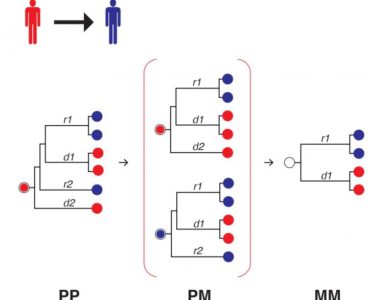
Computer Simulations Predict the Spread of HIV
In a recently published study in the journal Nature Microbiology, researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory show that computer simulations can accurately predict the transmission of HIV across populations, which could aid in preventing the disease. The simulations were consistent with actual DNA data obtained from a global public HIV database, developed and maintained by…
TNT Could Be Headed for Retirement After 116 Years on the Job
One Step Closer to Understanding Explosive Sensitivity With Molecule Design
Explosives have an inherent problem – they should be perfectly safe for handling and storage but detonate reliably on demand. Using computer modeling and a novel molecule design technique, scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory have replaced one “arm” of an explosive molecule to help unravel the first steps in the detonation process and better…
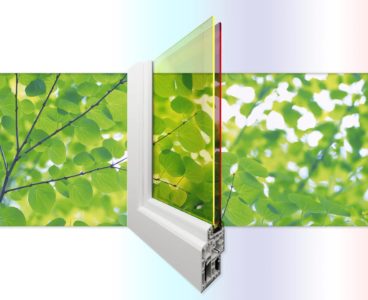
Tweaking Quantum Dots Powers-Up Double-Pane Solar Windows
Using two types of “designer” quantum dots, researchers are creating double-pane solar windows that generate electricity with greater efficiency and create shading and insulation for good measure. It’s all made possible by a new window architecture which utilizes two different layers of low-cost quantum dots tuned to absorb different parts of the solar spectrum. “Because…
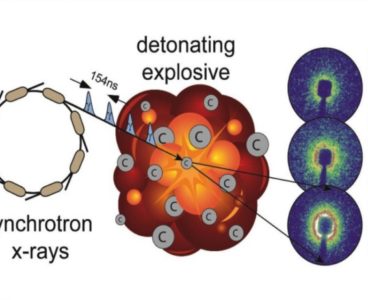
First-Ever U.S. Experiments at New X-Ray Facility May Lead to Better Explosive Modeling
For the first time in the U.S., time-resolved small-angle x-ray scattering (TRSAXS) is used to observe ultra-fast carbon clustering and graphite and nanodiamond production in the insensitive explosive Plastic Bonded Explosive (PBX) 9502, potentially leading to better computer models of explosive performance. “Carbon clusters are produced during the chemical process of detonation in high explosives,”…
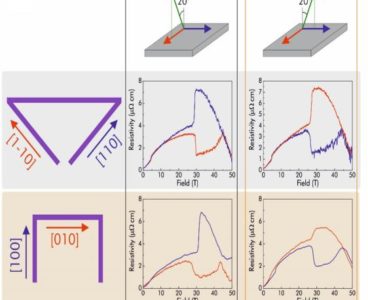
Superconductivity Research Reveals Potential New State of Matter
A potential new state of matter is being reported in the journal Nature, with research showing that among superconducting materials in high magnetic fields, the phenomenon of electronic symmetry breaking is common. The ability to find similarities and differences among classes of materials with phenomena such as this helps researchers establish the essential ingredients that cause…
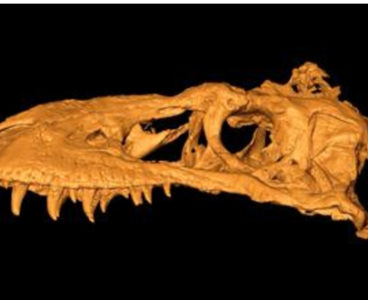
Unique Imaging of a Dinosaur’s Skull Tells Evolutionary Tale
Researchers using Los Alamos’ unique neutron-imaging and high-energy X-ray capabilities have exposed the inner structures of the fossil skull of a 74-million-year-old tyrannosauroid dinosaur nicknamed the Bisti Beast in the highest-resolution scan of tyrannosaur skull ever done. The results add a new piece to the puzzle of how these bone-crushing top predators evolved over millions…
