Is there anything MXene materials can’t do?
Since the discovery of a large new family of two-dimensional materials by Drexel University researchers in 2011, continued exploration has revealed their exceptional ability to store energy, block electromagnetic interference, purify water, and even ward off bacteria. And, as recent research now suggests, MXenes are also very durable — the strongest material of its kind, according to a new study in the journal Science Advances.
The finding, presented by researchers at Drexel University and the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, shows that MXenes rate the highest among two-dimensional materials produced by solution processing — the standard method for making scalable, practically useful materials in the lab — in a measure called “elastic modulus.”
In a side-by-side comparison with graphene oxide or reduced graphene oxide, promising new materials that are already being used to add strength to rubber and polymers, a flake of the MXene titanium carbide proved to be about 50 percent stiffer.
This test of strength is performed by placing a single sheet of a material over a silicon wafer test surface with holes. Then a sharp tip of an atomic force microscope pokes the material, making an indentation. As this is happening, the probe is also measuring the force it takes to make the indentation – thus determining the strength and elastic modulus of the material. The team repeated the test 36 times and found the material’s modulus to be the highest recorded for a solution-processed material and comparable even to the strongest material membranes currently known to researchers: pure graphene and molybdenum disulfide.
“This work opens the pathway to study the mechanical properties of monolayers of other MXenes and extends the already broad range of MXenes’ applications,” says Yury Gogotsi, PhD, Distinguished University and Bach Professor in the College of Engineering, who was the lead author of the research.
While the results weren’t exactly unexpected — researchers have anecdotally noted the strength of MXene in the lab over the years — it has taken some time to formally collect this data due to the challenges of creating large enough single-layer samples of the material and mechanically testing the sheets that are just few atoms thick.
But Drexel researchers have now improved their ability to produce larger flakes of titanium carbide MXene. And through collaboration with the team from Nebraska, were able to perform the testing with an atomic force microscope to determine their strength.
The latest research pointed toward graphene as the strongest two-dimensional material, in terms of modulus, so it was relevant for the team to measure a MXene against the processed version of graphene – graphene oxide. Not only do they report that MXene is stronger, the researchers also showed that while a graphene film breaks catastrophically when the indenter pokes a hole in the film, MXene does not.
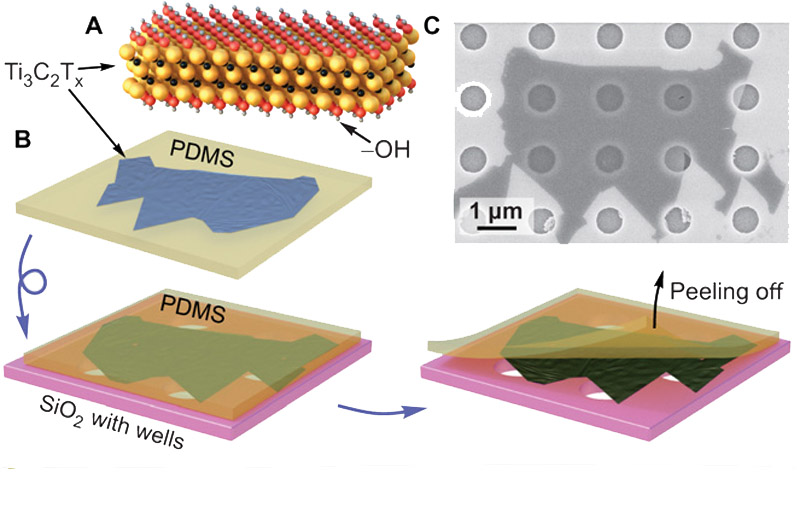
Preparation of MXene membranes.
The discovery of MXene’s superior mechanical properties suggests that it could be a useful additive to structural composites, such as fiber glass. It could also be used in protective coatings and membranes, as a way to increase their durability. And with about 30 MXenes already produced, there is a good chance of finding even stronger varieties than the titanium carbide tested in this study.
“Knowing the mechanical properties of single-sheet MXene is absolutely critical for developing super-strong, tough and hard composite materials,” Gogotsi says. “The next step for MXenes will be adding them to polymers, metals and ceramics to see how their properties can be improved. For example, adding titanium carbide to ceramics and polymers may increase their mechanical strength and conductivity at the same time — these composites may be used for structural applications, electromagnetic shielding and many other purposes.”
Source: Drexel University