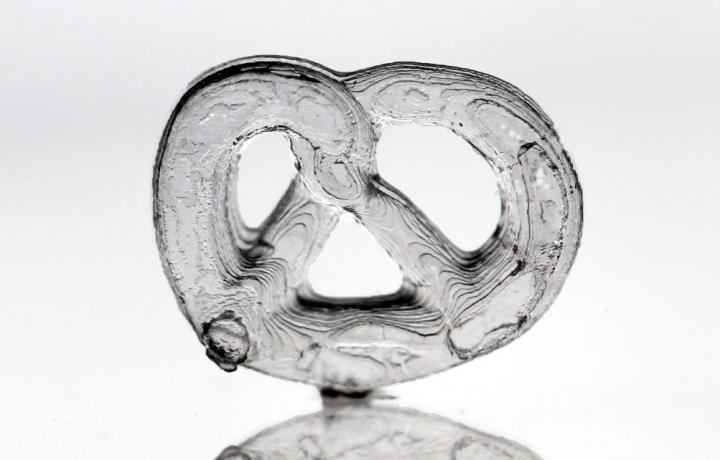
Complicated high-precision structures made of glass can be manufactured in a 3-D-printing process developed at the KIT. Credit: KIT
Glass is one of mankind’s oldest materials. It was used as far back as in ancient Egypt and ancient Rome and has found a place now also in manufacturing technology of the 21st century. An interdisciplinary team at the KIT led by mechanical engineer Dr. Bastian E. Rapp developed a process using glass for additive manufacturing techniques. The scientists mix nanoparticles of high-purity quartz glass and a small quantity of liquid polymer and allow this mixture to be cured by light at specific points – by means of stereolithography. The material, which has remained liquid, is washed out in a solvent bath, leaving only the desired cured structure. The polymer still mixed in this glass structure is subsequently removed by heating. “The shape initially resembles that of a pound cake; it is still unstable, and therefore the glass is sintered in a final step, i.e. heated so that the glass particles are fused,” explains Rapp. He conducts research at the KIT Institute of Microstructure Technology and heads a working group of chemists, electrical engineers, and biologists. The scientists present the method in the Nature journal under the title of “Three-dimensional Printing of Transparent Fused Silica Glass.”
The variety of 3D-printing techniques available so far have been used on polymers or metals, but never on glass. Where glass was processed into structures, for instance by melting and application by means of a nozzle, the surface turned out to be very rough, the material was porous and contained voids. “We present a new method, an innovation in materials processing, in which the material of the piece manufactured is high-purity quartz glass with the respective chemical and physical properties,” explains Rapp. The glass structures made by the KIT scientists show resolutions in the range of a few micrometers – one micrometer corresponding to one thousandth of a millimeter. However, the structures may have dimensions in the range of a few centimeters, emphasizes Rapp.
3D-formed glass can be used, for instance, in data technology. “The next plus one generation of computers will use light, which requires complicated processor structures; 3D-technology could be used, for instance, to make small, complex structures out of a large number of very small optical components of different orientations,” explains the mechanical engineer. For biological and medical technologies, very small analytical systems could be made out of miniaturized glass tubes. In addition, 3D-shaped microstructures of glass could be employed in a variety of optical areas, from eyeglasses meeting special requirements to lenses in laptop cameras.
The development by scientists under Junior Scientist Group Leader Bastian E. Rapp is a result of the “NanoMatFutur” junior scientist funding scheme run by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) to support the development of innovative materials for industry and society. The work performed by the research group headed by Rapp has been funded by the BMBF since 2014 for a total of four years to the tune of approx. € 2.8 million. “Our research benefits very much from the interdisciplinary cooperation of various KIT institutes. Besides the Institute of Microstructure Technology, colleagues of the Institute of Nuclear Waste Management and the Institute of Applied Materials, among others, are involved in the project,” says Rapp.