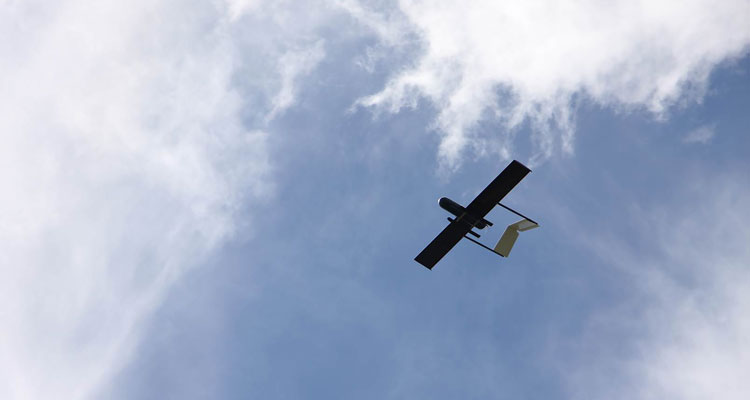
Prospero, the first model aircraft to incorporate a graphene skinned wing, was successfully flown at the Farnborough International Air Show in the U.K. earlier this year. Prospero, an example of how graphene might be used within the aerospace sector, will be exhibited at Composites Europe in Düsseldorf, Germany, from Nov. 29 to Dec. 1.
Graphene exhibits impressive mechanical, thermal, electrical and barrier properties which are important features within the aerospace and automotive sector. It can be used as a nano-additive within thermoplastics and thermosets to improve the mechanical properties of the base material and also reduce weight. Upon further optimization, thermal, electrical and barrier properties can also be imparted into a material, opening opportunities for multifunctional performance.
The test flight of Prospero represents a new stage in a research partnership which is investigating the effects of graphene in drag reduction, thermal management, and ultimately the ability to achieve lightning strike protection for aerospace and other related sectors. This research is a joint collaboration between The University of Manchester and the University of Central Lancashire and several SMEs, including Haydale Composite Solutions.
The University of Manchester is a partner of the Graphene Flagship, EU’s largest ever research initiative. During Composites Europe the Graphene Connect Workshop will highlight the wide range of applications for graphene in the aerospace sector.
James Baker, Graphene Business Director at the National Graphene Institute, says, “This collaboration between academia and industry is a great example of how graphene might be used as a potentially disruptive technology in a market like aerospace and help maintain Europe’s position in the market. At Composite Europe 2016 we will also launch a drone with graphene-polypropylene propeller blades that shows improvement in both mechanical and thermal properties. Graphene as a material is still relatively new but already we are seeing a range of applications not only for aerospace but also in many other markets.”
Billy Beggs, Engineering Innovation Manager at the University of Central Lancashire, says, “The tests were very encouraging and proved to us that graphene has huge potential for aerospace; it is very strong, yet lightweight and flexible at the same time. Through the data collected from those initial flights our research has now moved on to the next level by developing processes of infusing graphene into composite structures. This newly skinned wing, produced by our industrial partner, Haydale Composite Solutions, is enabling us to test the structural and weight saving benefits of graphene. The research team is still in the early stages of flight testing with the new remotely piloted aircraft but initial test data is already very encouraging. In terms of impact resistance, the new wing is showing increased levels of impact resistance of up to 60 percent over a conventionally-skinned carbon fiber wing.”
Source: Graphene Flagship