XRPBS: X-ray Polarizing Beam Splitter
Category: IT/Electrical
Developers: Nevada National Security Site
Co-Developers: Sandia National Laboratory, Argonne National Laboratory, Ecopulse
United States
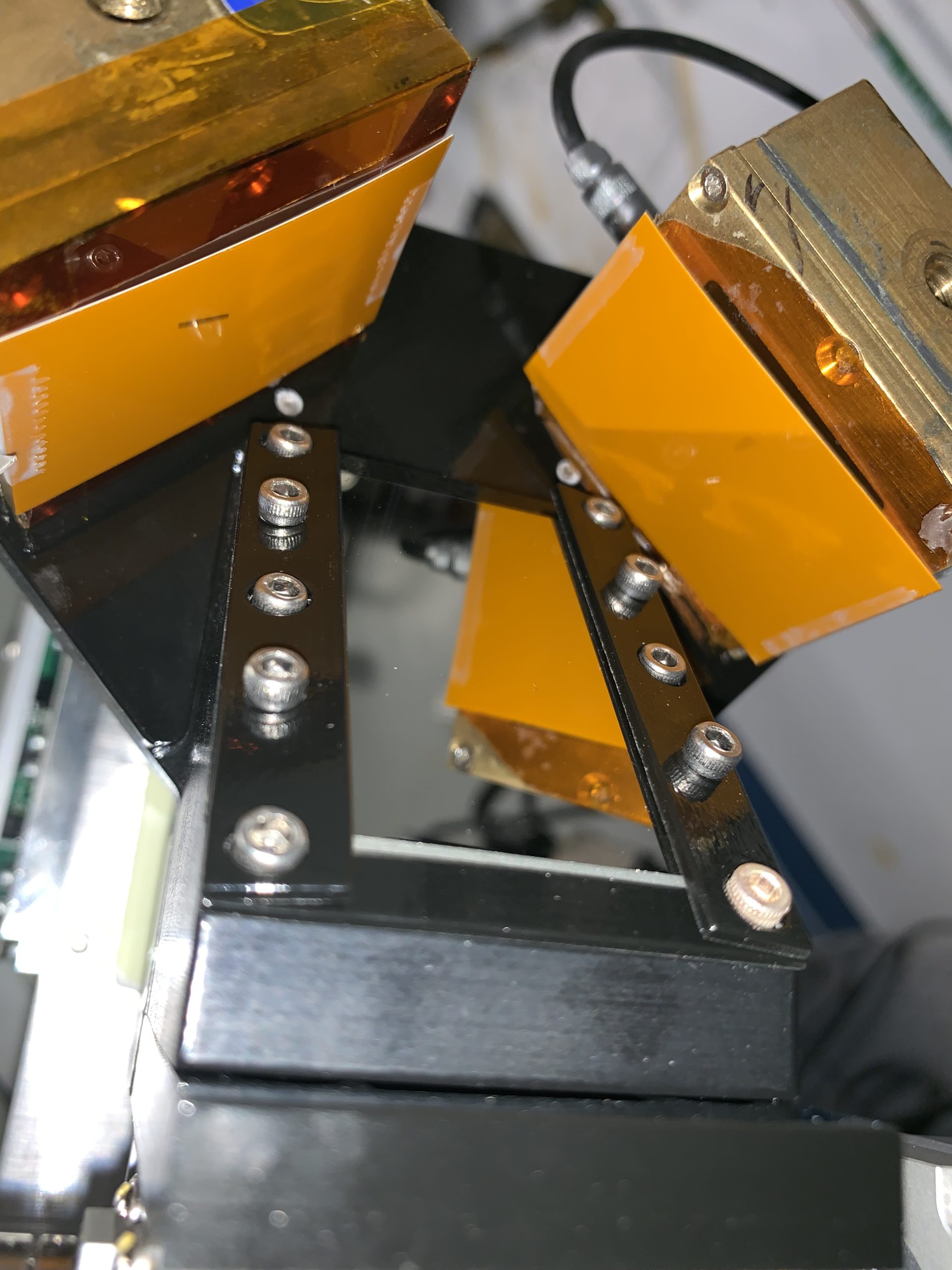
Product Description:The X-ray Polarizing Beam Splitter (XRPBS), developed by Neveda National Security Site, is a compact x-ray optical component that uses a perfect crystal to split an incident x-ray beam into two beams with mutually orthogonal linear polarizations. The two outgoing beams emerge in directions perpendicular to each other and to the direction of the incoming beam. This spatial separation enables using x-ray detectors that are the most appropriate for the actual measurement and is advantageous for other applications at advanced x-ray sources. The XRPBS is most impactful on the x-ray polarization spectroscopy of laboratory and astrophysical plasmas, where it can greatly improve measurement accuracy, decrease instrument size, reduce measurement time and simplify the alignment process. Additionally, this technique simplifies the study of the magnetic and structural properties of materials probed with synchrotron radiation. In a different type of application, the XRPBS can be used as synchrotrons and x-ray free electron lasers for in situ beam monitoring, for beam multiplexing to enable beam sharing or as a component of delay lines for beam characterization or pump-probe experiments.
Developers: Nevada National Security Site
Co-Developers: Sandia National Laboratory, Argonne National Laboratory, Ecopulse
United States
Product Description:The X-ray Polarizing Beam Splitter (XRPBS), developed by Neveda National Security Site, is a compact x-ray optical component that uses a perfect crystal to split an incident x-ray beam into two beams with mutually orthogonal linear polarizations. The two outgoing beams emerge in directions perpendicular to each other and to the direction of the incoming beam. This spatial separation enables using x-ray detectors that are the most appropriate for the actual measurement and is advantageous for other applications at advanced x-ray sources. The XRPBS is most impactful on the x-ray polarization spectroscopy of laboratory and astrophysical plasmas, where it can greatly improve measurement accuracy, decrease instrument size, reduce measurement time and simplify the alignment process. Additionally, this technique simplifies the study of the magnetic and structural properties of materials probed with synchrotron radiation. In a different type of application, the XRPBS can be used as synchrotrons and x-ray free electron lasers for in situ beam monitoring, for beam multiplexing to enable beam sharing or as a component of delay lines for beam characterization or pump-probe experiments.
APS_crystal_refl.jpg
