Overlapping metal arms shaped like a bowtie form a “rectenna” that captures free, renewable infrared energy. Image: © 2017 Atif Shamim
Most sunlight striking the Earth is absorbed by its surfaces, oceans and atmosphere. As a result of this warming, infrared radiation is emitted constantly all around us — estimated to be millions of Gigawatts per second. A King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) team has now developed a device that can tap into this energy, as well as waste heat from industrial processes, by transforming quadrillionth-of-a-second wave signals into useful electricity.
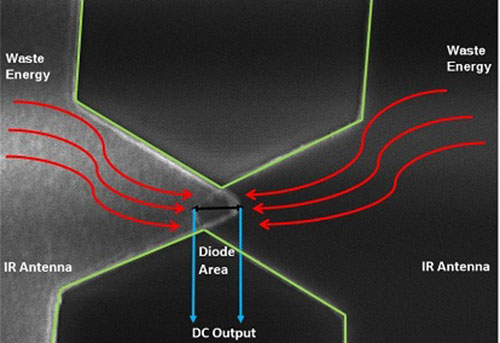
Unlike solar panels that are limited by daylight hours and weather conditions, infrared heat can be harvested 24 hours a day. One way to achieve this is to treat waste or infrared heat as high-frequency electromagnetic waves. Using appropriately designed antennas, collected waves are sent to a rectifier, typically a semiconductor diode, that converts alternating signals to direct current charge for batteries or power devices.
Putting these “rectenna” designs into practice has been difficult. Because infrared emissions have very small wavelengths, they need micro- or nanoscale antennas that are not easy to fabricate or test. Additionally, infrared waves oscillate thousands of times faster than a typical semiconductor can move electrons through its junction. “There is no commercial diode in the world that can operate at such high frequency,” says Atif Shamim, project leader from KAUST. “That’s why we turned to quantum tunneling.”
Tunneling devices, such as metal-insulator-metal (MIM) diodes, rectify infrared waves into current by moving electrons through a small barrier. Since this barrier is only a nanometer thin, MIM diodes can handle high-frequency signals on the order of femtoseconds. To generate the intense fields needed for tunneling, the team turned to a unique “bowtie-shaped” nano-antenna that sandwiches the thin insulator film between two slightly overlapped metallic arms.
“The most challenging part was the nanoscale overlap of the two antenna arms, which required very precise alignment,” says postdoctoral researcher Gaurav Jayaswal. “Nonetheless, by combining clever tricks with the advanced tools at KAUST’s nanofabrication facility we accomplished this step.”
By choosing metals with different work functions, the new MIM diode could catch the infrared waves with zero applied voltage, a passive feature that switches the device on only when needed. Experiments with infrared exposure revealed the bowtie successfully harvested energy solely from the radiation, and not from thermal effects, as evidenced by a polarization-dependent output voltage.
“This is just the beginning — a proof of concept,” says Shamim. “We could have millions of such devices connected to boost overall electricity generation.”