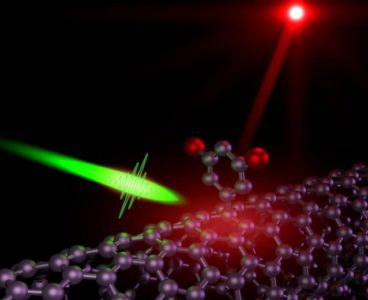
Single-Photon Emitter Has Promise for Quantum Info-Processing
Los Alamos National Laboratory has produced the first known material capable of single-photon emission at room temperature and at telecommunications wavelengths. These carbon nanotube quantum light emitters may be important for optically-based quantum information processing and information security, while also being of significant interest for ultrasensitive sensing, metrology and imaging needs and as photon sources…
‘Charliecloud’ Simplifies Big Data Supercomputing
At Los Alamos National Laboratory, home to more than 100 supercomputers since the dawn of the computing era, elegance and simplicity of programming are highly valued but not always achieved. In the case of a new product, dubbed “Charliecloud,” a crisp 800-line code helps supercomputer users operate in the high-performance world of Big Data without…
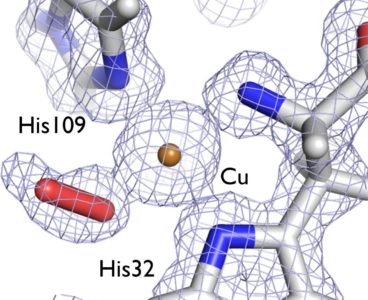
Insight into Enzyme’s 3D Structure Could Cut Biofuel Costs
Using neutron crystallography, a Los Alamos research team has mapped the three-dimensional structure of a protein that breaks down polysaccharides, such as the fibrous cellulose of grasses and woody plants, a finding that could help bring down the cost of creating biofuels. The research focused on a class of copper-dependent enzymes called lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases…
Managing Disease Spread Through Accessible Modeling
A new computer modeling study from Los Alamos National Laboratory is aimed at making epidemiological models more accessible and useful for public-health collaborators and improving disease-related decision making. “In a real-world outbreak, the time is often too short and the data too limited to build a really accurate model to map disease progression or guide…
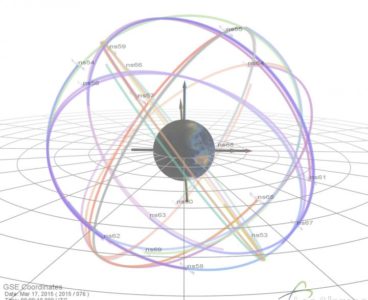
First-Ever GPS Data Released to Boost Space-Weather Science
Today, more than 16 years of space-weather data is publicly available for the first time in history. The data comes from space-weather sensors developed by Los Alamos National Laboratory on board the nation’s Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. The newly available data gives researchers a treasure trove of measurements they can use to better understand…
New Class of Fuel Cells Offer Increased Flexibility, Lower Cost
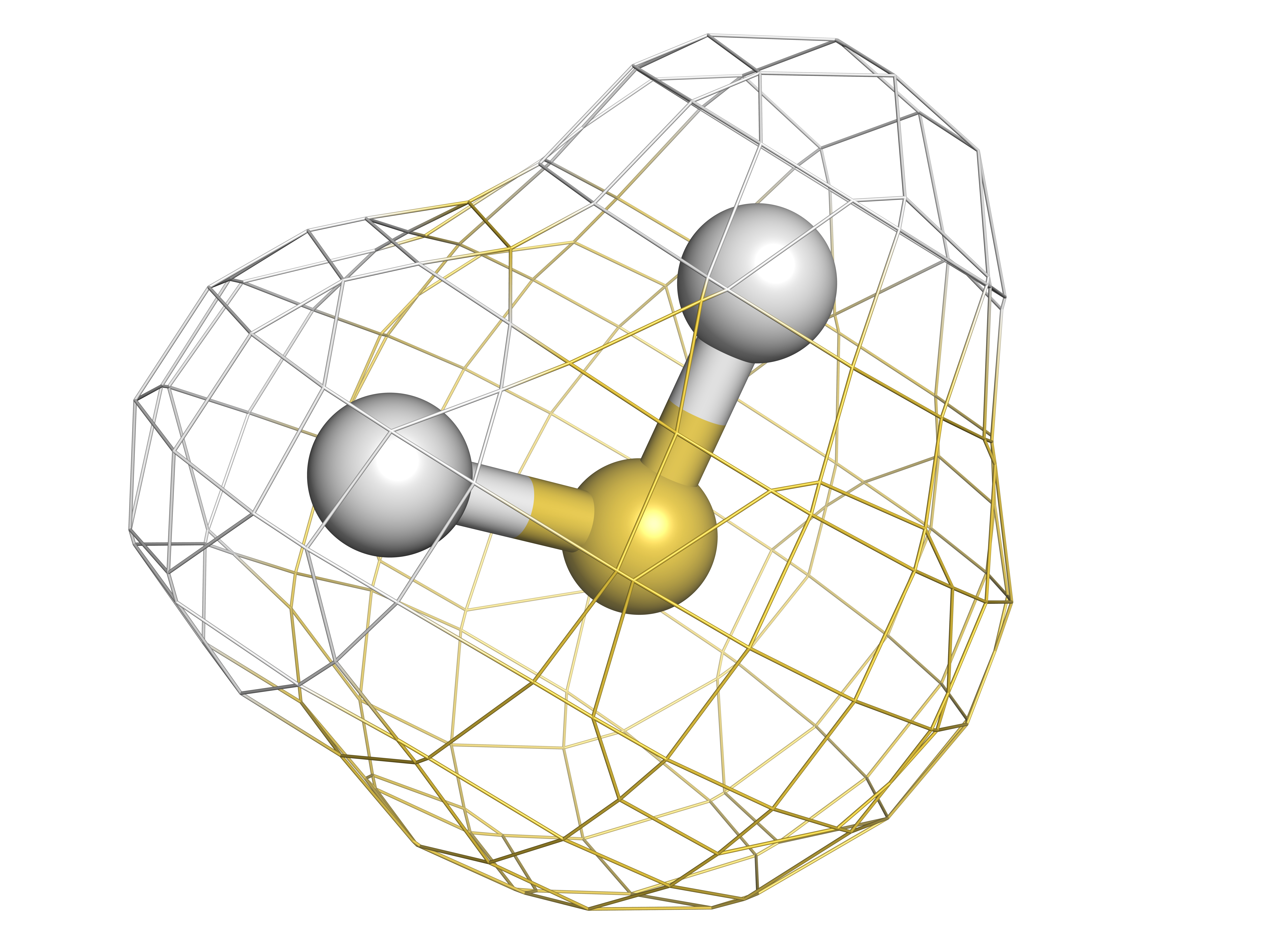
Model Predicts Once-Mysterious Chemical Reactions
A team of researchers from Los Alamos National Laboratory and Curtin University in Australia developed a theoretical model to forecast the fundamental chemical reactions involving molecular hydrogen (H2), which after many decades and attempts by scientists had remained largely unpredicted and unsolved. “Chemical reactions are the basis of life so predicting what happens during these…