gives instructions to the instruments over the cloud. RDW Index member IBM also has a cloud-based AI service called RoboRXN that allows scientists from anywhere in the world to synthesize or create molecules using a robot based in Switzerland. Most of the CMU Cloud instruments will employ machine-learning techniques and a network of sensors.
Illinois-based medical technology company Baxter International is noted to be in advanced talks to purchase medical-gear company Hill-Rom Holdings for about $10 billion, about 4% more than an earlier bid which had been rejected. In June, a group of private equity firms reached a deal to acquire Medline Industries, which if completed would be the largest leveraged buyout in nearly 15 years. Also, Illinois-based pharmaceutical Catalent last week announced that it will purchase nutritional supplement manufacturer Bettera Holdings for $1 billion. With this acquisition, Catalent hopes to expand its oral dose and softgels formulation and manufacturing business. Bettera has four U.S. manufacturing sites, while Catalent has sites in North and South America, Europe and Japan.
Pfizer-BioNTech is likely to get the regulatory go-ahead to administer a third (booster) COVID-19 within the next week, according to government officials. Pfizer booster vaccines may be available by September 20, but only for high-risk groups. Moderna has submitted its COVID-19 booster data to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) over the past week, but the FDA has commented that the data may take longer to review than that submitted by Pfizer. The FDA may only recommend a lower dosage (50%) for the Moderna booster.
The European Union (EU) announced last week that it had met its target of having 70% of European adults vaccinated against COVID-19 by the end of the summer. There are large variations between countries and the World Health Organization (WHO) warned last week that the pace of vaccinations in Europe has slowed with higher health risks in those European countries with lower vaccination rates, especially to the newer highly infectious Delta variant.
R&D World’s R&D Index is a weekly stock market summary of the top international companies involved in R&D. The top 25 industrial R&D spenders in 2019 were selected based on the latest listings from Schonfeld & Associates’ June 2020 R&D Ratios & Budgets. These 25 companies include pharmaceutical (10 companies), automotive (6 companies) and ICT (9 companies) who invested a cumulative total of nearly 260 billion dollars in R&D in 2019, or approximately 10% of all the R&D spent in the world by government, industries and academia combined, according to R&D World’s 2021 Global R&D Funding Forecast. The stock prices used in the R&D World Index are tabulated from NASDAQ. NYSE, and OTC common stock prices for the companies selected at the close of stock trading business on the Friday preceding the online publication of the R&D World Index.


Tell Us What You Think!