In the race to produce a quantum computer, a number of projects are seeking a way to create quantum bits — or qubits — that are stable, meaning they are not much affected by changes in their environment. This normally needs highly nonlinear non-dissipative elements capable of functioning at very low temperatures.
In pursuit of this goal, researchers at École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL)’s Laboratory of Photonics and Quantum Measurements LPQM (STI/SB), have investigated a nonlinear graphene-based quantum capacitor, compatible with cryogenic conditions of superconducting circuits, and based on two-dimensional (2D) materials. When connected to a circuit, this capacitor has the potential to produce stable qubits and also offers other advantages, such as being relatively easier to fabricate than many other known nonlinear cryogenic devices, and being much less sensitive to electromagnetic interference. This research was published in 2D Materials and Applications.
Normal digital computers operate on the basis of a binary code composed of bits with a value of either 0 or 1. In quantum computers, the bits are replaced by qubits, which can be in two states simultaneously, with arbitrary superposition. This significantly boosts their calculation and storage capacity for certain classes of applications. But making qubits is no mean feat: quantum phenomena require highly controlled conditions, including very low temperatures.
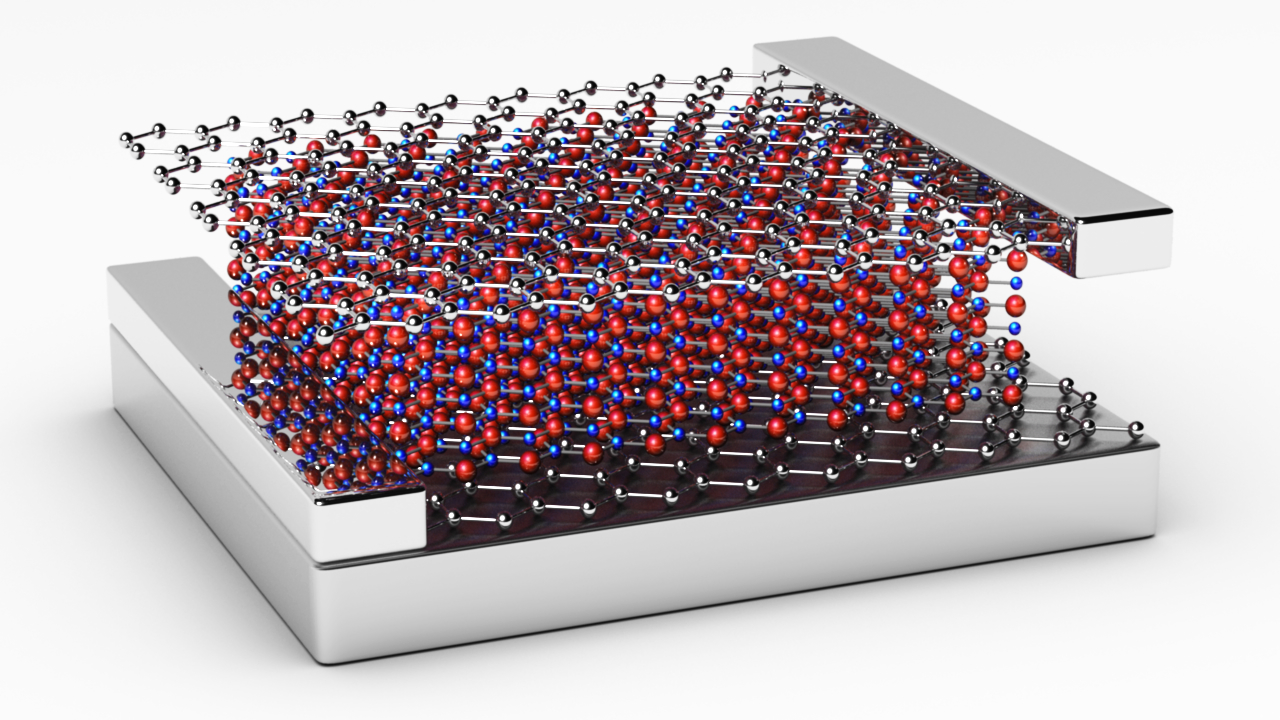
An insulating boron nitride sandwiched between two graphene sheets. Image: ©EPFL/ LPQM
To produce stable qubits, one promising approach is to use superconducting circuits, most of which operate on the basis of the Josephson effect. Unfortunately, they are difficult to make and sensitive to perturbing stray magnetic fields. This means the ultimate circuit must be extremely well shielded both thermally and electromagnetically, which precludes compact integration.
At EPFL’s LPQM, this idea of a capacitor that’s easy to make, less bulky, and less prone to interference has been explored. It consists of insulating boron nitride sandwiched between two graphene sheets. Thanks to this sandwich structure and graphene’s unusual properties, the incoming charge is not proportional to the voltage that is generated. This nonlinearity is a necessary step in the process of generating quantum bits. This device could significantly improve the way quantum information is processed but there are also other potential applications too. It could be used to create very nonlinear high-frequency circuits — all the way up to the terahertz regime — or for mixers, amplifiers, and ultra-strong coupling between photons.