Using data from field experiments and modeling of ground faults, researchers at Tufts University have discovered that the practice of subsurface fluid injection used in “fracking” and wastewater disposal for oil and gas exploration could cause significant, rapidly spreading earthquake activity beyond the fluid diffusion zone. Deep fluid injections—greater than one kilometer deep—are known to…
Threads Can Detect Gases When Woven into Clothing
Tufts University engineers have developed a novel fabrication method to create dyed threads that change color when they detect a variety of gases. The researchers demonstrated that the threads can be read visually, or even more precisely by use of a smartphone camera, to detect changes of color due to analytes as low as 50…
Researchers 3D Print Metamaterials With Novel Optical Properties
A team of engineers at Tufts University has developed a series of 3-D printed metamaterials with unique microwave or optical properties that go beyond what is possible using conventional optical or electronic materials. The fabrication methods developed by the researchers demonstrate the potential, both present and future, of 3-D printing to expand the range of…
Scientists Grow Functioning Human Neural Networks in 3D from Stem Cells
A team of Tufts University-led researchers has developed three-dimensional (3D) human tissue culture models for the central nervous system that mimic structural and functional features of the brain and demonstrate neural activity sustained over a period of many months. With the ability to populate a 3D matrix of silk protein and collagen with cells from…
New Materials Move When Confronted with Light
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering have developed magnetic elastomeric composites that move in different ways when exposed to light, raising the possibility that these materials could enable a wide range of products that perform simple to complex movements, from tiny engines and valves to solar arrays that bend toward the sunlight. The research…
Food Intake Tracked by Tiny Tooth-Mounted Sensors
Monitoring in real time what happens in and around our bodies can be invaluable in the context of health care or clinical studies, but not so easy to do. That could soon change thanks to new, miniaturized sensors developed by researchers at the Tufts University School of Engineering that, when mounted directly on a tooth…
Researchers Develop Optical Tools to Detect Metabolic Changes Linked to Disease
Metabolic changes in cells can occur at the earliest stages of disease. In most cases, knowledge of those signals is limited, since we usually detect disease only after it has done significant damage. Now, a team led by engineers at Tufts University School of Engineering has opened a window into the cell by developing an…
Researchers Devise a New, Inexpensive Way to Fabricate Microneedles
Getting an injection at the doctor’s office is never a fun thing, but a new approach is on the horizon, using what are called microneedles, arrays of tiny needles that deliver medication through the skin without causing pain. But fabricating microneedles is costly, requiring cleanrooms and expensive equipment. Now a Tufts research team has devised…
Climate Change Projected to Significantly Increase Harmful Algal Blooms in U.S. Freshwaters
Harmful algal blooms known to pose risks to human and environmental health in large freshwater reservoirs and lakes are projected to increase because of climate change, according to a team of researchers led by a Tufts University scientist. The team developed a modeling framework that predicts that the largest increase in cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms…
Bioelectricity New Weapon to Fight Dangerous Infection
Blind Tadpoles Learn Visually With Eyes Grafted Onto Tail, Neurotransmitter Drug Treatment
Blind tadpoles were able to process visual information from eyes grafted onto their tails after being treated with a small molecule neurotransmitter drug that augmented innervation, integration, and function of the transplanted organs, according to a paper published online today by researchers at the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University in npj Regenerative Medicine, a Nature Research journal.…
Silk Nanofibers Withstand 4,000 Times Their Weight
Researchers at Tufts University’s School of Engineering have developed a new bioinspired technique that transforms silk protein into complex materials that are easily programmable at the nano-, micro-, and macro-scales as well as ultralight and robust. Among the varied structures generated was a web of silk nanofibers able to withstand a load 4,000 times its…
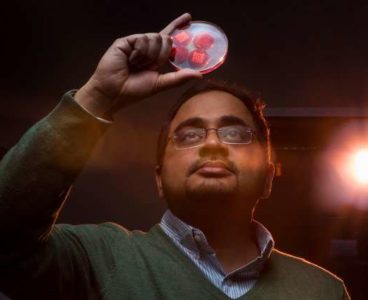
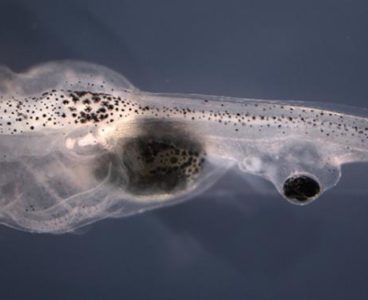
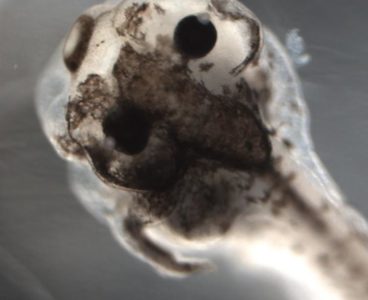
A.I. Uncovers New Insight into Biophysics of Cancer
Scientists from Tufts University’s School of Arts and Sciences, the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts, and the University of Maryland, Baltimore County have used artificial intelligence to gain insight into the biophysics of cancer. Their machine-learning platform predicted a trio of reagents that was able to generate a never-before-seen cancer-like phenotype in tadpoles. The research,…
Artificial Intelligence Uncovers New Insight into Biophysics of Cancer
Scientists from Tufts University’s School of Arts and Sciences, the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts, and the University of Maryland, Baltimore County have used artificial intelligence to gain insight into the biophysics of cancer. Their machine-learning platform predicted a trio of reagents that was able to generate a never-before-seen cancer-like phenotype in tadpoles. The research,…
Chip-Sized, High-Speed Terahertz Modulator Raises Possibility of Faster Data Transmission
Tufts University engineers have invented a chip-sized, high-speed modulator that operates at terahertz (THz) frequencies and at room temperature at low voltages without consuming DC power. The discovery could help fill the “THz gap” that is limiting development of new and more powerful wireless devices that could transmit data at significantly higher speeds than currently…
Mantis Shrimp Use UV Color Spots, Chemical Cues to Size Up Opponents
Mantis shrimp, often brightly colored and fiercely aggressive sea creatures with outsized strength, use the ultraviolet reflectance of their color spots as well as chemical signals to assess the likelihood of victory in combat, according to research led by a Tufts University doctoral candidate. The findings, published today in Royal Society Open Science, mark the first…
“Smart” Thread Sutured into Tissue Collects Data
For the first time, researchers led by Tufts University engineers have integrated nanoscale sensors, electronics, and microfluidics into threads — ranging from simple cotton to sophisticated synthetics — that can be sutured through multiple layers of tissue to gather diagnostic data wirelessly in real time, according to a paper published online this week in Microsystems…