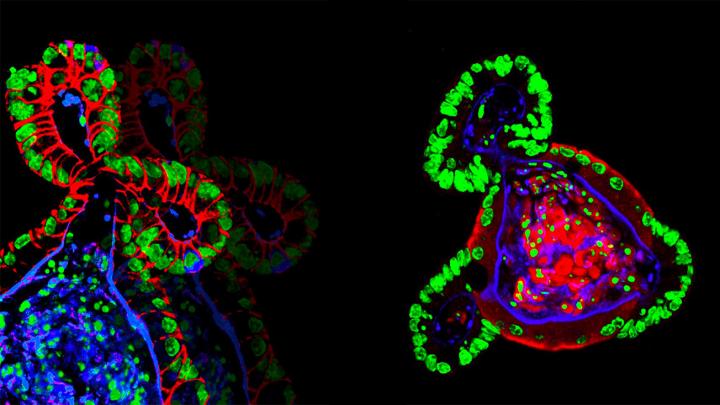
Two fluorescent microscopy images of intestinal organoids growing in synthetic hydrogels. Source: N. Gjorevski/EPFL
EPFL scientists have developed a gel for growing miniaturized body organs that can be used in clinical diagnostics and drug development.
Organoids are miniature organs that can be grown in the lab from a person’s stem cells. They can be used to model diseases, and in the future could be used to test drugs or even replace damaged tissue in patients. But currently organoids are very difficult to grow in a standardized and controlled way, which is key to designing and using them. EPFL scientists have now solved the problem by developing a patent-pending “hydrogel” that provides a fully controllable and tunable way to grow organoids. The breakthrough is published in Nature.
Organoids need a 3D scaffold
Growing organoids begins with stem cells — immature cells that can grow into any cell type of the human body and that play key roles in tissue function and regeneration. To form an organoid, the stem cells are grown inside three-dimensional gels that contain a mix of biomolecules that promote stem cell renewal and differentiation.
The role of these gels is to mimic the natural environment of the stem cells, which provides them with a protein- and sugar-rich scaffold called the “extracellular matrix”, upon which the stem cells build specific body tissues. The stem cells stick to the extracellular matrix gel, and then “self-organize” into miniature organs like retinas, kidneys, or the gut. These tiny organs retain key aspects of their real-life biology, and can be used to study diseases or test drugs before moving on to human trials.
But the current gels used for organoid growth are derived from mice, and have problems. First, it is impossible to control their makeup from batch to batch, which can cause stem cells to behave inconsistently. Second, their biochemical complexity makes them very difficult to fine-tune for studying the effect of different parameters (e.g. biological molecules, mechanical properties, etc.) on the growth of organoids. Finally, the gels can carry pathogens or immunogens, which means that they are not suitable for growing organoids to be used in the clinic.
A hydrogel solution
The lab of Matthias Lütolf at EPFL’s Institute of Bioengineering has developed a synthetic “hydrogel” that eschews the limitations of conventional, naturally derived gels. The patent-pending gel is made of water and polyethylene glycol, a substance used widely today in various forms, from skin creams and toothpastes to industrial applications and, as in this case, bioengineering.
Nikolce Gjorevski, the first author of the study, and his colleagues used the hydrogel to grow stem cells of the gut into a miniature intestine. The functional hydrogel was not only a goal in and of itself, but also a means to identify the factors that influence the stem cells’ ability to expand and form organoids. By carefully tweaking the hydrogel’s properties, they discovered that separate stages of the organoid formation process require different mechanical environments and biological components.
One such factor is a protein called fibronectin, which helps the stem cells attach to the hydrogel. Lütolf’s lab found that this attachment itself is immensely important for growing organoids, as it triggers a whole host of signals to the stem cell that tell it to grow and build an intestine-like structure. The researchers also discovered an essential role for the mechanical properties, i.e. the physical stiffness, of the gel in regulating intestinal stem cell behavior, shedding light on how cells are able to sense, process and respond to physical stimuli. This insight is particularly valuable – while the influence of biochemical signals on stem cells is well-understood, the effect of physical factors has been more mysterious.
Because the hydrogel is man-made, it is easy to control its chemical composition and key properties, and ensure consistency from batch to batch. And because it is artificial, it does not carry any risk of infection or triggering immune responses. As such, it provides a means of moving organoids from basic research to actual pharmaceutical and clinical applications in the future.
Lütolf’s lab is now researching other types of stem cells in order to extend the capacities of their hydrogel into other tissues.




