University of Groningen physicists in collaboration with a theoretical physics group from Universität Regensburg have built an optimized bilayer graphene device that displays both long spin lifetimes and electrically controllable spin-lifetime anisotropy. It has the potential for practical applications such as spin-based logic devices.
The results were published in Physical Review Letters.
Miniaturizing the elements of computer systems over the last 60 years has increased their capability, enabling them to spread into nearly all aspects of daily life. Microprocessors have now reached scales below 100 atoms and are approaching fundamental limits.
Due to higher demands, new concepts are required that can provide enhanced functionalities.
In this context, researchers are studying the use of spin for the transport and storage of information. Spin is a quantum mechanical property of electrons, which gives them a magnetic moment that could be used to transfer or store information.
The field of spin-based electronics (spintronics) has already made its way into the hard drives of computers, and also promises to revolutionize processing units.
Graphene is an excellent conductor of electron spins, but it is hard to control spins in this material because of their weak interaction with the carbon atoms (the spin-orbit coupling).
Previous work by the University of Groningen Physics of Nanodevices group led by Professor Bart van Wees placed graphene in close proximity to a transition metal dichalcogenide, a layered material with a high intrinsic spin-orbit coupling strength.
The high spin-orbit coupling strength was transferred to graphene via a short-range interaction at the interface. This made it possible to control the spin currents, but only at the cost of reduced spin duration.
In the new study, the researchers managed to control spin currents in a graphene bilayer.
“This was actually predicted in a theoretical paper in 2012, but the technology to measure the effect accurately only became available recently,” explains Christian Leutenantsmeyer, a Ph.D. student in the Van Wees group and first author of the PRL paper.
The paper is a collaboration between the Van Wees group and a theoretical physics group from Universität Regensburg in Germany.
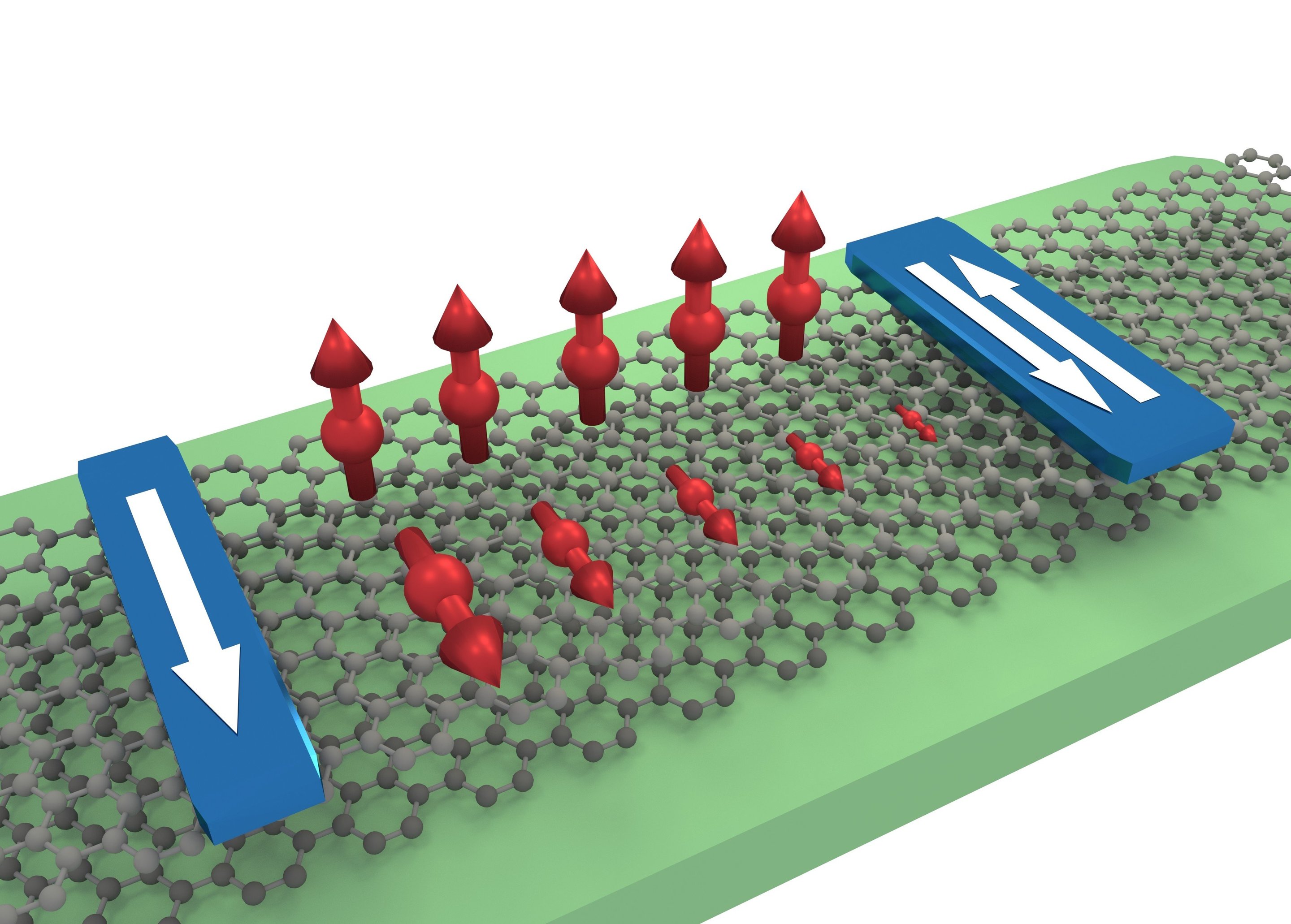
Illustration of anisotropic spin transport in a bilayer graphene flake between injector and detector electrodes. The out-of-plane spins are well transmitted whereas the in-plane spins decay fast. Image: Talieh Ghiasi/Van Wees Lab/University of Groningen
The 2012 paper predicted anisotropic spin transport in graphene bilayers as a consequence of spin-orbit coupling in bilayer graphene. Anisotropic spin transport describes the situation in which spins pointing either in or out of the graphene plane are conducted with different efficiencies.
This was observed in the devices Leutenantsmeyer and his colleagues produced.
The spin current could also be controlled using spin-lifetime anisotropy since in-plane spins live much shorter than out-of-plane ones, and could be used in devices to polarize spin currents.
Leutenantsmeyer says, “We found that the strength anisotropy is comparable to graphene/transition metal dichalcogenide devices, but we observed a 100 times larger spin lifetime. We therefore achieved both efficient spin transport and efficient control of spins.”
The work provides insight into the fundamental properties of spin-orbit coupling in bilayer graphene.
“And furthermore, our findings open up new avenues for the efficient electrical control of spins in high-quality graphene, a milestone for graphene.”
Source: University of Groningen