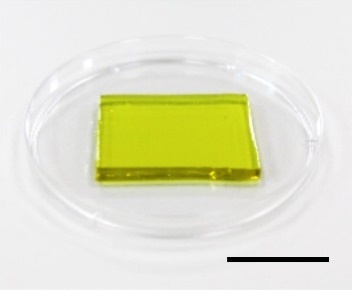
A hydrogel can cool off electronics and generate electricity from their waste heat. Scale bar, 2 cm.
Credit: Adapted from Nano Letters 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c00800
Using electronic devices for too long can cause them to overheat, which might slow them down, damage their components or even make them explode or catch fire. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
Some components of electronic devices, including batteries, light-emitting diodes (known as LEDs) and computer microprocessors, generate heat during operation. Overheating can reduce the efficiency, reliability and lifespan of devices, in addition to wasting energy. Xuejiao Hu, Kang Liu, Jun Chen and colleagues wanted to design a smart thermogalvanic hydrogel that could convert waste heat into electricity, while also lowering the temperature of the device. So far, scientists have developed devices that can do one or the other, but not both simultaneously.
The team made a hydrogel consisting of a polyacrylamide framework infused with water and specific ions. When they heated the hydrogel, two of the ions (ferricyanide and ferrocyanide) transferred electrons between electrodes, generating electricity. Meanwhile, water inside the hydrogel evaporated, cooling it. After use, the hydrogel regenerated itself by absorbing water from the surrounding air. To demonstrate the new material, the researchers attached it to a cell phone battery during fast discharging. Some of the waste heat was converted into 5 μW of electricity, and the temperature of the battery decreased by 68°F. The reduced working temperature ensures safe operation of the battery, and the electricity harvested is sufficient for monitoring the battery or controlling the cooling system.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Department of Bioengineering at UCLA.
For more information, email Xuejiao Hu, Ph.D., at [email protected]