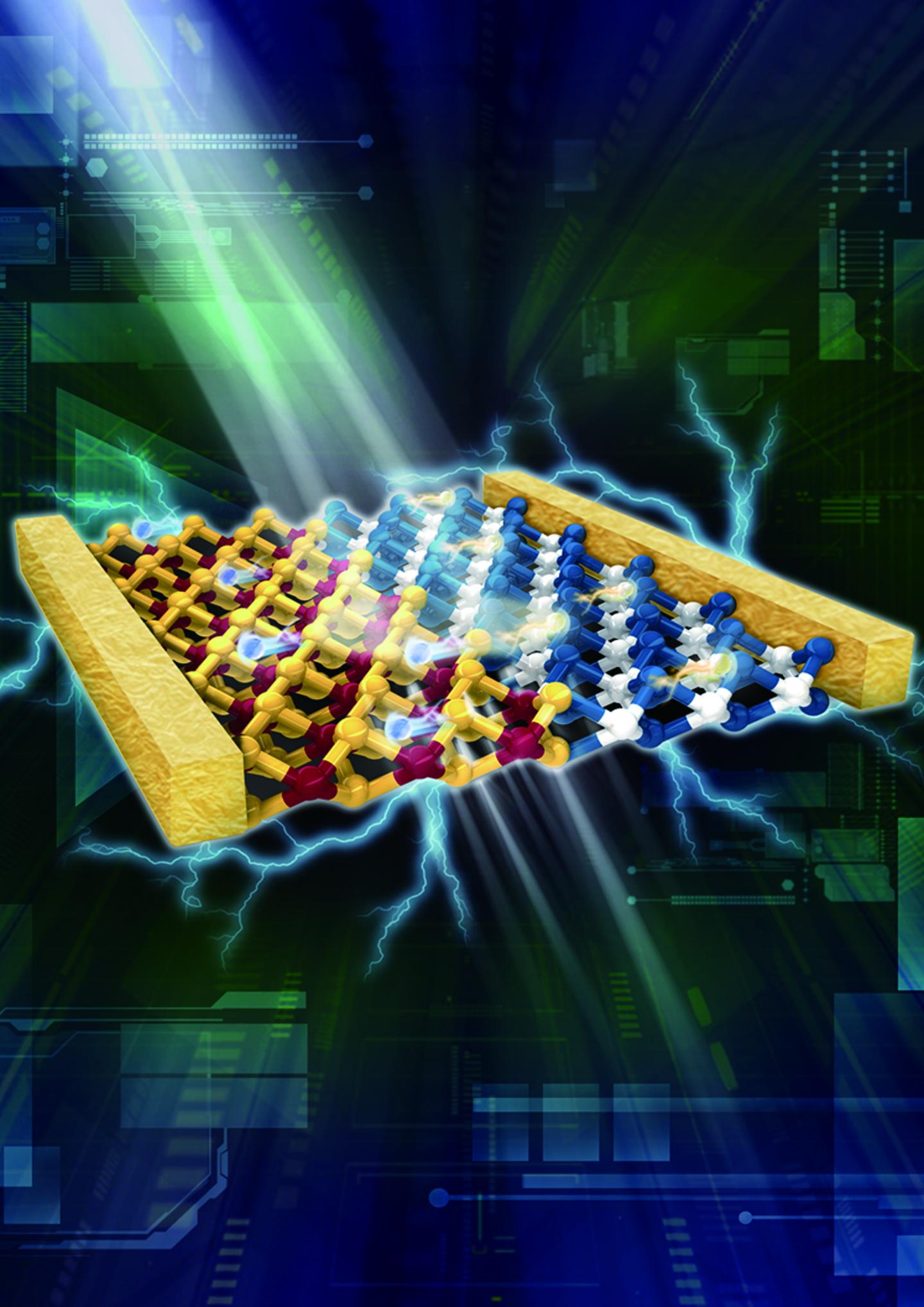
Solar power conversion using a lateral WSe2–MoS2 heterojunction. Image: © 2017 WILEY VCH
Super thin photovoltaic devices underpin solar technology and gains in the efficiency of their production are therefore keenly sought. King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) researchers have combined and rearranged different semiconductors to create so-called lateral p-n heterojunctions — a simpler process they hope will transform the fabrication of solar cells, self-powered nanoelectronics, as well as ultrathin, transparent, flexible devices.
Two-dimensional semiconductor monolayers, such as graphene and transition-metal dichalcogenides like WSe2 and MoS2, have unique electrical and optical properties that make them potential alternatives to conventional silicon-based materials. Recent advances in material growth and transfer techniques have allowed scientists to manipulate these monolayers. Specifically, vertical stacking has led to ultrathin photovoltaic devices but requires multiple complex transfer steps. These steps are hampered by various issues, such as the formation of contaminants and defects at the monolayer interface, which limit device quality.
“Devices obtained using these transfer techniques are usually unstable and vary from sample to sample,” says lead researcher and former visiting student of Associate Professor, Jr-Hau He, Meng-Lin Tsai, who adds that transfer-related contaminants significantly affect device reliability. Electronic properties have also proven difficult to control by vertical stacking.
To fully harness the exceptional properties of these two-dimensional materials, Tsai’s team, under the mentorship of He, created monolayers featuring lateral WSe2-MoS2 heterojunctions and incorporated them into solar cells. Under simulated sunlight, the cells achieved greater power conversion efficiency than their vertically stacked equivalents.
To do this, first the researchers synthesized the heterojunctions by consecutively depositing WSe2 and MoS2 on a sapphire substrate. Next, they transferred the materials onto a silicon-based surface for photovoltaic device fabrication.
High-resolution microscopy revealed that the lateral junction displayed a clear separation between the semiconductors at the interface. Also, the researchers detected no discernable height difference between semiconductor regions, consistent with an atomically thin interface.
These interfacial characteristics signaled success. “Our structures are cleaner and more ideal than vertically stacked assemblies because we didn’t need the multi-step transfer procedure,” explains Tsai.
Furthermore, the lateral heterojunctions mostly retained their efficiency despite changes to the orientation of the incident light. Being able to take light coming from any direction means expensive solar tracking systems will become redundant.
According to Tsai, the implementation of lateral heterojunctions in more complex circuits and interconnects may result in higher performance than in conventional solar cells and so the team is working on the next steps. “We are trying to understand the underlying kinetics and thermodynamics of these heterojunctions to design more efficient cells,” he adds.