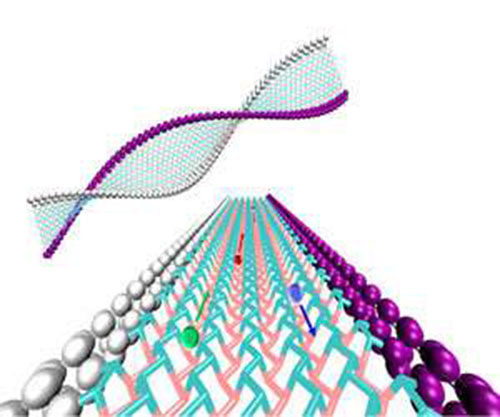
Tube-like atomic structures on the edges of phosphorous-based nanoribbons help keep this 2D material conductive during times of thermal or tensile stress. Image: A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing
Black phosphorene, an unusual two-dimensional (2-D) compound, may offer strategies for avoiding damaging hot spots in nanoscale circuits, a new study from A*STAR researchers has revealed.
While carbon atoms in graphene films sit perfectly flat on a surface, black phosphorene has a distinct wrinkled shape due to the bonding preferences of its phosphorus atoms. Investigations suggest that the zig-zag structure of this 2-D film enables it to behave differently in different orientations: it can transport electrons slowly along one axis, for example, but rapidly in the perpendicular direction.
Xiangjun Liu, from the A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing notes that black phosphorene’s capabilities stretch beyond high-speed electronics.
“It has optical, mechanical, and thermal properties that all exhibit directional dependence,” he says.
“This stems from the unique puckered structure, which really impressed me when I first saw it.”
Researchers theorize that excess heat could be drawn from nanoscale circuits using precisely controlled phonons — “quanta” or packets of vibrational energy — present in black phosphorene components.
Liu and co-workers focused their study on an important structural issue that can affect phosphorene thermal conductivity—the atom structures at the edges of the 2-D film. Researchers have predicted that phosphorene may either have a dimer edge formed by coupling of two terminal atoms, or an energetically stable tube-shaped edge created by multi-atom bonding.
To understand how different edge structures impact thermal conductivity, the A*STAR team used computer algorithms that simulate phonon transfer across a temperature gradient. They modeled phosphorene films as narrow, rectangular nanoribbons and observed that heat conductivity was mostly uniform in pristine nanoribbons.
The dimer and tube-terminated models, on the other hand, preferred to direct heat to central regions away from the edges.
Further calculations revealed that the tube-edged models produced different phonon excitations from the other phosphorene structures — they exhibited a new type of twisting movement, as well as geometric expansions and contractions referred to as breathing modes.
These additional movements, explains Liu, are probably why tube edges work so well in scattering thermal vibrations and remaining cool.
Normally, 2-D materials have reduced ability to diffuse heat when strained laterally. Tube-terminated nanoribbons, however, have nearly constant thermal conductivity under strain — a property that may be useful in future wearable technology.
“The strain-independent thermal behavior could benefit devices that need stable performance while being strained or twisted,” says Liu.
“Phosphorene has great potential for applications of soft and flexible electronics.”
Source: A*STAR