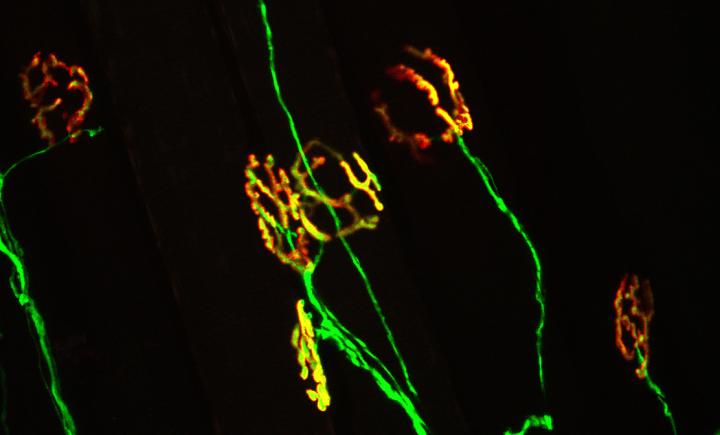
The neuromuscular junction is the synapse where motor neurons communicate with muscle to initiate voluntary movement. A healthy neuromuscular junction (yellow) is characterized by perfect apposition between the motor neuron (green) and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the muscle (red). This synapse is damaged early in ALS, a change believed to contribute the onset and progression of the disease. Source: Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute
Researchers at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute have identified a naturally occurring molecule that has the potential for preserving sites of communication between nerves and muscles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and over the course of aging — as well as a molecule that interferes with this helpful process.
The discovery in mice has implications for patients with ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease.
Publishing this week as an early release research article in The Journal of Neuroscience, the research team, led by Gregorio Valdez, an assistant professor at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute and in the Department of Biological Sciences at Virginia Tech, describes a growth factor called FGFBP1, which is secreted by muscle fibers and maintains neuromuscular junctions — a critical type of synapse that allows the spinal cord to communicate with muscles, sending signals from the central nervous system to create movements.
ALS strikes approximately 6,000 people in the U.S. each year, according to the ALS Association.
In mouse models of ALS, a growth factor associated with the immune system, called TGF-beta, emerges and prevents muscles from secreting factors needed to maintain their connections with neurons.
“TGF-beta is upregulated in ALS and in turn blocks expression of FGFBP1, which is released by muscle fibers to preserve the integrity of the neuromuscular junction,” Valdez said. “The body is trying to help itself by generating more TGF-beta. Unfortunately, TGF-beta accumulates at the synapse where it blocks expression of FGFBP1, accelerating degeneration of the neuromuscular junction.”
FGFBP1 also gradually decreases during aging, but more precipitously in ALS, because of TGF-beta accumulates at the synapse, according to Thomas Taetzsch, a postdoctoral fellow in the Valdez lab and a co-first author of the study.
Milagros Tenga, a postdoctoral fellow in the Valdez lab also contributed to this discovery and is also a co-first author in the paper.
In people, ALS progresses rapidly, attacking nerve cells that control voluntary muscles. Eventually, all muscles under voluntary control are affected, and individuals lose their strength and the ability to move their arms, legs, and body, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Most people with ALS die from respiratory failure, usually within three to five years from the onset of symptoms.
“Our findings suggest that targeting these molecules may allow these important synapses to stay in place, and slow the progression of ALS,” Valdez said.




