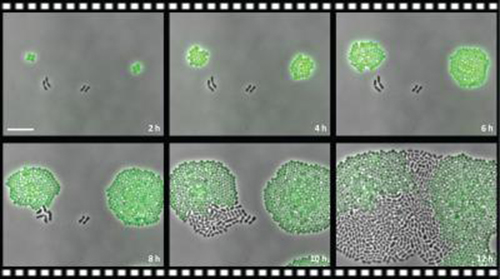
Staphylococci bacteria, which have been labelled with a green fluorescent protein, express a resistance gene for the antibiotic chloramphenicol. Black Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria do not have the resistance gene. In a medium containing the antibiotic, the green cells begin to grow and divide whereas the non-resistant black cells don’t. After a time, individual black cells begin to divide and they even outgrow their green companions. Photo: Sorgt et al,/University of Groningen
Bacteria that are susceptible to antibiotics can survive when enough resistant cells around them are expressing an antibiotic-deactivating factor. This new take on how the microbial context can compromise antibiotic therapy was published by a team of microbiologists from the University of Groningen microbiologists, together with colleagues from San Diego, in the journal PLOS Biology on 27 December.
The entire paper is summed up nicely in a short video clip of a crucial experiment in the study. We see Staphylococci bacteria, which have been labelled with a green fluorescent protein, expressing a resistance gene for the antibiotic chloramphenicol. Next to them are black Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria that do not have the resistance gene. In a medium containing the antibiotic, the green cells begin to grow and divide whereas the non-resistant black cells don’t. After a time, individual black cells begin to divide and they even outgrow their green companions.
What is going on here? Microbiologist Robin Sorg, first author of the paper, explains: ‘The resistant cells take up the chloramphenicol and deactivate it. At a certain point, the concentration in the growth medium drops below a critical level and the non-resistant cells start growing.’ Something like this has been seen before. ‘Cells with resistance to penicillin can secrete beta-lactamase enzymes which break down the antibiotic. But in our case, the antibiotic is deactivated inside the resistant cells.’
Time lapse
The discovery was made using time-lapse microscopy, and confirmed with computational modelling and a mouse pneumonia model. ‘In the mice, we observed that susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria survive the chloramphenicol treatment when the animals are co-infected with resistant bacteria.’ Furthermore, the results ruled out a transfer of the resistance gene. The data is in line with anecdotal evidence from the clinic, where antibiotic-susceptible bacteria are sometimes cultured from patients who were unsuccessfully treated with antibiotics. Sorg: ‘This always puzzled physicians. Our work might provide one possible explanation.’
So susceptible bacteria can survive longer when resistant bacteria are present, and in the end even outcompete them. What does this mean for the spread of antibiotic resistance? ‘It is complicated’, Sorg says. ‘We know that antibiotic usage results in selection for resistance. However, we do not fully understand the processes, nor why antibiotic resistance can develop so fast. Single cell studies like ours help to fill in some of these details.’
Metabolism
One thing that should be noted is that the susceptible cells in the experiment stop growing, but don’t die. ‘Many antibiotic-induced killing mechanisms rely on dividing cells, or at least on cells with an active metabolism.’ What doesn’t kill the cells will perhaps not make them stronger, but certainly gives them time to pick up resistance genes from their environment.
This knowledge can inform doctors when treating a patient with antibiotics. ‘We know that we should use these drugs with discretion, but we may need to be even more careful than we thought.’ Sorg sketches a personalized-medicine approach, in which the non-pathogenic microbes present in a patient are checked for resistance genes. ‘That would increase the risk of a transfer to pathogens.’
To prevent the occurrence of resistance in non-pathogenic microorganisms, it is of course important to use antibiotics as sparingly as possible. And perhaps one day, when our understanding of the mechanisms responsible for the spread of antibiotic resistance is more complete, we may find a way to stop it.




