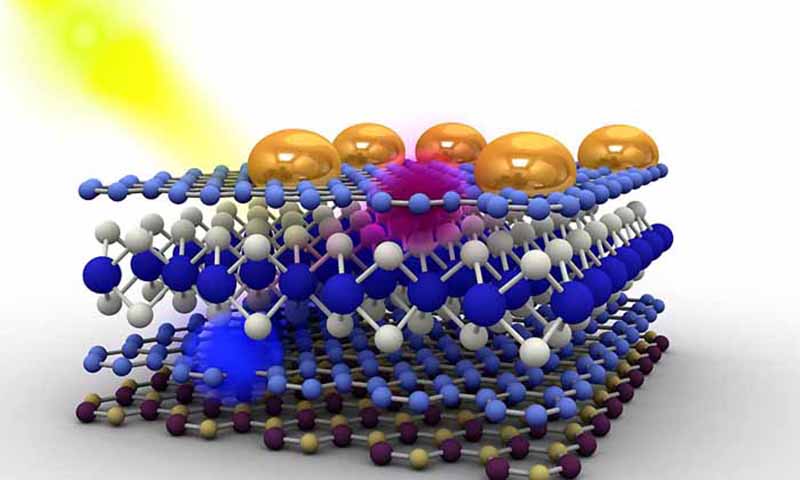
Writing in Science, leading 2D materials researchers estimate that research on combining materials of just a few atomic layers in stacks called heterostructures is at the same stage that graphene was 10 years ago, and can expect the same rapid progress graphene has experienced.
Graphene was the first 2D material, isolated at The University of Manchester in 2004. Its range of superlative properties, including fantastic strength, conductivity, flexibility and transparency, has paved the way for applications ranging from water filtration to bendable smartphones; from rust-proof coatings to anti-cancer drug delivery systems.
Combining graphene with other materials, which individually have excellent characteristics complimentary to the extraordinary properties of graphene, has resulted in exciting scientific developments and could produce applications as yet beyond our imagination.
The authors of the review article, from The University of Manchester and National University of Singapore, state that early applications could be high-mobility transistors for superfast electronics and LED devices using graphene as a transparent electrode.
However, such in the range of possible combinations of materials, researchers believe that heterostructures could deliver designer materials, made to order to meet the demands of industry.
The family of 2D crystals is expanding all the time, meaning that new possibilities for combining them in stacks can be explored.
The next challenge is to work out how to mass produce 2D materials; a similar problem that faced graphene in the early years after it was isolated.
Sir Kostya Novoselov, who together with Professor Sir Andre Geim won the Nobel prize for Physics in 2010 for demonstrating the remarkable properties of graphene, believes 2D materials are one of the most exciting and promising areas of research.
He said: “With 2D materials, we are currently where we were about 10 years ago with graphene – plenty of interesting science and unclear prospects for mass production.
“Given the fast progress of graphene technology over the past few years, we can expect similar advances in the production of heterostructures, making the science and applications more achievable.”
Co-author Professor Antonio Castro Neto, Director of the Centre for Advanced 2D Materials at the National University of Singapore, added: “In the search for revolutionary and disruptive new technologies, van der Waals heterostructures and devices based on two dimensional materials emerge as major players.
“This review covers the latest developments in one of the fastest growing fields that bridges science, materials science, and engineering.”
Source: The University of Manchester