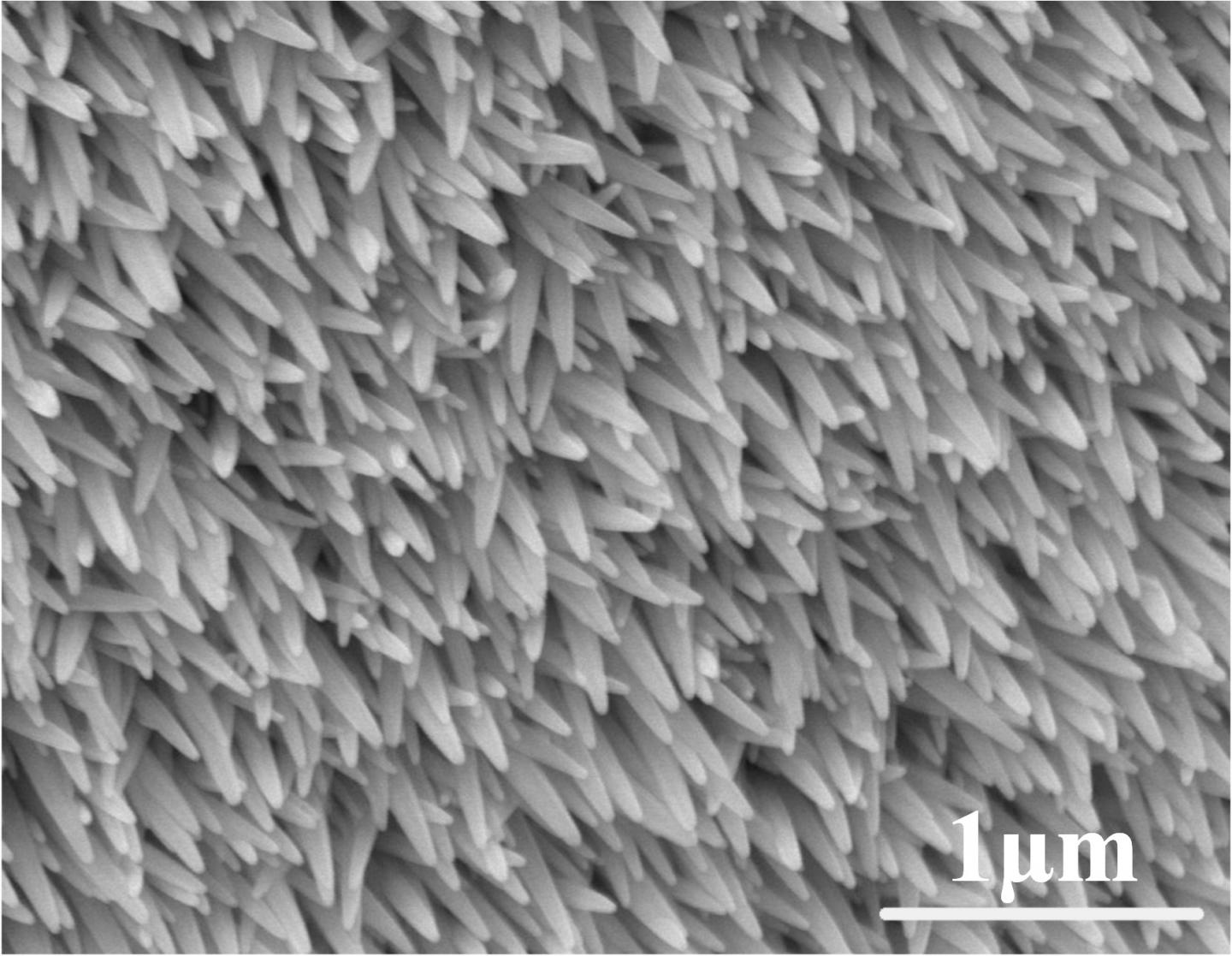
Nanostructures on an artificial bug eye resemble a shag carpet when viewed with a powerful microscope. Credit: American Chemical Society
Single lens eyes, like those in humans and many other animals, can create sharp images, but the compound eyes of insects and crustaceans have an edge when it comes to peripheral vision, light sensitivity and motion detection. That’s why scientists are developing artificial compound eyes to give sight to autonomous vehicles and robots, among other applications. Now, a report in ACS Nano describes the preparation of bioinspired artificial compound eyes using a simple low-cost approach.
Compound eyes are made up of tiny independent repeating visual receptors, called ommatidia, each consisting of a lens, cornea and photoreceptor cells. Some insects have thousands of units per eye; creatures with more ommatidia have increased visual resolution. Attempts to create artificial compound eyes in the lab are often limited by cost, tend to be large and sometimes include only a fraction of the ommatidia and nanostructures typical of natural compound eyes. Some groups are using lasers and nanotechnology to generate artificial bug eyes in bulk, but the structures tend to lack uniformity and are often distorted, which compromises sight. To make artificial insect eyes with improved visual properties, Wenjun Wang and colleagues developed a new strategy with improved structural homogeneity.
As a first step, the researchers shot a laser through a double layer of acrylic glass, focusing on the lower layer. The laser caused the lower layer to swell, creating a convex dome shape. The researchers created an array of these tiny lenses that could themselves be bent along a curved structure to create the artificial eye. Then, through several steps, the researchers grew nanostructures on top of the convex glass domes that, up close, resemble a shag carpet. The nanostructures endowed the microlenses with desirable antireflective and water-repellent properties.




