Volkswagen Group of America, Inc. is boosting its automotive research in the United States to further accelerate electric mobility and sustainable transportation innovation. The company continues to center strategic areas of research in dedicated technology units across the country, as well as foster co-innovation with universities and federal research facilities. One key unit is in Tennessee: Volkswagen’s Innovation Hub in Knoxville is driving applied materials science in collaboration with the University of Tennessee (UT) and Oakridge National Lab (ORNL). There, integrated teams are pushing breakthroughs in automotive lightweight composites, recyclable interior materials, and EV wireless charging.
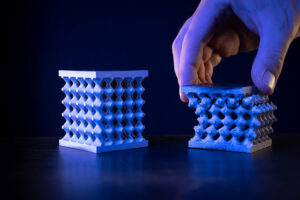
Volkswagen researchers are researching new material structures optimized with artificial intelligence. This structure can be 3D-printed from liquid resins and holds 30,000 times its own 0.15-lb weight (68 g).
“We are accelerating innovation within electric vehicles and contributing to more sustainable transportation in America by focusing our efforts on some of the most transformative automotive research being done in the country,” said Pablo Di Si, president, and CEO at Volkswagen Group of America Inc. “Our technology teams in Tennessee are a great example. There, we are tapping American ingenuity fostered by the unique blend of world-class academic research and Volkswagen’s leading industry capabilities.”
Opened in 2020, Volkswagen’s Innovation Hub is located at the University of Tennessee Research Park at Cherokee Farm in Knoxville, in a region referred to as ‘the Materials Valley’ due to the concentration of research facilities. This includes the ORNL, of which VWGoA has also established research collaborations. Volkswagen researchers, UT faculty, and doctoral students as well as ORNL scientists collectively drive research and co-innovation of applied materials research.
“Centering more knowledge in the United States is part of Volkswagen’s strategy for growth and is vital for sourcing and developing talent,” said Di Si.
“The Volkswagen Innovation Hub is a powerful example of the kind of scientific advances and industry-ready technology that you can bring to market when you locate scientists and researchers from across disciplines and organizations together in one place.”, said UT Chancellor Donde Plowman. “With partners like Volkswagen, Oak Ridge National Lab, and other industry leaders and tech startups located at UT’s Research Park, we have created a thriving innovation ecosystem.”
The Innovation Hub teams lead research in the following key projects:
AI-optimized material structures to increase electric vehicle range
Volkswagen researchers are working on new material structures to reduce vehicle weight, which helps to increase the range of electric vehicles (EVs). As a first pilot, the team has chosen the steel frame that houses the EV battery pack in the vehicle and shields it from physical impacts.

Volkswagen researchers are developing new material structures optimized with artificial intelligence to reduce vehicle weight and increase electric vehicle range.
By running a deep learning algorithm (artificial intelligence) with up to millions of parameters on UT’s high-performance computing cluster, the team has developed a modular repeating structure in the shapes of tiny pyramids. This structure can be 3D-printed from liquid resins and holds 30,000x its own 0.15 lb-weight (68 g). A newly created frame would be up to 60% lighter. Hardcore durability tests showed that it exceeds the conventional steel frame in energy absorption, and could serve as a lightweight, yet ultra-robust alternative.
Paper-based materials for vehicle interior design
The hub team at UT’s Center for Renewable Carbon is developing recyclable alternatives to plastic parts and foils in the vehicle interior. Their focus: paper. The team has patented a method of preforming and hot-pressing cellulose fiber-reinforced thermoplastics into the durable interior parts customers expect.
These paper-based composites are not only recyclable, they can also be transformed into various interior shapes and sizes, including backlit and ambient light options. The team has also innovated ways to add different textures and colors, so vehicle interior designers enjoy flexibility and creative freedom.
The Volkswagen brand is already checking opportunities to include these paper-based interior parts in future model lines and work to support industry-scale production.
New fiber composites for lightweight vehicle parts

The hub team of Volkswagen and UT researchers is developing recyclable alternatives to plastic parts and foils in the vehicle interior – made of paper
The Volkswagen team kicked off lightweight materials research with UT by recreating the lift gate of a MY2020 Volkswagen Atlas using sheet molding compound (SMC), a type of fiberglass-reinforced plastic. The new liftgate proved to be 13 lb lighter than the conventional metal-based version; a weight savings of more than 35%, which could help to increase the range of electric vehicles and those powered with a combustion engine. In addition, the alternative composite lift gate does not need changes in assembly sequence compared to conventional versions – meaning those components are fit for high volumes.
The team’s research breakthrough has already found its way into vehicle production. Bentley and Lamborghini have adopted these new materials and the molding process for the Bentley Continental and in the Lamborghini Aventador. The team in Knoxville has also started a research project to explore lightweight options for pickup beds and rugged components.
More recently, Volkswagen and UT researchers have further refined molding processes and ways to optimize durability, quality, and design options. One specific take is to optimize the fiber-matrix interface a process called “sizing” — essentially creating the smoothest, most durable coat for fibers possible.
New high-power wireless EV charging concepts
Volkswagen’s team has patented a unique coil and charging pad design with silicon-carbide materials to optimize charging speed and safety. Their goal: Help make charging an electric vehicle as easy and comfortable as pulling into a normal garage spot.
In the first early trials with a silicon-carbide inverter, this prototype system has shown high efficiency. Using Volkswagen’s expertise in vehicle power electronics, ORNL’s capabilities in high-power wireless charging, and UT’s knowledge of power electronics optimization, the research team has been able to increase the charging power level up to 120 kW with this prototype from an earlier 6.6kW prototype, with a future goal of 300 kW.
Volkswagen’s Innovation Hub Knoxville is contributing to the global Volkswagen Group’s larger innovation ecosystem, including innovation centers in Belmont, California; Wolfsburg, Germany; and Beijing, along with hubs in Singapore, Tel Aviv, and Tokyo.





Tell Us What You Think!