LAVA: Large-Scale Vulnerability Addition
Category: Software/Services
Developers: MIT Lincoln Laboratory
Co-Developers: New York University Northeastern University
United States
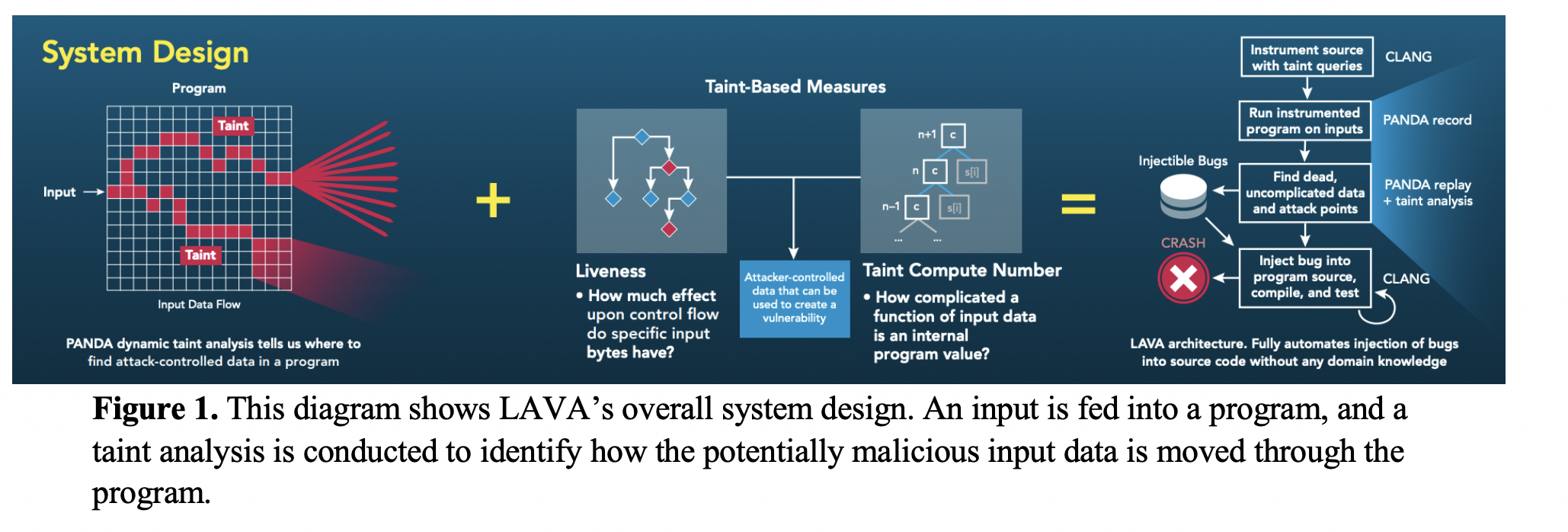
Product Description:Work on automating software vulnerability discovery has long been hampered by a shortage of ground truth corpora with which to evaluate tools and techniques. This lack of ground truth prevents authors and users of tools from being able to measure fundamental quantities such as the miss and false alarm rates of bug-finding systems. Large-scale Automated Vulnerability Addition (LAVA), developed by MIT Lincoln Laboratory, is a novel system based on dynamic taint analysis that is capable of producing ground truth corpora by quickly and automatically injecting large numbers of realistic bugs into program source code. Every LAVA bug is accompanied by an input that triggers it, whereas normal inputs are extremely unlikely to do so. LAVA-generated vulnerabilities are synthetic but still realistic, as they are embedded deep within programs and triggered by real inputs. LAVA forms the basis of an approach for generating large ground truth vulnerability corpora on demand, enabling rigorous tool evaluation and providing a high-quality target for tool developers.
Developers: MIT Lincoln Laboratory
Co-Developers: New York University Northeastern University
United States
Product Description:Work on automating software vulnerability discovery has long been hampered by a shortage of ground truth corpora with which to evaluate tools and techniques. This lack of ground truth prevents authors and users of tools from being able to measure fundamental quantities such as the miss and false alarm rates of bug-finding systems. Large-scale Automated Vulnerability Addition (LAVA), developed by MIT Lincoln Laboratory, is a novel system based on dynamic taint analysis that is capable of producing ground truth corpora by quickly and automatically injecting large numbers of realistic bugs into program source code. Every LAVA bug is accompanied by an input that triggers it, whereas normal inputs are extremely unlikely to do so. LAVA-generated vulnerabilities are synthetic but still realistic, as they are embedded deep within programs and triggered by real inputs. LAVA forms the basis of an approach for generating large ground truth vulnerability corpora on demand, enabling rigorous tool evaluation and providing a high-quality target for tool developers.
LAVA Figure 1
