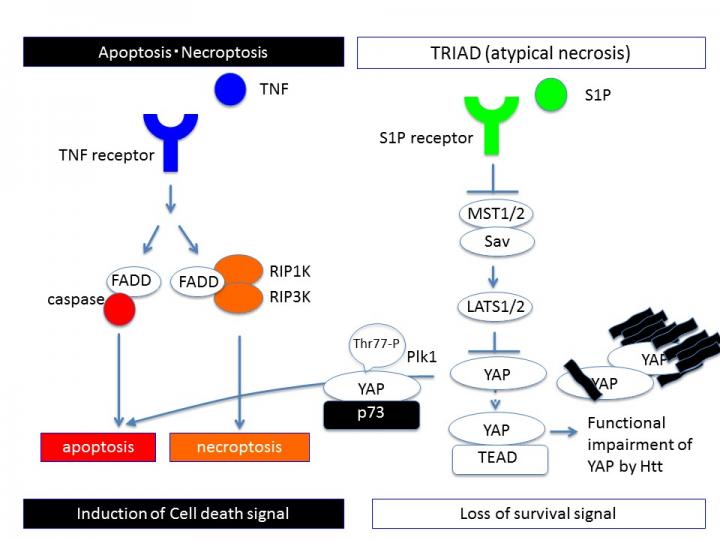
Apoptosis or necroptosis is induced by cell death signaling. Contrarily, transcriptional repression-induced cell death (TRIAD) is induced by the loss of survival signal mediated by Hippo pathway. Phosphorylation of YAP by LATS1/2 or sequestration of YAP by mutant Htt prevents nuclear translocation of YAP and TEAD-YAP transcription that is essential for cell survival of neurons. Source:
Researchers centered at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify novel type of cell death in Huntington’s disease that may uncover new treatments.
Tokyo – In Huntington’s disease (HD), the huntingtin gene is mutated, causing progressive neuronal death. This leads to defects in movement, behavior, and cognitive ability. Apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis are the three main types of cell death, but researchers have not yet been able to determine what type of cell death causes neurodegeneration in the brain of HD patients.
In a new study, Tokyo Medical and Dental University-led researchers examined the nature of cell death in HD using newly developed imaging techniques. The effects of mutant huntingtin in neuronal cells were visualized by live cell imaging. With this approach, the authors identified a novel type of cell death associated with mutant huntingtin, which they called ballooning cell death (BCD). These cells gradually expanded like a balloon, until they ruptured.
To characterize the specific nature of BCD, the authors examined different cellular organelles by live cell imaging. “The endoplasmic reticulum was the main origin of ballooning,” study first author Ying Mao explains. “Rupture of the endoplasmic reticulum into the cytosol was followed by gradual cell body ballooning, nuclear shrinkage, and cell rupture.”
The authors observed the same phenomena in vivo using two-photon endoplasmic reticulum imaging in a HD mouse model.
Pharmacological inhibitors and genetic interventions showed that BCD was not like apoptosis or autophagy. “We noticed multiple similarities between BCD and a unique form of necrosis called TRIAD, which is caused by inhibition of RNA polymerase II in neurons,” corresponding author Hitoshi Okazawa explains. “Based on our existing knowledge of how TRIAD is regulated, we were able to show that BCD is mediated by impaired TEAD/YAP transcription.”
These revelations provided the opportunity to test potential therapeutic targets for HD. The researchers introduced S1P and up-regulated TEAD/YAP transcription in HD mice. This stabilized endoplasmic reticulum and completely stopped the decline of motor function, suggesting that targeting TEAD/YAP-dependent necrosis may lead to development of effective therapies for HD.




