Cancer cells often have mutations in their DNA that can give scientists clues about how the cancer started or which treatment may be most effective. Finding these mutations can be difficult, but a new method may offer more complete, comprehensive results. A team of researchers has developed a new framework that can combine three existing…
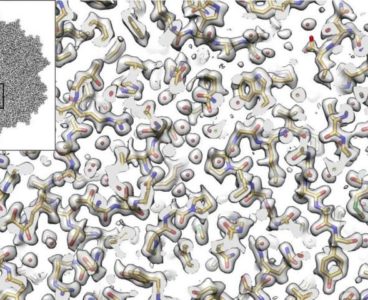
Electron Microscopy Provides New View of Tiny Virus With Therapeutic Potential
The imaging method called cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) allows researchers to visualize the shapes of biological molecules with an unprecedented level of detail. Now, a team led by researchers from the Salk Institute and the University of Florida is reporting how they used cryo-EM to show the structure of a version of a virus called an…
Boosting the Effects of Vitamin D to Tackle Diabetes
Boosting the Effects of Vitamin D to Tackle Diabetes
More than 27 million people in the United States are living with type 2 diabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As the population ages and a growing percentage of people become overweight or obese, that number is expected to increase. In a paper published May 10, 2018, in Cell, researchers from the…
Grafted Brain Organoids Provide Insight into Neurological Disorders
Many neurological disorders—Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia, autism, even depression—have lagged behind in new therapies. Because the brain is so complex, it can be difficult to discover new drugs and even when a drug is promising in animal models, it often doesn’t work for humans. Scientists are aiming to change that with stem cell technology by taking skin…
Tumor Suppressor Protein Targets Liver Cancer
Curb Your Immune Enthusiasm
Normally when we think of viruses, from the common cold to HIV, we want to boost people’s immunity to fight them. But for scientists who develop therapeutic viruses (to, for example, target cancer cells or correct gene deficiencies) a more important question is: How do we keep people’s natural immune responses at bay? In these…
Scientists Crack the Structure of HIV Machinery
Salk Institute scientists have solved the atomic structure of a key piece of machinery that allows HIV to integrate into human host DNA and replicate in the body, which has eluded researchers for decades. The findings describing this machinery, known as the “intasome,” appear Jan. 6, 2017, in Science and yield structural clues informing the development of…
Immune Receptors Amplify ‘Invader’ Signals By Turning into Mini-Machines
When a receptor on the surface of a T cell — a sentry of the human immune system — senses a single particle from a harmful intruder, it immediately kicks the cell into action, launching a larger immune response. But exactly how the signal from a single receptor, among thousands on each T cell, can…
Disregarded Plant Molecule Actually a Treasure
The best natural chemists out there are not scientists—they’re plants. Plants have continued to evolve a rich palette of small natural chemicals and receptors since they began to inhabit land roughly 450 million years ago. Now, research by Salk Institute scientists published August 11, 2016 in the journal Cell reveals an unexpected role for a small, often…